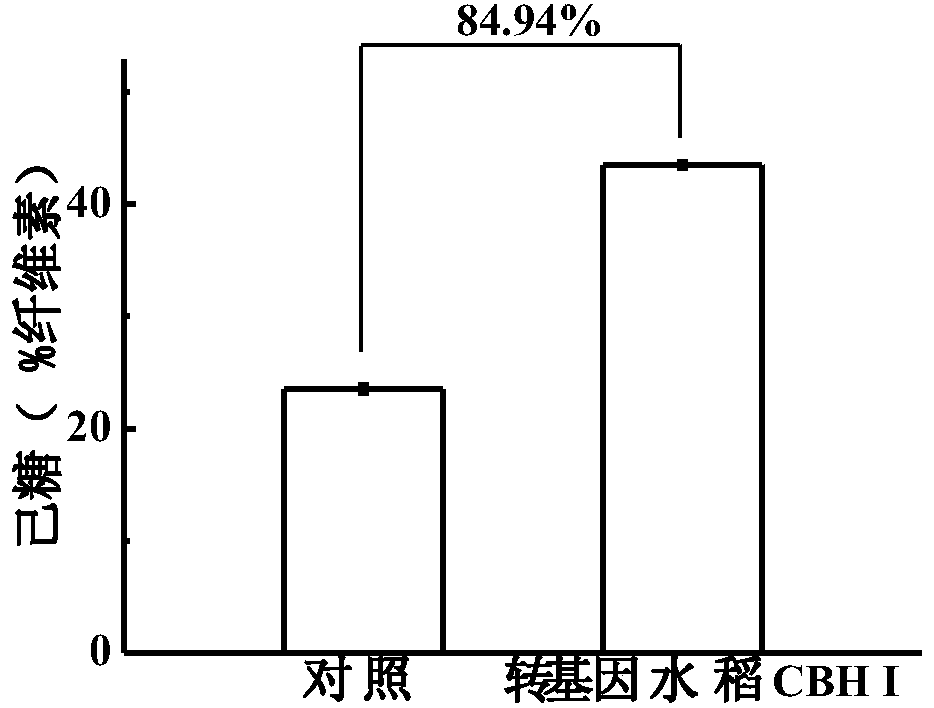
Method for Improving Rice Straw Degradation Transformation Efficiency Using Exoglucanase
An exoglucanase and rice straw technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, glycosylase, botanical equipment and methods, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing expression and improving transformation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1: Cloning and optimization of CBH Ⅰ gene full-length cDNA
[0043]1. Clone the full-length cDNA of CBH Ⅰ gene from Trichoderma reesei, and optimize the codon of CBH Ⅰ gene by site-directed mutagenesis.
[0044] Among them, the optimized codons of the full-length cDNA of CBH Ⅰ gene are:
[0045] The codon CTA of leucine at position 77 was optimized as CTC, and the CGA of arginine at position 319 was optimized as CGC;
[0046] 2. The codon-optimized site-directed mutagenesis method of the CBH Ⅰ gene
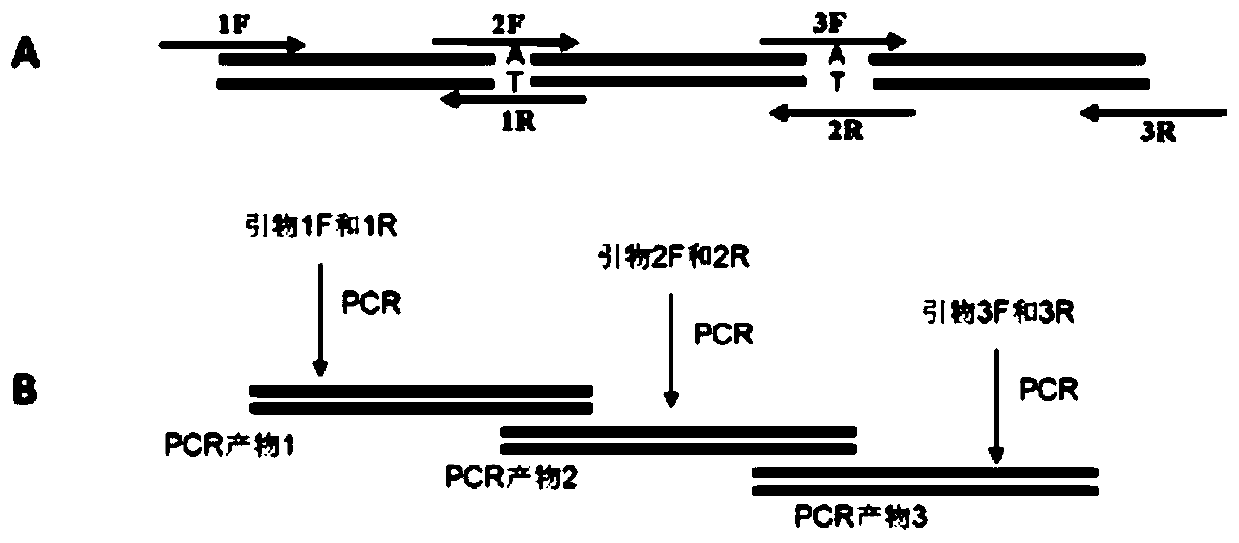
[0047] ——If there are two sites in the gene that need site-directed mutation, 3 pairs of primers need to be synthesized and cloned into the vector, see figure 2 -A; where primers 1F and 3R are added with restriction enzyme sites required by the carrier, primers 2F and 1R, 3F and 2R are completely complementary to each other, and the base to be mutated is placed in the middle of the primers, and the length of the primers is greater than 20 bp;
[0048] ——Respecti...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Embodiment 2: Construction of expression vector
[0053] 1. Rice Rbcs promoter overexpresses CBH Ⅰ of Trichoderma reesei and localizes to chloroplast
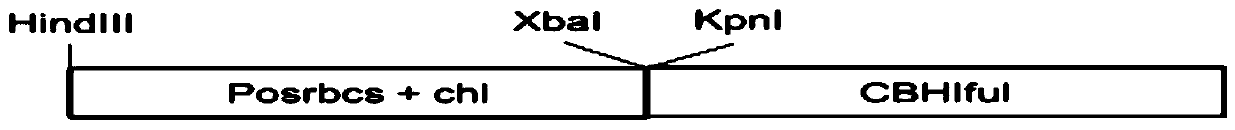
[0054] Construction of the vector (pC1300T-osrbcs-chl-CBH Ⅰ ful) (see image 3 ):
[0055] ——Taking Nipponbare's genomic DNA as a template, synthesize primers to amplify the rbcs promoter (including signal peptide-47 AAs).
[0056] ——Synthetic primers amplify the full length of CBH Ⅰ (codon optimization, including stop codon, without signal peptide), the sequence is shown in sequence 1
[0057] Forward primer: GGGGTACC(KpnΙ)CAGTCGGCCTGCACTCT
[0058] Reverse primer: ATGATACGGGCTCACCAA
[0059] ——Connect the promoter and CBH Ⅰ full-length cDNA sequence to the T vector respectively, digest with restriction enzymes, and transfer to the expression vector pC1300T.
Embodiment 3
[0060] Embodiment 3: Plant expression vector transforms Agrobacterium
[0061] 1. Agrobacterium activation
[0062] Draw the preserved Agrobacterium (EHA105) on the solid LB medium (add antibiotic: Kan, if no antibiotics are added, the Ti plasmid of these strains may be lost, resulting in the lack of infectivity of Agrobacterium), the antibiotic concentration is: 50μg / mL, culture at 28°C for 1-2 days, then transfer to a new solid LB medium with antibiotics and culture for another 2 days;
[0063] 2. Preparation of Agrobacterium Competent Cells
[0064] Inoculate 100 μL into 1 mL of LB liquid medium, shake at 150 rpm at 28°C overnight;
[0065] Take 1mL of the bacterial liquid and inoculate it into 100mL of liquid medium and cultivate until OD600=0.5;
[0066] Place the bacterial solution on ice for 30 minutes, and cool the culture to 0°C;
[0067] Centrifuge at 5000rpm for 30s at 4°C and discard the supernatant;
[0068] Precipitate with 60mL 0.1M CaCl 2 Suspended, ice-b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com