Identification method of competitive endogenous RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) network
An identification method and competitive technology, applied in the field of identification of competitive endogenous RNA networks, can solve the problem of inability to verify whether different transcripts constitute a competitive regulatory relationship, inability to more accurately clarify the regulatory mechanism of different transcripts, and ceRNA network regulation Issues that have not yet been clearly understood, to achieve the effect of good sequence splicing, fast sequencing speed, and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
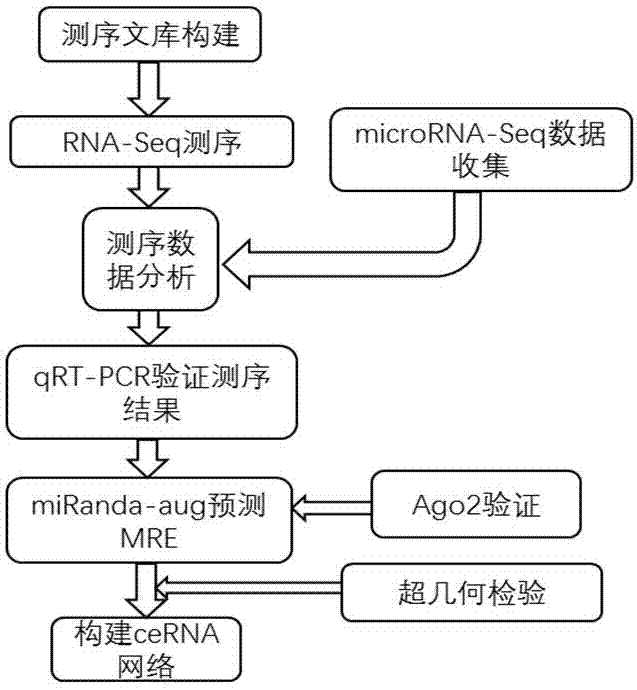
[0045] Build a sequencing library
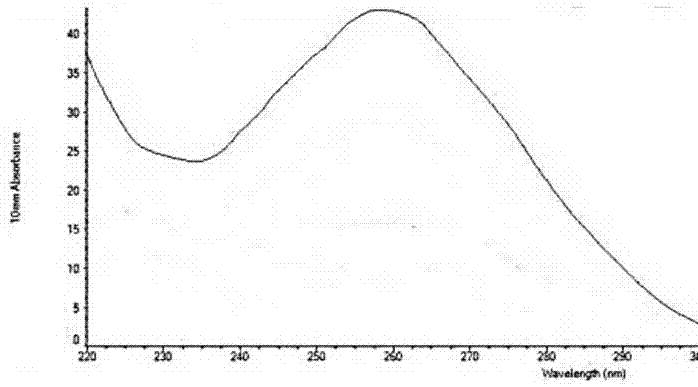
[0046] Human liver cancer cells (HepG2) were resuscitated, saturated with DMEM medium (Gibco) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (Hyclone), 100U / mL penicillin and 100U / mL streptomycin (Hyclone) at 37°C, 5% CO2 Cultured in a humidified cell culture incubator. Cells in the logarithmic phase were inoculated in 60mm culture dishes at a density of 5.0×106 cells / mL, and when they grew to about 80%, HepG2 cells were treated with 1 μg / mL doxorubicin (Beijing Huafeng) in the experimental group, and HepG2 cells in the control group were added Equal volume of PBS. After 24 hours, cells were collected by centrifugation after 0.25% (mass percent) trypsinization. The collected HepG2 cells were extracted according to the experimental instructions of TRIzol (Invitrogen), and the total RNA of the cells was extracted, and then the purity and integrity of the RNA were identified. Then send samples for sequencing. After the sample is qualified, the library is ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Screen differentially expressed mRNAs and lncRNAs as well as microRNAs
[0051] The original images obtained by HiSeq 4000 are converted into original sequencing sequences through base calling analysis, and the results are stored in the FASTQ file format. Filter reads with adapters and low quality in the original sequencing sequence to obtain CleanReads. Use Hisat2 (2.03-beta) to align clean reads to the human reference genome (hg19), use Cufflins (1.3.0) to assemble transcripts, use cuffmerge to fuse multiple annotation files generated, and use Cuffdiff to identify differentially expressed RNAs, Calculated by edgeR, according to q value <0.05, |log2(Fold change)|≥1 as the threshold value to screen to obtain differentially expressed lncRNA and mRNA respectively.
[0052] From the GEO (Gene Expression Omnibus) database, the sequencing data of p53-regulated microRNA in liver cancer cell HepG2 were obtained by small RNA sequencing (Small RNA-seq). v1.5) Statistical reads...
Embodiment 3
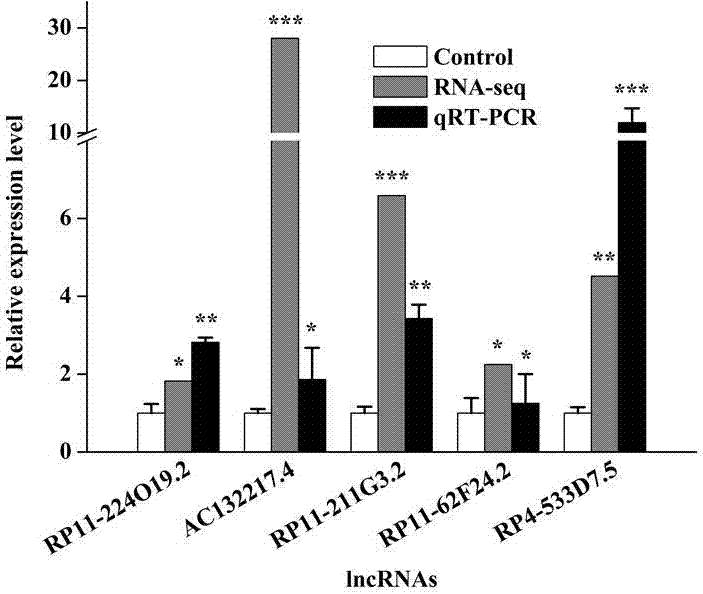
[0055] Verification of the accuracy of sequencing results
[0056] HepG2 cells were cultured to about 80% in a 10cm culture dish according to the culture conditions in Example 1. After 0.25% (mass percentage) trypsinization, the 5 cells / well were plated in 60 mm Petri dishes and cultured overnight. When the cells grew to about 70%, the control group was added with DMEM medium containing 10% FBS, and the experimental group was added with doxorubicin at a final concentration of 1 μg / mL, and cultured in a 37°C, 5% CO2 incubator. After 48 hours, 0.25% (mass percent) trypsin was digested and centrifuged to collect the cells, and the total RNA was extracted with Trizol, and the RNA was reverse-transcribed into cDNA using oligo(dT) primers and M-MLV reverse transcriptase, and some mRNAs and lncRNAs were randomly detected expression level to verify the accuracy of the sequencing results.
[0057] By doxorubicin treatment, the activity of p53 in the cells was increased. The qRT-PCR ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com