A polyamino acid/mos 2 Preparation methods and applications of nanoclusters
A polyamino acid and nano-cluster technology, which is applied in medical preparations with non-active ingredients, medical preparations containing active ingredients, and pharmaceutical formulas, can solve the problem of low photothermal conversion efficiency of nano-clusters and synthesis efficiency of nano-clusters. Low cost, cumbersome surface modification, etc., to achieve excellent photothermal conversion performance, good cell compatibility, and good colloidal stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Weigh 0.1 g ammonium tetrathiomolybdate and 1 g γ-PGA (molecular weight 1000kDa), mix with 20 mL distilled water, and stir at room temperature for 0.5 h to obtain a clear and transparent solution. The resulting solution was transferred to a 100 mL volume stainless steel reaction kettle lined with p-polyphenylene and sealed. Put the reaction kettle into a high-temperature oven for heat treatment at 220 °C for 12 h. After cooling down to room temperature naturally, the reaction mixture was centrifuged and washed three times with 50% (volume fraction, the same below) ethanolamine solution and distilled water to obtain γ- PGA / MoS 2 nanoclusters.
Embodiment 2
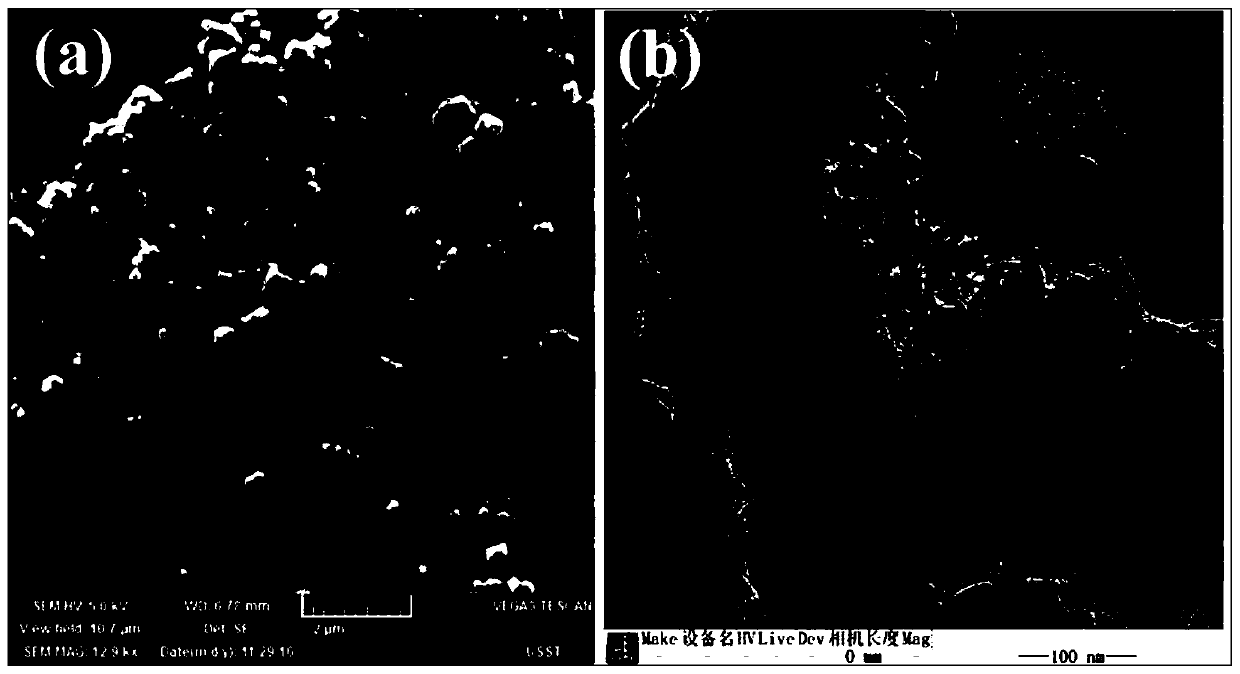
[0031] Observe the microscopic morphology of the material by TEM: Disperse an appropriate amount of nano-clusters in absolute ethanol, and disperse evenly by ultrasonic, then immerse the copper mesh coated with carbon film in the above-mentioned absolute ethanol. After the samples were naturally dried, they were observed and photographed by TEM, and the operating voltage of TEM was 200 kV. The diameters of nanoclusters were measured with Image J 1.40G software (http: / / rsb.info.nih.gov / ij / download.html, National Institutes of Health, USA) (at least 50 measurements per sample). TEM observation results ( figure 1 a) shows that the obtained γ-PGA / MoS 2 Nanoclusters have a sheet structure. The diameter of nanoclusters was measured with Image J 1.40G software (http: / / rsb.info.nih.gov / ij / download.html, National Institutes of Health, USA) (at least 50 different cluster particles were measured), γ-PGA / MoS 2 The diameter of the nanoclusters is 197.3 ± 26.6 nm.
Embodiment 3
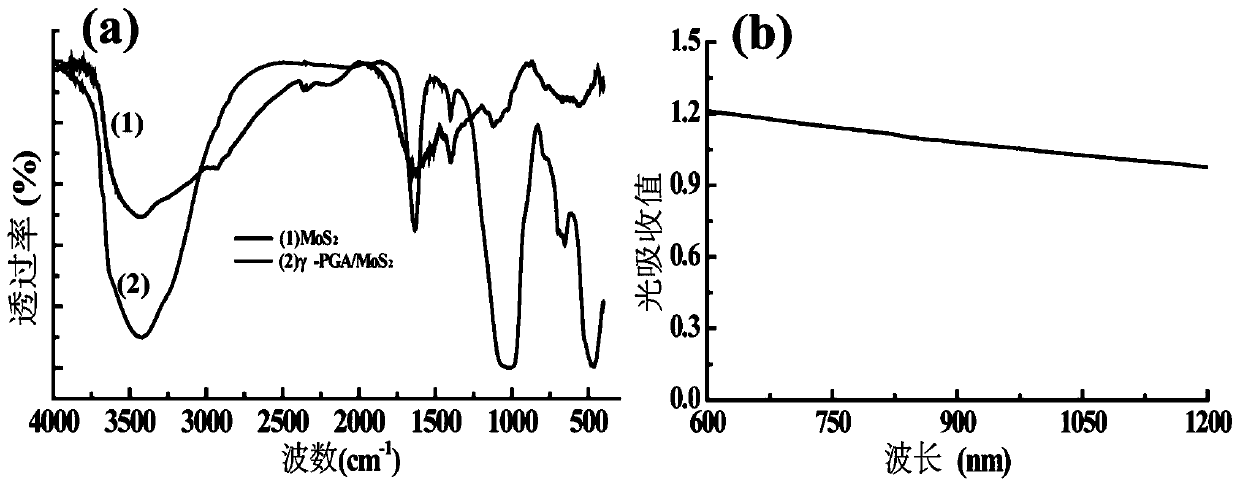
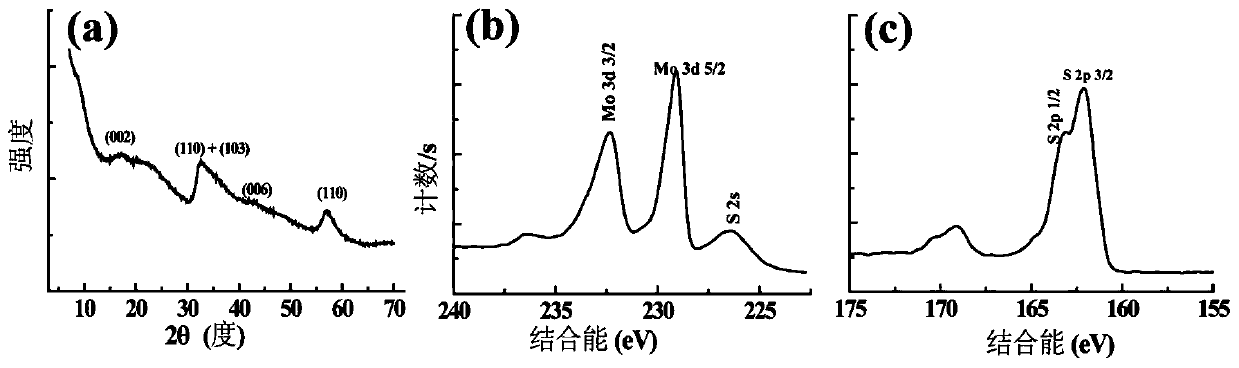
[0033] The valence of Mo and S elements in nanoclusters was characterized by ESCAlab250 X-ray photoelectron spectrometer (XPS) from Thermal Scientific Company. The excitation source is monochromator Al Kα X-rays (λ = 0.8339 nm), the energy is 1486eV, the linewidth is 0.9 eV, and the power is 150 W. The binding energy was corrected with the 1s peak of C (284.8 eV). The crystal structure of the XRD diffraction pattern of the nanoclusters was investigated using XRD (Rigaku D / max-2200 PC, Japan). With Cu2Kα rays as the light source, the operating voltage is 40 kV, the current is 200 mA, and the scanning angle (2θ) ranges from 3° to 70°. Using FTIR (Nicolet Nexus 670 infrared spectrometer) and UV-Vis-NIR (Lambda 25, Perkin Elmer Company, USA) 2 Nanocluster Characterization. For FTIR characterization, a small amount of powder and PGA powder (control group) were taken, mixed with dry KBr powder, ground evenly, and then compressed into tablets. Placed on a Nicolet Nexus 670 infrar...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com