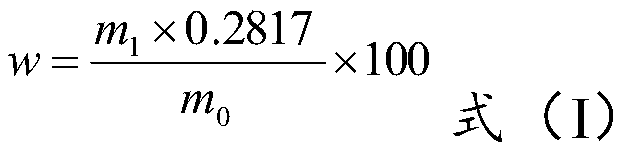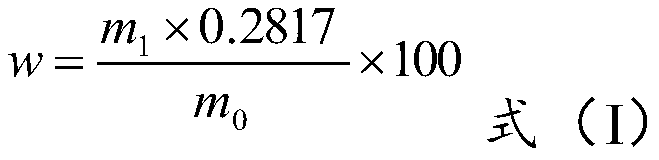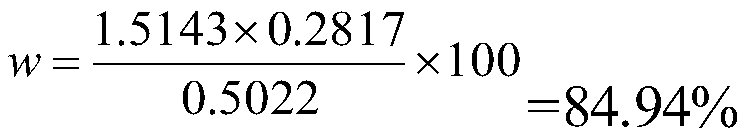A method for measuring selenium content in crude selenium
A crude selenium and content technology, which is applied in the direction of removing certain components and weighing, can solve the problems of cumbersome determination process, etc., and achieves the effects of cheap and easy-to-obtain reagents, easy-to-master, and simple methods.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Weigh 0.5022g (m 0 ), placed in a 250mL conical flask. Add about 100 mL of water, heat it to a slight boil, and add 4 g of hydroxylamine hydrochloride. Low temperature heating. Filter with slow quantitative filter paper. Wash the sediment and the beaker 3 times with water. Transfer the precipitate to the original beaker, add 19mL HNO 3 , Heat at low temperature on a hot plate, wait until the brown smoke is exhausted, remove and cool. Add 4.5mL hydrogen peroxide and 4mL perchloric acid, and heat at low temperature until the reaction is complete. Remove, slowly add about 40mL of sodium hydroxide (200g / L), adjust the solution to weak acid, heat at low temperature, and cool slightly. Slowly add about 21 mL of barium nitrate solution (150 g / L), heat at low temperature until the reaction is complete, and cool. Filter with a slow quantitative filter paper and rinse the precipitate with dilute nitric acid. The precipitate is dried in an electric thermostatic drying oven at...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Weigh 0.4981g (m 0 ), placed in a 250mL conical flask. Add about 110mL of water, heat to a slight boil, and add 3.5g of hydroxylamine hydrochloride. Low temperature heating. Filter with slow quantitative filter paper. Wash the sediment and the beaker 3 times with water. Transfer the precipitate to the original beaker, add 22 mL of hydrochloric acid, and heat it at low temperature on a hot plate. When the brown smoke is exhausted, remove it and cool. Add 5mL hydrogen peroxide and 5mL perchloric acid, and heat at low temperature until the reaction is complete. Remove, slowly add about 45mL of potassium hydroxide (220g / L), adjust the solution to weak acid, heat at low temperature, and cool slightly. Slowly add about 23mL barium nitrate solution (150g / L), heat at low temperature until the reaction is complete, and cool. Filter with a slow quantitative filter paper and rinse the precipitate with dilute nitric acid. The precipitate is dried in an electric thermostatic dr...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Weigh 0.5009g (m 0 ), placed in a 250mL conical flask. Add about 100mL of water, heat to a slight boil, and add 5g of hydrazine hydrate. Low temperature heating. Filter with slow quantitative filter paper. Wash the sediment and the beaker 3 times with water. Transfer the precipitate to the original beaker, add 20mL HNO 3 , Heat at low temperature on a hot plate, wait until the brown smoke is exhausted, remove and cool. Add 6g potassium permanganate and heat at low temperature until the reaction is complete. Remove, slowly add about 42mL of sodium hydroxide (200g / L), adjust the solution to weak acidity, heat at low temperature and cool slightly. Slowly add about 20mL barium chloride solution (170g / L), heat at low temperature until the reaction is complete, and cool. Filter with a slow quantitative filter paper and rinse the precipitate with dilute nitric acid. The precipitate is dried in an electric thermostatic drying oven at 105℃±5℃ for about 2 hours, and weighed ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com