Method for separating mesenchymal stem cells from placentas and digestive enzyme composition adopted in method
A technology of mesenchymal stem cells and digestive enzymes, applied in the field of separating stem cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0097] Embodiment 1, the separation of placental MSC
[0098] Within four hours after delivery, the placenta leaflets were cut off under aseptic conditions, and the placenta leaflets were fully washed with PBS buffer solution containing 10% volume FBS to remove residual blood in the placenta leaflets. First cut the placenta leaflet into 1cm 3 Tissue pieces of the same size were added to PBS buffer containing 0.1mg / mL dispase, 0.25mg / mL trypsin, 0.25mg / mL DNase I, 1mg / mL collagenase IV, 1mg / mL hyaluronidase for digestion at 37°C After 15 minutes, an appropriate amount of FBS was added to terminate the digestion. Then filter the tissue block and cell suspension together with a 200-mesh copper mesh and grind the tissue block with a syringe plunger, collect the filtered cell suspension and add it to a centrifuge tube for 10 minutes at 1000rpm, pour off the supernatant, and wash with 10% FBS Resuspend cells in PBS buffer. Then use density gradient centrifugation to separate an...
Embodiment 2
[0099] Embodiment 2, subculture of placental MSC and cryopreservation thereof
[0100] After about 10 days, after the scattered adherent cells formed colonies, they were digested with 0.05% trypsin / 2mM EDTA. 2 Carry out subculture. Afterwards, subculture was digested when the cells reached about 70% confluency. Take 3×10 after digestion 6 The cells were added to 1ml of cell freezing solution (containing 50% low-sugar DMEM culture medium, 40% FBS, 10% dimethyl sulfoxide), and were cooled by a program, and finally entered into a liquid nitrogen tube for freezing.
Embodiment 3
[0101] Embodiment 3, biological characteristic identification of placental MSC
[0102] 1. Cell growth and morphological characteristics
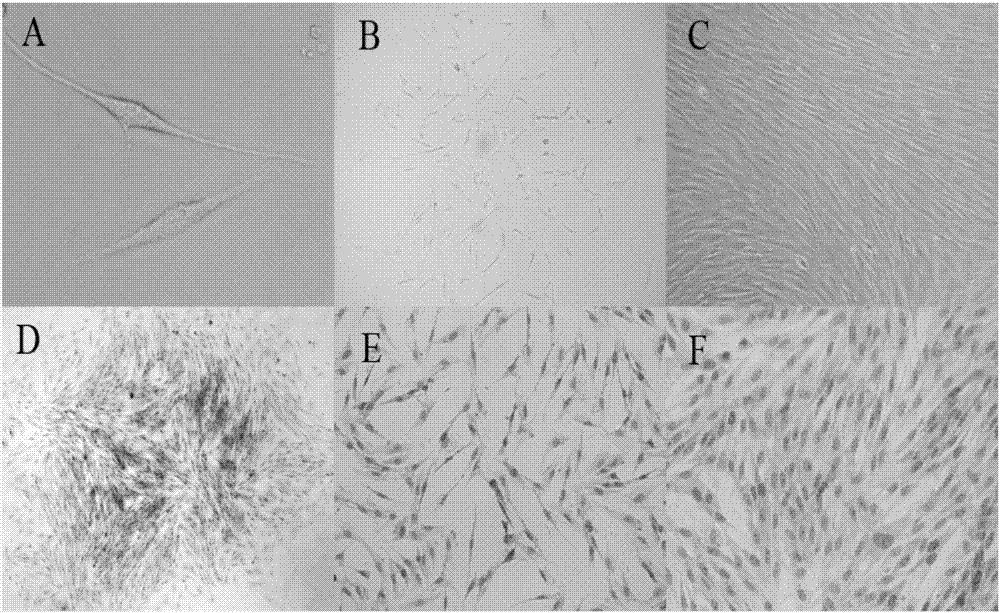
[0103] By the isolation culture of embodiment 1 and embodiment 2, the placental mononuclear cells can be clearly seen under the microscope after the placental mononuclear cells are cultured for 72 hours. Spindle-shaped adherent cells ( figure 1 A), about 10 days will form turbine-shaped cell clones ( figure 1 B. figure 1 D), after digestion and passage, about 80% of the fusion adherent layer will be formed ( figure 1 C. figure 1 E. figure 1 F). During the culture process, it was found that the cell shape was relatively uniform, the proliferation speed was fast, the adhesion speed was fast, and it was easily digested by trypsin. After passage to more than 15 generations, its shape and growth characteristics did not change significantly.
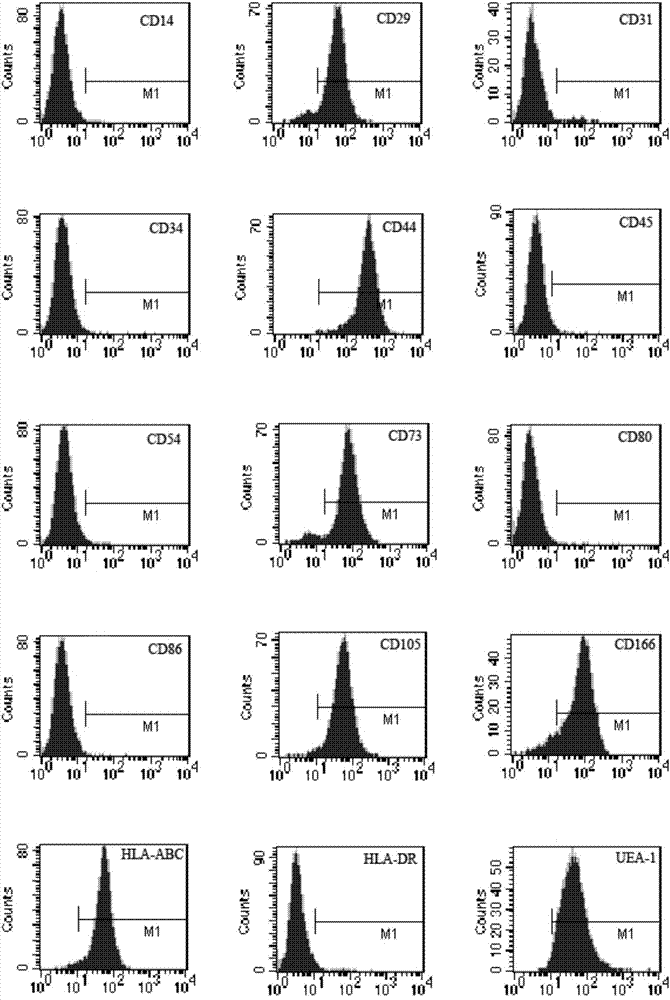
[0104] 2. Identification of MSC surface markers by flow cytometry
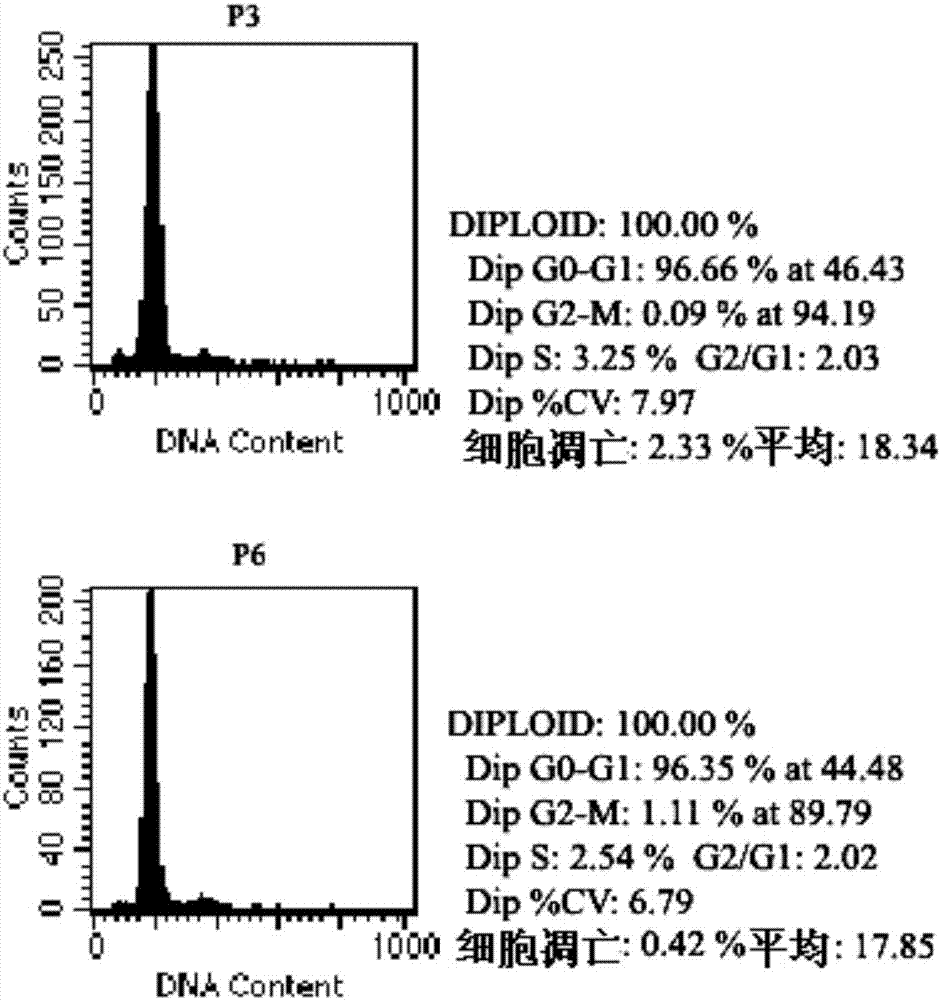
[0105] The 3rd, 6...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com