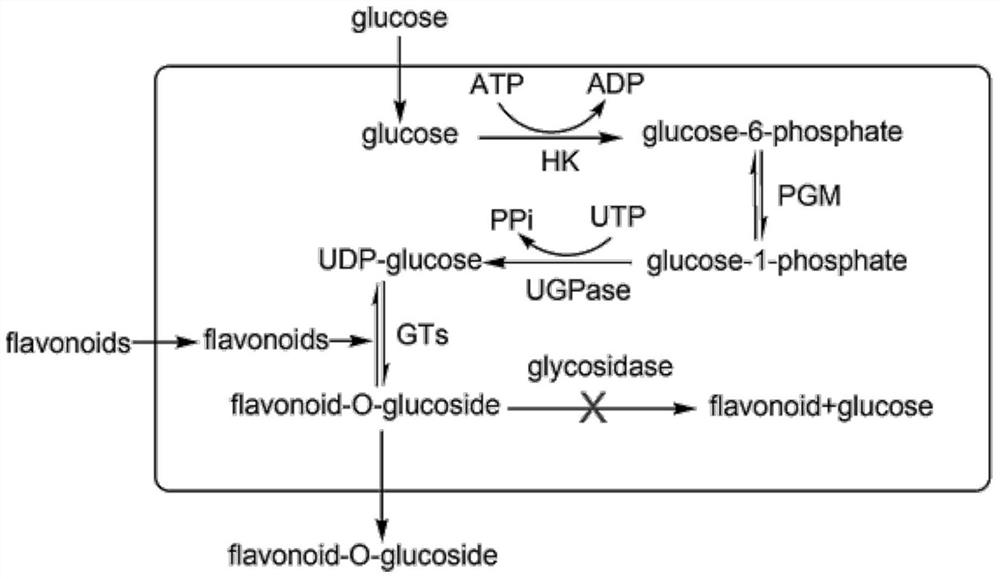
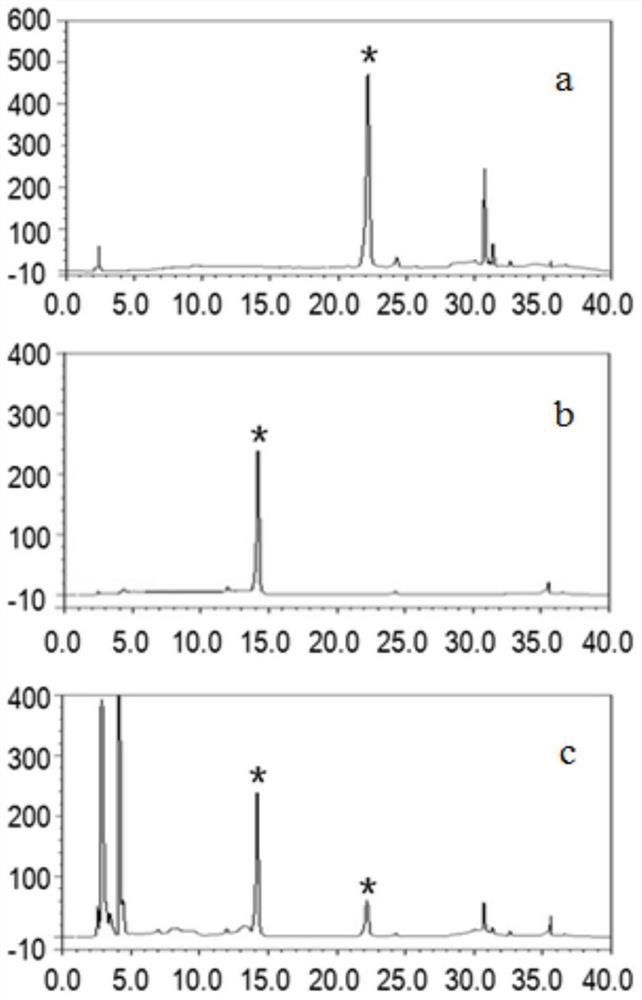
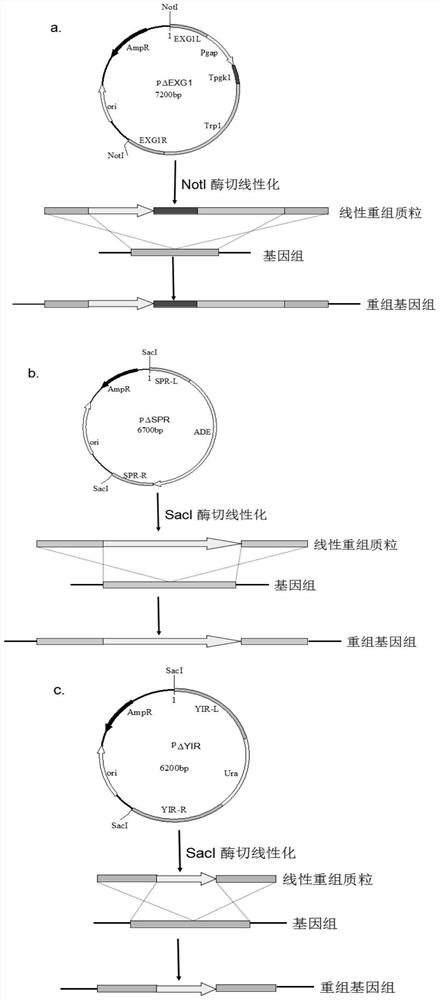
A genetically engineered bacterium that catalyzes the glucosidation of flavonoids and its application
A technology of flavonoids and genetically engineered bacteria, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering and can solve problems such as accumulation of unfavorable flavonoid glucoside products and improvement of yield.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] Embodiment 1: Preparation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria
[0066] Step 1: Genomic DNA extraction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Use the Yeast Genomic DNA Extraction Kit of Beijing Kangwei Century Biotechnology Co., Ltd. to extract genomic DNA. The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0067] (1) Pick a single clone and inoculate it in 10mL liquid YPD (10g / L yeast extract, 20g / L tryptone, 20g / Lglucose) medium, culture at 30°C, 250rpm for 15-20h (logarithmic phase).
[0068] (2) 12000rpm, 1min multiple centrifugation to collect the bacterial cells in a 1.5mL EP tube (4-5 times), and discard the supernatant by centrifugation.
[0069] (3) Removal of yeast cell wall: add 600 μL Lyticase Working Buffer (before use, add β-mercaptoethanol to make the final concentration 0.1%), and add 5 μL Lyticase (10 U / μL), mix well, 30 Treat at ℃ for 30 min, centrifuge at 4000 rpm for 10 min, discard the supernatant, and collect the precipitate.
[0070] (4) Add 200 μ...
Embodiment 2
[0146] Example 2: Analysis of the activity of scutellarein catalyzed by glycosyltransferase SbGT34 in engineering bacteria knocked out of glycoside hydrolase
[0147] Engineering bacteria W303-1b / ES / SbGT34 was the experimental group. Based on the original bacteria W303-1b, the engineered bacteria W303-1b / SbGT34 containing only the glycosyltransferase SbGT34 was obtained by LiAc transformation; The gene SbGT34 was used to obtain the engineering strain W303-1b / ES / SbGT34. Using scutellarein as a substrate to identify the changes in the glycosylation activity of flavonoid substrates before and after the completion of knockout of glycoside hydrolase, the specific method is as follows:
[0148] (1) The single clone generated by transformation was inoculated in YPD liquid medium, 30°C, 220rpm, cultured to OD 600 to around 3.0.
[0149] (2) Transfer to SC synthetic medium according to 1% inoculum amount, and cultivate for about 10 h at 30° C. and 220 rpm.
[0150] (3) Regulate the...
Embodiment 3
[0154] Example 3: Effects of Saccharomyces cerevisiae sugar metabolism pathway PGM2 and UGP1 genes on conversion rate of flavone substrates catalyzed by engineering bacteria
[0155] The engineering bacteria W303-1b / ES / PU / SbGT34 was used as the experimental group, and the engineering bacteria W303-1b / ES / SbGT34 was used as the control group to identify the effects of PGM2 and UGP1 genes on the conversion rate of flavonoid substrates catalyzed by engineering bacteria. Using scutellarein as a substrate to identify the changes in the glycosylation activity of flavonoid substrates before and after the completion of knockout of glycoside hydrolase, the specific method is as follows:
[0156] (1) The single clone generated by transformation was inoculated in YPD liquid medium, 30°C, 220rpm, cultured to OD 600 to around 3.0.
[0157] (2) Transfer to SC synthetic medium according to 1% inoculum amount, and cultivate for about 10 h at 30° C. and 220 rpm.
[0158] (3) Regulate the biom...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com