Construction of drug penetration dynamic model based on three-dimensional cell model and application of drug penetration dynamic model to drug evaluation
A kinetic model, cell model technology, applied in medical simulation, special data processing applications, informatics and other directions, can solve the problems of the model can not predict the distribution, the integration is not high, the repeatability and universality are poor.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific example 1
[0018] Specific example 1 Establish a three-dimensional spheroid cell model with high spheroidization rate and good repeatability, which proves that it has a similar physiological state and drug distribution to in vivo tumor tissue, and can better reflect the kinetic behavior of drug penetration in in vivo tumor tissue .
[0019](1) Exploration of three-dimensional spheroid cell culture conditions: Human liver cancer cell HepG2 was used as the model cell. The physiological and biochemical state and three-dimensional structure of the spheroid cells were detected by microscope bright field observation and scanning electron microscope, and the optimal spot plate density was finally determined to be 7500 cells / well, and the optimal culture time was 7 days. The stability and repetition rate of cell spheroid formation under the optimal culture method were investigated based on three aspects: the distribution of the ratio of length to short diameter, the distribution of cross-section...
specific example 2
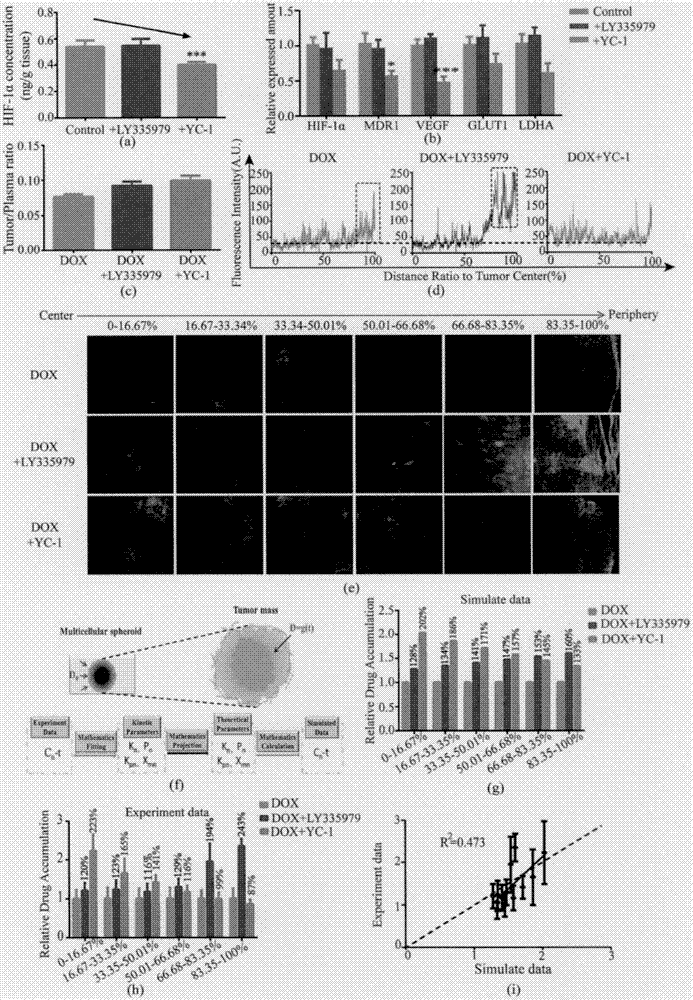
[0021] Specific example 2 Based on the three-dimensional spheroid cell model, the accumulation and penetration kinetics of commonly used anti-tumor drugs were evaluated. The results indicated that the speed and degree of drug uptake by the cells in the central area were significantly lower than those in the peripheral cells, which eventually resulted in the average accumulation of drugs in the spheroid cells. amount decreased.
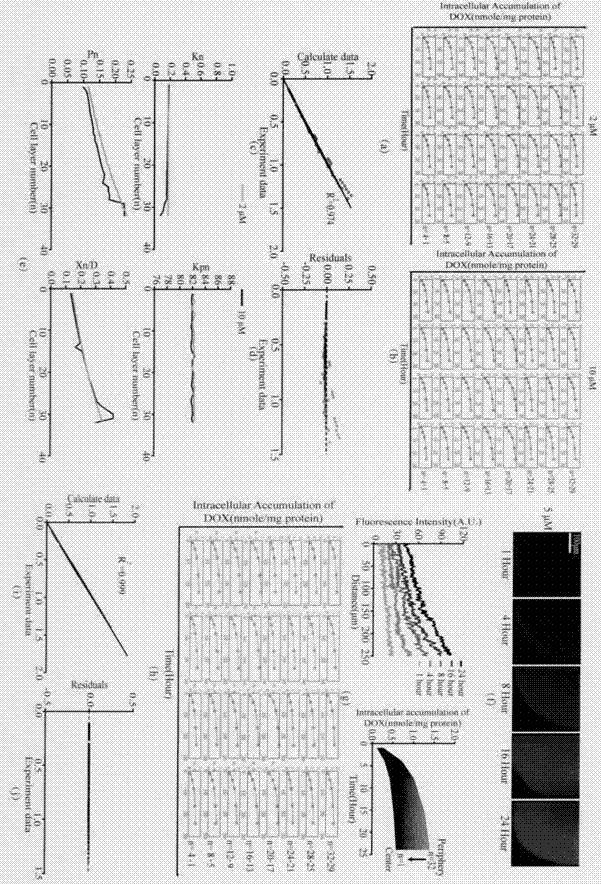
[0022] (1) Evaluation of uptake kinetics based on monolayer cell model and spheroid cell model. (a) Monolayer cells: Administer 10 μM doxorubicin or 5 μM paclitaxel, incubate at 37°C for 1h, 2h, 4h, 8h, 16h, 24h, then withdraw the drug, disrupt the cells by reverse ultrasonication, and store them at -80°C for later use. (b) Spheroid cells: 150 μl of serum-free medium containing 10 μM doxorubicin or 5 μM paclitaxel was added to each well, and incubated in a cell culture incubator for 1 h, 2 h, 4 h, 8 h, 16 h, and 24 h. After the reaction, the MCTS in e...
specific example 3
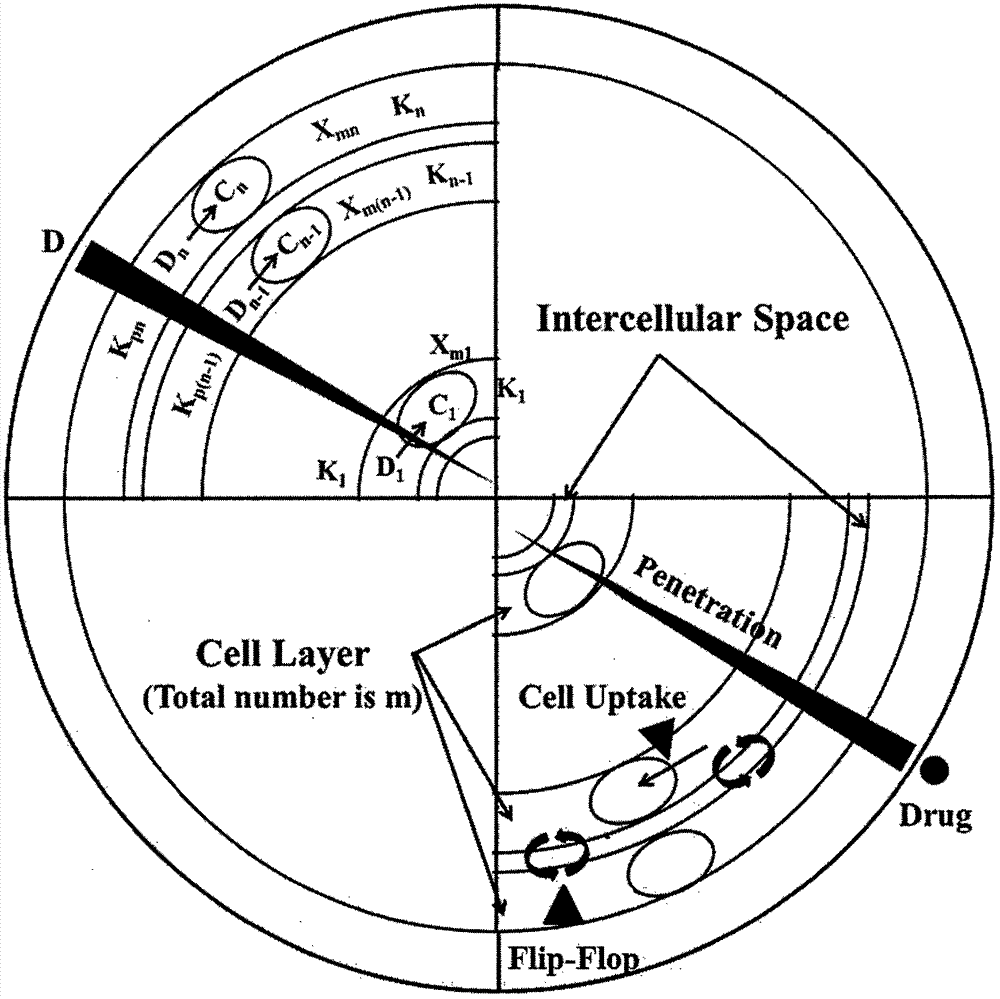
[0029] Specific Example 3 A mathematical model was established to quantitatively describe the kinetic process of drug penetration and accumulation in spheroid cells, and it was confirmed that the model has good descriptiveness and high accuracy. And based on molecular biology methods, the influencing factors of parameter changes are analyzed, and the transformation from in vitro evaluation to in vivo evaluation is realized.
[0030] The model assumes that the cultured cell spheres are regular spheres with a diameter of 500 μm and are composed of multiple layers of cells; the drug gradually diffuses from the periphery to the center, and the diffusion rate constant is a measure, and the diffusion rate is only related to the concentration difference; the same in the sphere model The cells in the same layer are in the same state and have the same drug uptake ability, and the drug uptake ability of the cells changes continuously with the radius; there is a certain gap between the ce...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com