Method for preparing seedling bed by using modified biogas residue fibers
A technology for raising seedling trays and biogas residues, which is applied in the field of preparing seedling trays using modified biogas residue fibers, which can solve the problems of long time-consuming degradation and modification, difficulty in large-scale utilization, and high cost, and achieve good feasibility and high comprehensive utilization rate , little toxicity and pollution effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
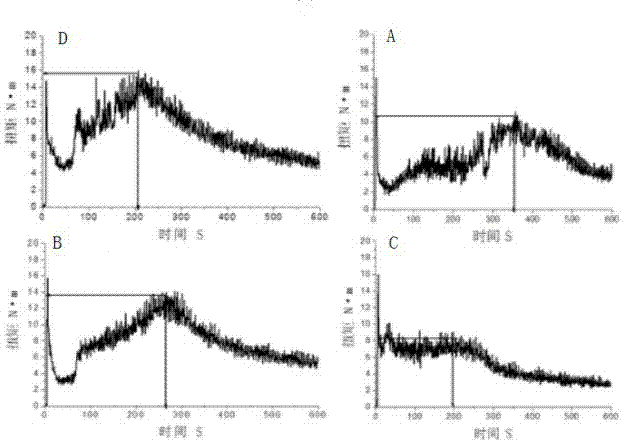
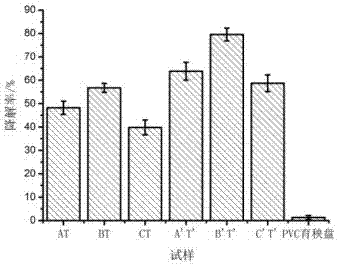
Examples
Embodiment 1
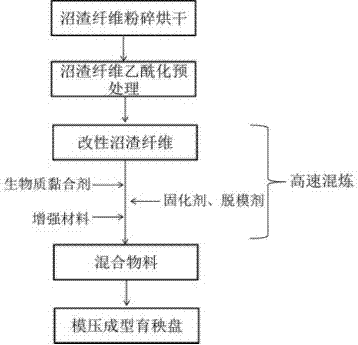
[0035] S1: Acetylation pretreatment of biogas residue fiber
[0036] The biogas residue fiber is naturally air-dried and pulverized to 20 mesh. Weigh 200g biogas residue fiber into a reactor containing 1000ml of toluene solvent, add 1200ml of acetyl chloride, and after uniformly stirring, add 8g of p-benzoic acid at a heating rate of 5℃ / Min. Raise temperature from 25℃ to 90℃, react for 6h, cool to 30℃~40℃, discharge the material, wash the material repeatedly with absolute ethanol and deionized water until it is neutral, put it in a blast drying box, 105±2℃ Bake to absolute dryness under the conditions to obtain acetylated modified biogas residue fiber A, and the grafting rate is calculated to be 58.39%.
[0037] S2: Preparation of biogas residue fiber seedling tray
[0038] 1000g of acetylated modified biogas residue fiber A, 500g of urea-formaldehyde prepolymer modified soybean protein binder (refer to the literature "Synthesis and Characterization of Soybean Protein Isolate Hydro...
Embodiment 2
[0042] S1: Acetylation pretreatment of biogas residue fiber
[0043] The biogas residue fiber (same as Example 1) was dried and pulverized to 80 mesh, and 400g of biogas residue fiber was weighed into a reaction kettle containing 1000ml of toluene solvent, 800ml of acetic anhydride was added, and after uniform stirring, 1.5g and 0.5 of p-benzoic acid were added. g sulfuric acid, heat up from 25°C to 140°C at a heating rate of 5°C / min, react for 0.5h, cool to 30°C~40°C, discharge the material, wash the material repeatedly with absolute ethanol and deionized water to neutrality, and place In a blast drying box, bake to absolute dryness at 105±2℃ to obtain acetylated modified biogas residue fiber B. The calculated grafting rate is 36.65%.
[0044] S2: Preparation of biogas residue fiber seedling tray
[0045] Combine 1000g of acetylated modified biogas residue fiber B, 3000g of urea-formaldehyde prepolymer modified soy protein binder, 80g of nano calcium carbonate (reinforcing filler),...
Embodiment 3
[0048] S1: Acetylation pretreatment of biogas residue fiber
[0049] The biogas residue fiber (same as Example 1) was dried and pulverized to 40 meshes. Weighed 300g biogas residue fiber into a reaction kettle containing 1000ml of toluene solvent, added 900ml of acetyl chloride, and after uniformly stirring, added 6g of p-benzoic acid. Rate 5℃ / min from 25℃ to 120℃, react for 3h, cool to 30℃~40℃, discharge, repeatedly wash with absolute ethanol and deionized water to neutrality, place in blast drying box, 105 Bake to absolute dryness at ±2℃ to obtain acetylated modified biogas residue fiber C. The calculated grafting rate is 72.77%.
[0050] S2: Preparation of biogas residue fiber seedling tray
[0051] Put 1000g of acetylated modified biogas residue fiber C, 1000g of urea-formaldehyde prepolymer modified soybean protein binder, 50g of titanium dioxide, 30g of Utopol, and 35g of liquid paraffin in a high-speed mixer at 55℃ at 380rpm Mix for 30 minutes at the rotating speed of the ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com