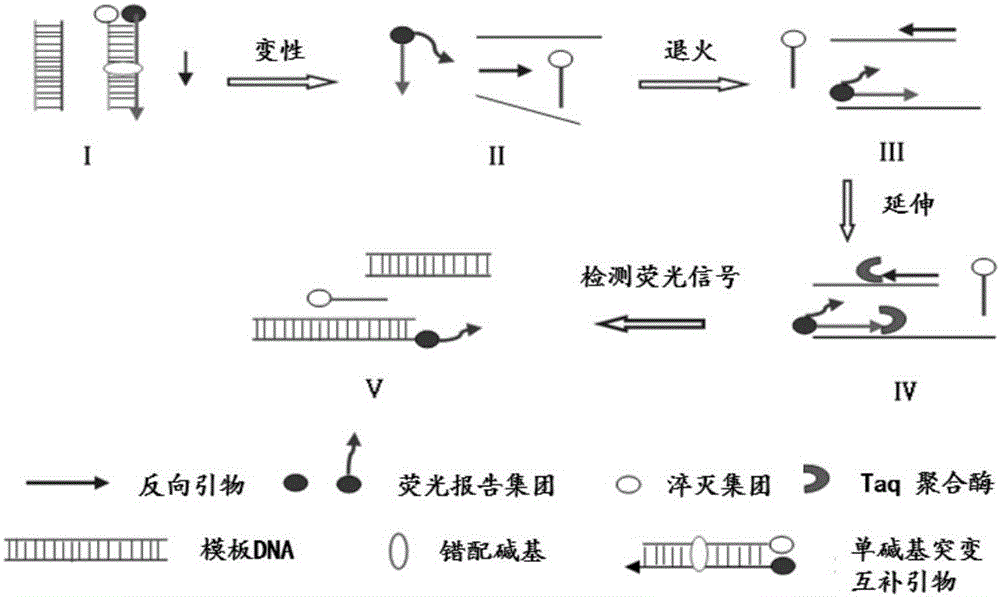
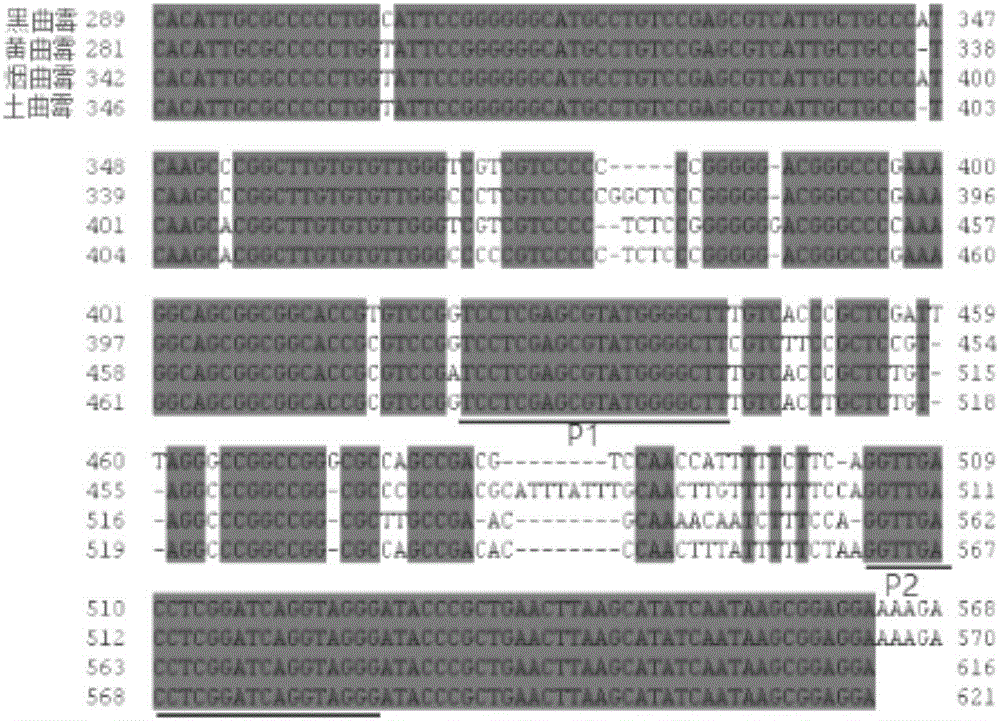
Dimer mutating fluorescent primer quantative PCR method for synchronous quantifying and genetic typing of four aspergilli
A genotyping and fluorescent primer technology, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., to achieve good social and economic benefits, high sensitivity, and suitable for popularization and application.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] [Example 1] Quantitative and Genotyping Detection of 4 Kinds of Aspergillus
[0056] Preparation of the amplification system:
[0057] (1) Required reagents: PCR-mix buffer (Takara), template DNA
[0058] (2) Primer mixture: a mixture of three primers of 2.0 μM each
[0059] 1. Fungal Culture and DNA Extraction
[0060] The standard strains of Aspergillus fumigatus (ATCC 36607), Aspergillus niger (ATCC 16888), Aspergillus flavus (ATCC 16883) and Aspergillus terreus (ATCC 16792) were cultivated in sandcastle weak medium, and the DNA was extracted with a fungal DNA extraction kit.
[0061] 2. Construct quantitative standard plasmid
[0062] Amplify Aspergillus niger DNA sequence with common PCR method:
[0063] The upstream primer sequence is: 5'-CCCTACCTGATCCGAGGTCAACC-3' (SEQ ID No.1);
[0064] The downstream primer sequence is: 5'-AAAGTAAGACAGGAAATGTG-3' (SEQ ID No.2).
[0065] Amplification conditions and systems are the same as Real-time PCR.
[0066] The ampl...
Embodiment 2
[0078] [Example 2] The method is analyzed for specificity and repeatability
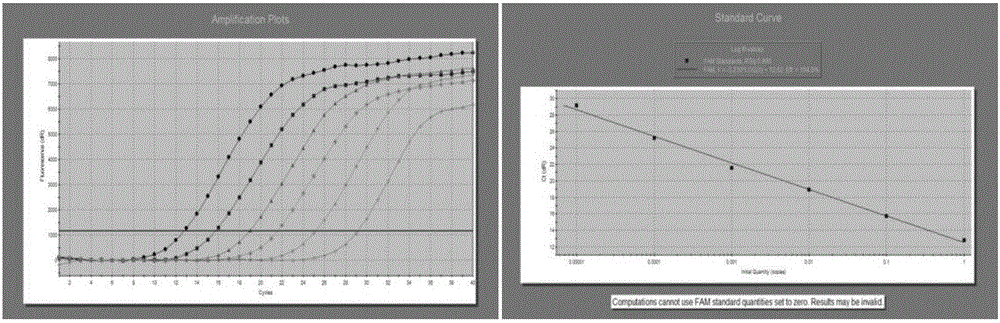
[0079] Specificity: Use this method to standard strains of Aspergillus and Candida albicans, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, standard strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Shigella, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Klebsiella pneumoniae And the Salmonella typhi DNA was extracted and tested with the established method to analyze the specificity of Real-time PCR detection. The amplification curve is shown in Figure 5 left.
[0080] Repeatability: The repeatability within the batch passed for 3 series of standard products (1×10 4 ~1×10 2 copies / ml) and 1.5×10 3 Concentration clinical samples were repeated to do 5 parallel tubes, and the quantitative results were calculated for SD and CV.
[0081] Standard plasmid 1×10 2 ~1×10 4Copies / ml, SD respectively: 0.707, 0.1845, 0.3172, CV respectively: 4.79%, 5.83%, 4.94%, see the amplification curve Figure 5 right.
[0082] The concentration of clini...
Embodiment 3
[0084] [Example 3] Determination of 4 clinical strains
[0085] According to the method described above, we collected four different types of Aspergillus strains that were biochemically verified from the clinic for detection. The results of the amplification curve and melting curve are as follows Figure 6 As shown, the present invention can simultaneously quantitatively detect 4 different types of Aspergillus.
[0086] Figure 6 Left: Amplification curves from left to right are Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus terreus;
[0087] Figure 6 Right: Melting curves from left to right represent A. niger, A. flavus, A. fumigatus, A. terreus.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com