A production system for dry tea
A production system and dried tea technology, which is applied in the field of food processing, can solve the problems of the loss of nutritional components of dried tea, the loss of nutritional value of dried tea, and the short shelf life and freshness period of dried tea products, so as to improve the foaming phenomenon and reduce resources. Effects of energy consumption and reduced cooking time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
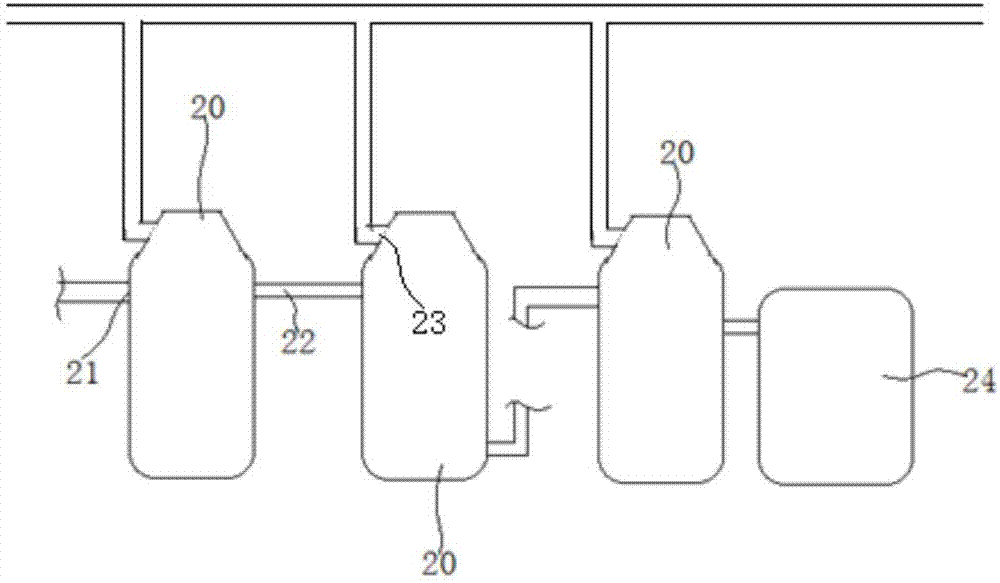
[0069] The preparation process of the new brine of the present invention is as follows: mixing and diluting soybean paste and normal temperature water according to the mass ratio of 1: (3-4), stirring evenly, heating to 98-100°C and boiling for 40-60 minutes, and then undergoing pressure filtration treatment That is the new halogen material. In this embodiment, after the new stewed material is stewed through the dried tea, it is filtered and left to stand, and the supernatant liquid is taken to obtain the old stewed material.
[0070] In this example, the mixture of new and old brine is used as the brine material, and at the same time, the mixing ratio of new brine and old brine, the specific brine making process parameters and the preparation process of new brine are optimized, so that the taste of the obtained dried tea can be effectively improved. and color.
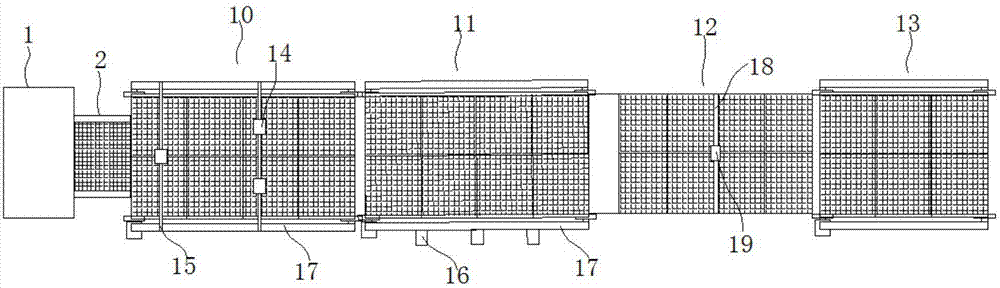
[0071] (7) Blow-drying and quenching treatment: more optimally, the dried sauce after marinating is transported to...
Embodiment 1
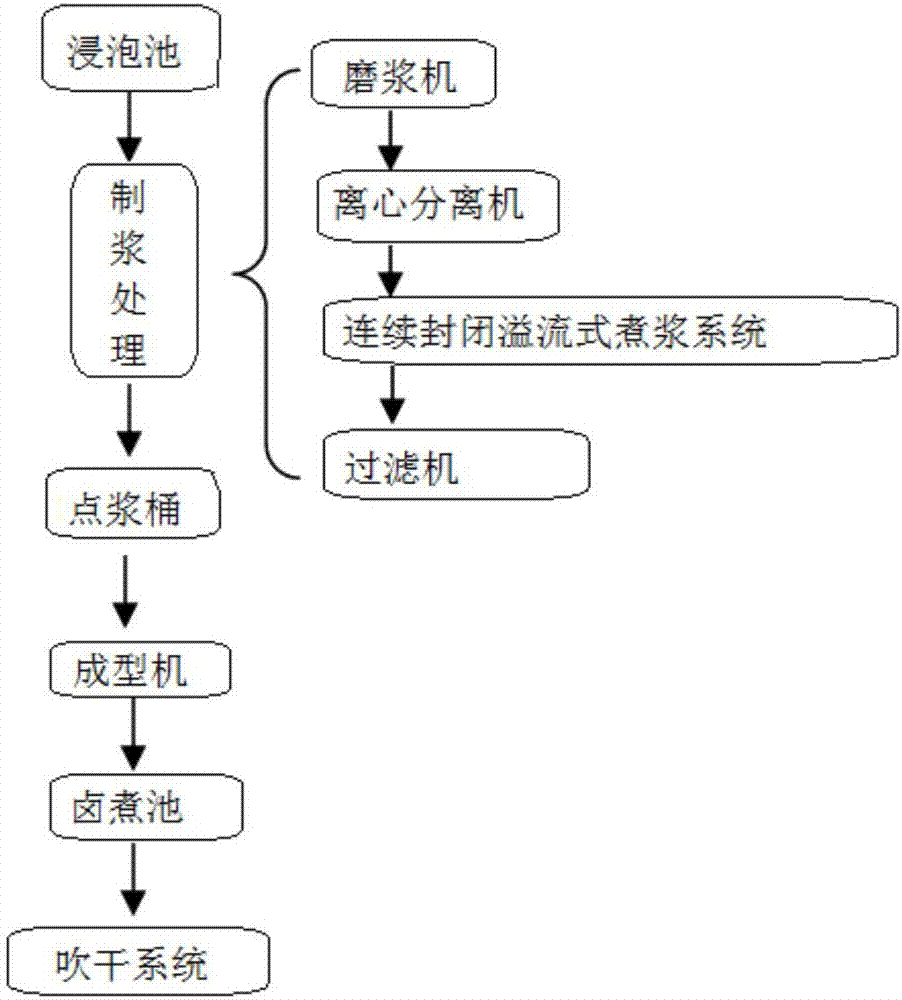
[0086] The dried tea production system of this embodiment includes a soaking tank, a pulping mechanism, a pulping tank, a forming machine and a stewing tank, and the specific steps of using this device for production are as follows:
[0087] (1) Bean selection and pretreatment: select soybeans with full grains, no insect erosion, and no impurities, and wash them to remove various bacteria adhering to the columnar cells of the soybean epidermis.
[0088] (2) Soaking: Soak the pretreated soybean raw materials in a soaking tank, wherein the mass ratio of soybeans to soaking water is 1:2.5, the pH value is 6.3, and the hardness of the soaking water is below 50 (50mgCa salt / L) , Fe content is below 0.3ppm. The soaked soybeans are washed again with clean water, so as to remove the silt and microorganisms attached to the soybean surface, and reduce the acidity of the soaked soybeans.
[0089] (3) Pulping: using soaked soybeans for pulping to obtain cooked pulp.
[0090] 1) Grinding...
Embodiment 2
[0102] The dried tea production system of the present embodiment has the same structure as in Example 1, and the specific steps of its production are:
[0103] (1) Bean selection and pretreatment: select soybeans with full grains, no insect erosion, and no impurities, and wash them to remove various bacteria adhering to the columnar cells of the soybean epidermis.
[0104] (2) Soaking: Soak the pretreated soybean raw materials in a soaking tank, wherein the mass ratio of soybeans to soaking water is 1:3, the pH value is 6.5, and the hardness of the soaking water is below 50 (50mgCa salt / L ), Fe content is below 0.3ppm. The soaked soybeans are washed again with clean water, so as to remove the silt and microorganisms attached to the soybean surface, and reduce the acidity of the soaked soybeans.
[0105] (3) Pulping: using soaked soybeans for pulping to obtain cooked pulp.
[0106] 1) Grinding and crushing (refining): After soaking soybeans, they are ground by a refiner, ther...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com