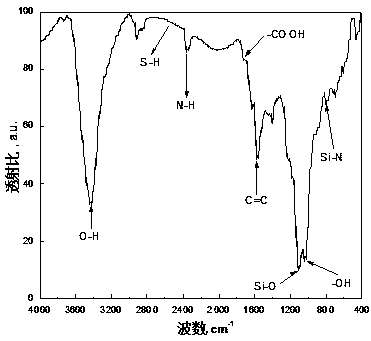
A method for efficiently removing heavy metal ions and organic matter in water
A technology for removing heavy metal ions and water, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, water/sewage treatment, etc. Convenient operation, increased specific surface area, excellent effect of adsorption and separation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Step 1 Pretreatment of carbon nanotubes:
[0038] Disperse 1 g of original multi-walled carbon nanotubes (prepared by chemical vapor deposition) into a mixed acid solution of 30 ml of concentrated sulfuric acid and 10 ml of concentrated nitric acid, stir and react at 60°C for 3 hours, wash with distilled water until neutral, and dry in vacuum at 80°C for 12 Stand by after hours.
[0039] The preparation of step 2 graphene oxide:
[0040] Use an electronic balance to take 2g of natural flake graphite; measure 50ml of concentrated sulfuric acid in a measuring cylinder and pour it into a 1000ml three-neck bottle, cool it to 0~5°C, add the weighed 2g of graphite into 50ml of concentrated sulfuric acid, and use Cool in an ice-water bath to 0~5°C and stir until the graphite is completely dissolved, add 1g of sodium nitrate and 6g of potassium permanganate at a certain speed while stirring vigorously, keep the temperature of the mixture below 10°C and continue stirring for 2....
Embodiment 2
[0051] Step 1 Pretreatment of carbon nanotubes:
[0052] Disperse 0.5g of original multi-walled carbon nanotubes (prepared by chemical vapor deposition) into a mixed acid solution of 15ml of concentrated sulfuric acid and 5ml of concentrated nitric acid, stir and react at 60°C for 3 hours, wash with distilled water until neutral, and dry in vacuum at 80°C Reserve after 12 hours.
[0053] The preparation of step 2 graphene oxide:
[0054] Use an electronic balance to take 1g of natural flake graphite; measure 25ml of concentrated sulfuric acid in a measuring cylinder and pour it into a 1000ml three-neck bottle, cool to 0~5°C, add the weighed 1g of graphite to 25ml of concentrated sulfuric acid, and use Cool in an ice-water bath to 0~5°C and stir until the graphite is completely dissolved. Add 0.5g of sodium nitrate and 3g of potassium permanganate at a certain speed while stirring vigorously to keep the temperature of the mixture below 10°C and continue stirring for 2.5 hours;...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Step 1 Pretreatment of carbon nanotubes:
[0065] Disperse 0.2g of original multi-walled carbon nanotubes (prepared by chemical vapor deposition) into a mixed acid solution of 6ml of concentrated sulfuric acid and 2ml of concentrated nitric acid, stir and react at 60°C for 3 hours, wash with distilled water until neutral, and dry in vacuum at 80°C Reserve after 12 hours.
[0066] The preparation of step 2 graphene oxide:
[0067] Use an electronic balance to take 1g of natural flake graphite; measure 23ml of concentrated sulfuric acid in a measuring cylinder and pour it into a 1000ml three-neck bottle, cool it to 0~5°C, add the weighed 1g of graphite to 23ml of concentrated sulfuric acid, and use Cool in an ice-water bath to 0~5°C and stir until the graphite is completely dissolved. Add 0.5g of sodium nitrate and 3g of potassium permanganate at a certain speed while stirring vigorously to keep the temperature of the mixture below 10°C and continue stirring for 2.5 hour...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com