Preparation method of mesoporous bioactive glass nanotube stent
A technology of bioactive glass and nanotubes, which is applied in the field of preparation of nanobiomedical materials, can solve the problems of no mesoporous structure in the tube wall, low bioactivity of polymer materials, easy to cause inflammation, etc., and achieves wide application prospects and large ratio The effect of surface area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0024] The preparation method of a mesoporous bioactive glass nanotube support proposed by the present invention uses silicate as a silicon source, calcium nitrate tetrahydrate or calcium chloride as a calcium source, and triethyl phosphate as a phosphorus source; Silicon-derived bacterial cellulose (Bacterial Cellulose, BC) and polyethylene oxide-polypropylene oxide-polyethylene oxide triblock copolymer (P123) are dual template agents, which are stirred in a water bath, hydrolyzed and polycondensed , the precursor hybrid material was prepared, and finally, the BC and P123 dual-template agent was removed by heat treatment technology, and the mesoporous bioactive glass nanotube scaffold was obtained. The method realizes the controllable preparation of the mesoporous bioactive glass nanotube scaffold, and the obtained product has the advantages of mesoporous, three-dimensional space network structure, uniform and adjustable wall thickness. The preparation process includes precur...
Embodiment 1
[0033] Embodiment 1: preparing a mesoporous bioactive glass nanotube scaffold with a wall thickness of about 6 nm, the specific steps are as follows:
[0034] 1) Prepare a mixed solution A with a molar concentration of 0.5M tetraethyl orthosilicate and absolute ethanol, and stir in a water bath at a temperature of 40°C and a stirring speed of 120r / min; under stirring conditions, soak BC in the above mixed solution In A, 10 mL of absolute ethanol corresponds to 25 mg of BC. After 2 days, the product was taken out, washed several times with absolute ethanol to remove excess precursor substances on the surface of the product, and BC with silicon source uniformly adsorbed on the surface and inside was obtained.
[0035] 2) Prepare a mixed solution B of absolute ethanol and distilled water with a volume ratio of 9:1, and stir in a water bath at a temperature of 40°C and a stirring speed of 120r / min; under stirring conditions, the surface obtained in the above step 1) and The BC wit...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Embodiment 2: preparing a mesoporous bioactive glass nanotube scaffold with a wall thickness of about 10 nm, specifically comprising the following steps:
[0040] It is basically the same as Example 1, except that the mixed solution A prepared in step 1) is a mixed solution A with a molar concentration of 0.7M tetraethyl orthosilicate and absolute ethanol; finally, a mesoporous, three-dimensional A bioactive glass nanotube scaffold with a spatial network structure and a wall thickness of 10nm.
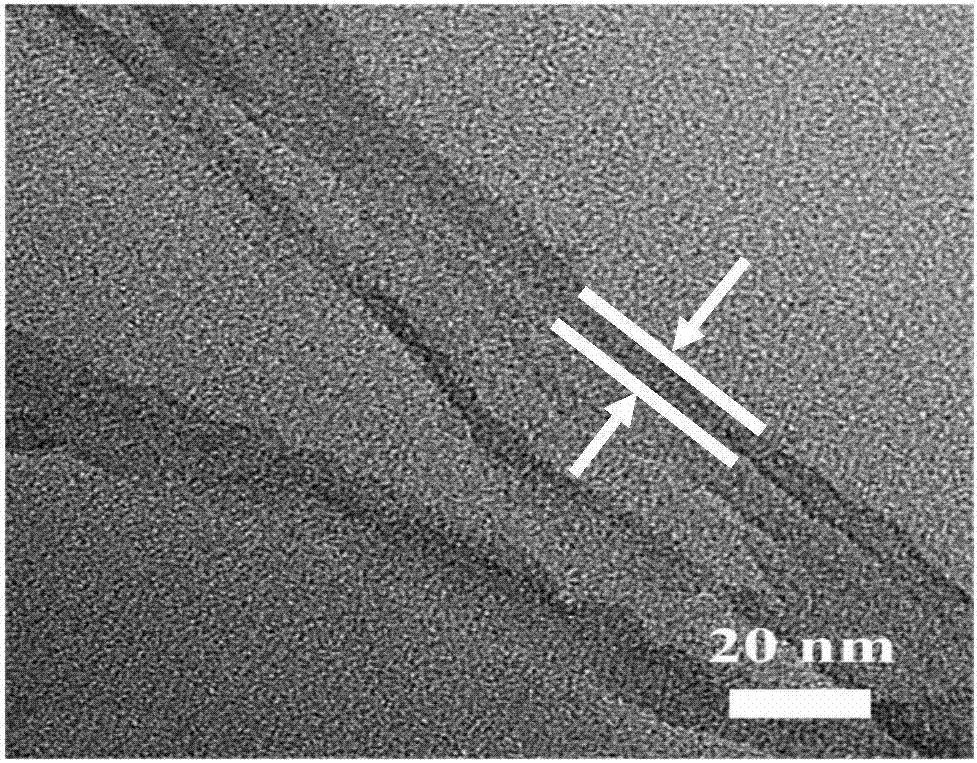
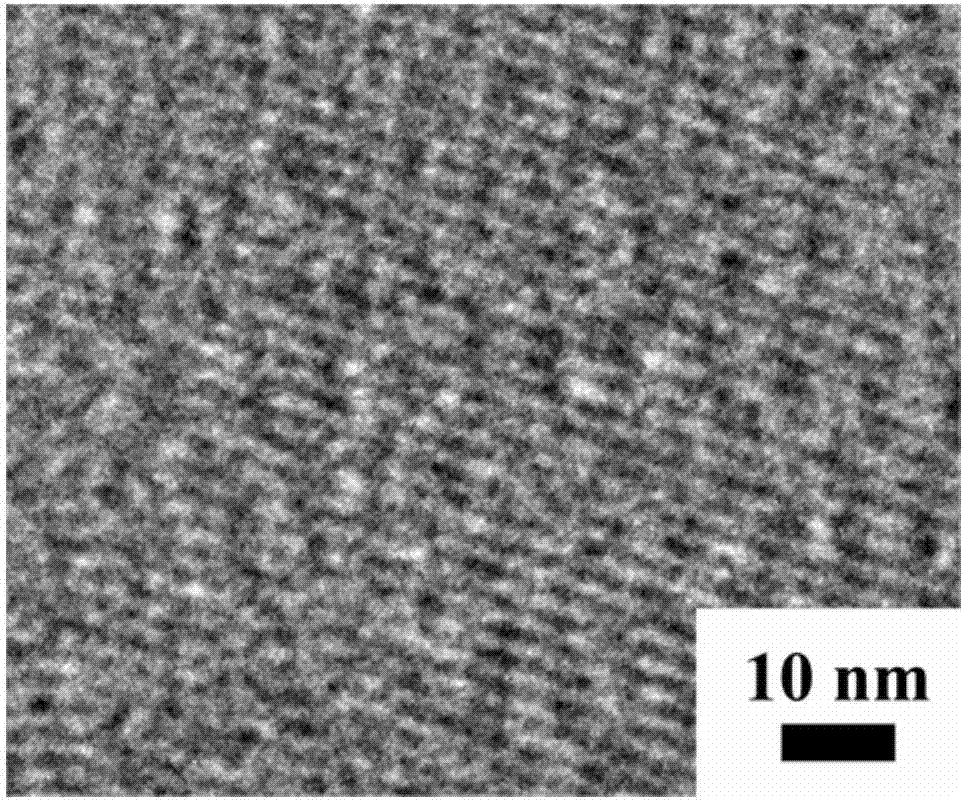
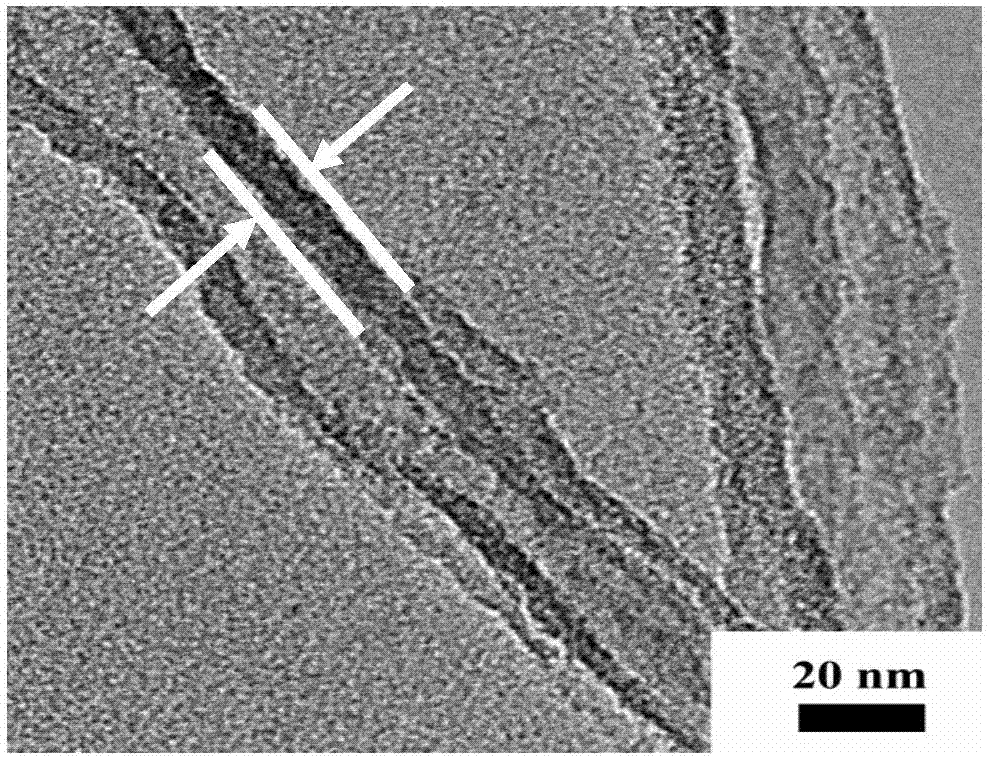
[0041] Figure 2(a) and Figure 2(b) are the TEM and HRTEM photographs of the mesoporous bioactive glass nanotube scaffold prepared in Example 2 respectively, from Figure 2(a) it can be concluded that the mesoporous bioactive glass nanotube The wall thickness of the tube scaffold is 10 nm (indicated by the white straight line area), and its wall thickness is uniform and its structure is clear.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com