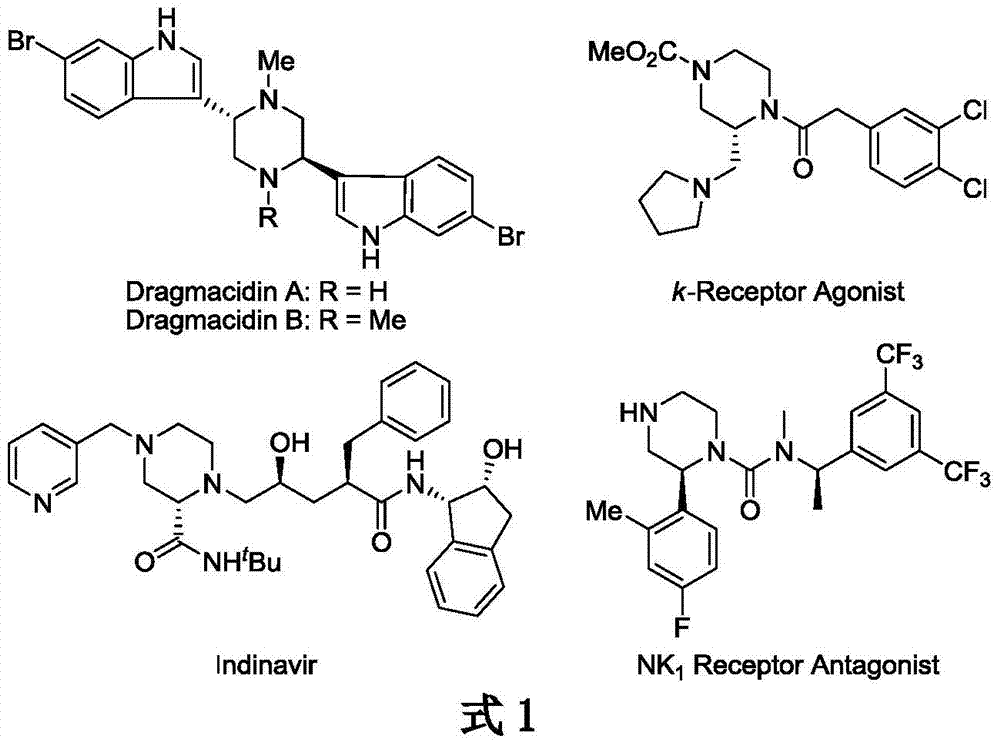
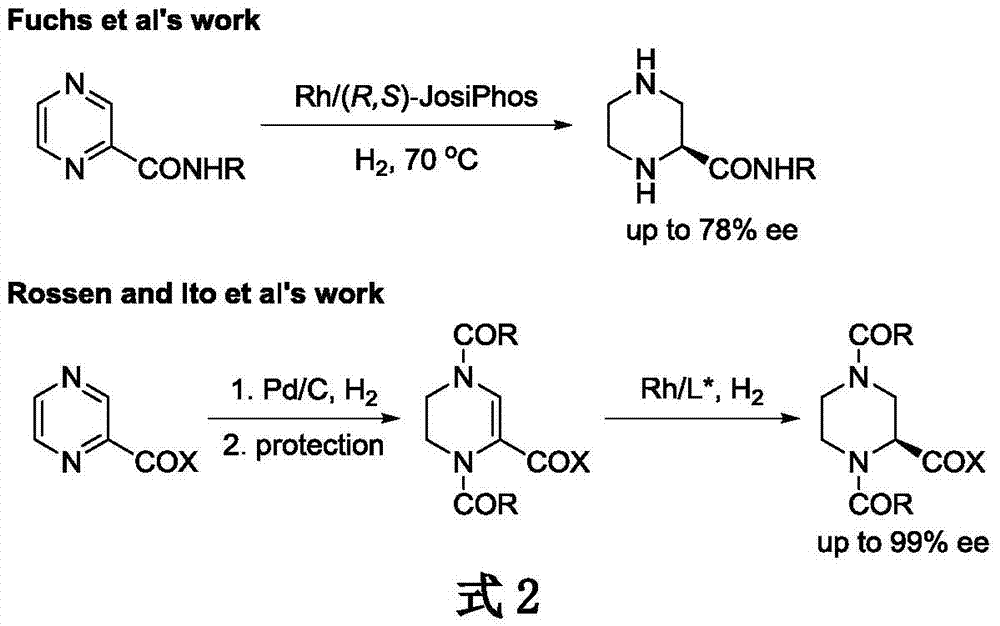
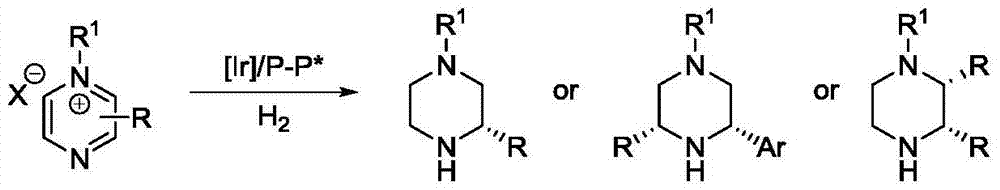
Iridium catalytic method for asymmetric hydrogenation to synthesize piperazine derivatives
An asymmetric and derivative technology, applied in organic chemistry methods, organic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as cumbersome steps and limited substrate range, and achieve simple preparation process, convenient separation, high reactivity and enantioselectivity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Embodiment 1: optimization of conditions
[0033] In a nitrogen-filled glove box, add (1,5-cyclooctadiene) iridium chloride dimer (0.002 mmol, 1.3 mg) and bisphosphine ligand (0.0044 mmol) to the reaction vial Add 1.0 ml of toluene solvent, stir at room temperature for 10-15 minutes, then transfer the prepared catalyst to another reaction flask containing raw material 3-phenylpyridinium salt 1a (0.20 mmol, 65.4 mg), 2.0 ml Wash the bottle with toluene, transfer the residual catalyst, and share 3 ml of solvent. The reaction bottle was put into a stainless steel autoclave, hydrogen gas was introduced at 600 psi, and the reaction was carried out at 30° C. for 36 hours. Slowly release hydrogen, filter the reaction solution, remove the solvent with a rotary evaporator, and then direct column chromatography (the volume ratio of the eluent dichloromethane and methanol is 20:1), and the pure product can be isolated. The reaction formula and formula The body is as follows:
...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2: Synthesis of 3-substituted piperazine derivatives by homogeneous iridium-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation
[0039] In a nitrogen-filled glove box, (1,5-cyclooctadiene) iridium chloride dimer (0.002 mmol, 1.3 mg) and (R,S p )- t Bu-JosiPhos (0.0044 mmol, 2.4 mg) was added into a reaction flask containing 1.0 ml of solvent toluene, stirred at room temperature for 10-15 minutes, and then the prepared catalyst was transferred to another container containing raw material 3-substituted pyrazine salt 1 (0.20 mmol) in the reaction flask, 0.5 ml of toluene and 1.5 ml of 1,4-dioxane solvent wash the bottle, transfer the residual catalyst, and share 3 ml of solvent. The reaction bottle was put into a stainless steel autoclave, hydrogen gas was introduced at 1200 psi, and the reaction was carried out at -20°C for 36 hours. The autoclave was taken out from the low temperature reactor, slowly raised to room temperature, and then hydrogen was released. Add excess sodium ...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Example 3: Synthesis of 3,5-disubstituted piperazine derivatives by homogeneous iridium-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation
[0059] In a nitrogen-filled glove box, (1,5-cyclooctadiene) iridium chloride dimer (0.002 mmol, 1.3 mg) and (R)-SegPhos (0.0044 mmol, 2.7 mg) Add 1.0 milliliters of solvent toluene to the reaction bottle, stir at room temperature for 10-15 minutes, then transfer the prepared catalyst to another reaction bottle containing raw material 3,5-disubstituted pyrazine salt 3 (0.20 mmol) 0.5 ml of toluene and 1.5 ml of 1,2-dichloroethane solvent to wash the bottle, transfer the residual catalyst, and share 3 ml of solvent. The reaction bottle was put into a stainless steel autoclave, hydrogen gas was introduced at 600psi, and the reaction was carried out at -20°C for 24 hours. The autoclave was taken out from the low temperature reactor, slowly raised to room temperature, and then hydrogen was released. Add excess sodium carbonate powder to the reaction ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com