Method for detecting Parp activity based on analysis of hemin-graphene composites
A composite material, graphene technology, applied in the measurement of color/spectral properties, etc., can solve problems such as cumbersome synthesis, and achieve the effects of simplified detection methods, low cost, and sensitivity and specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
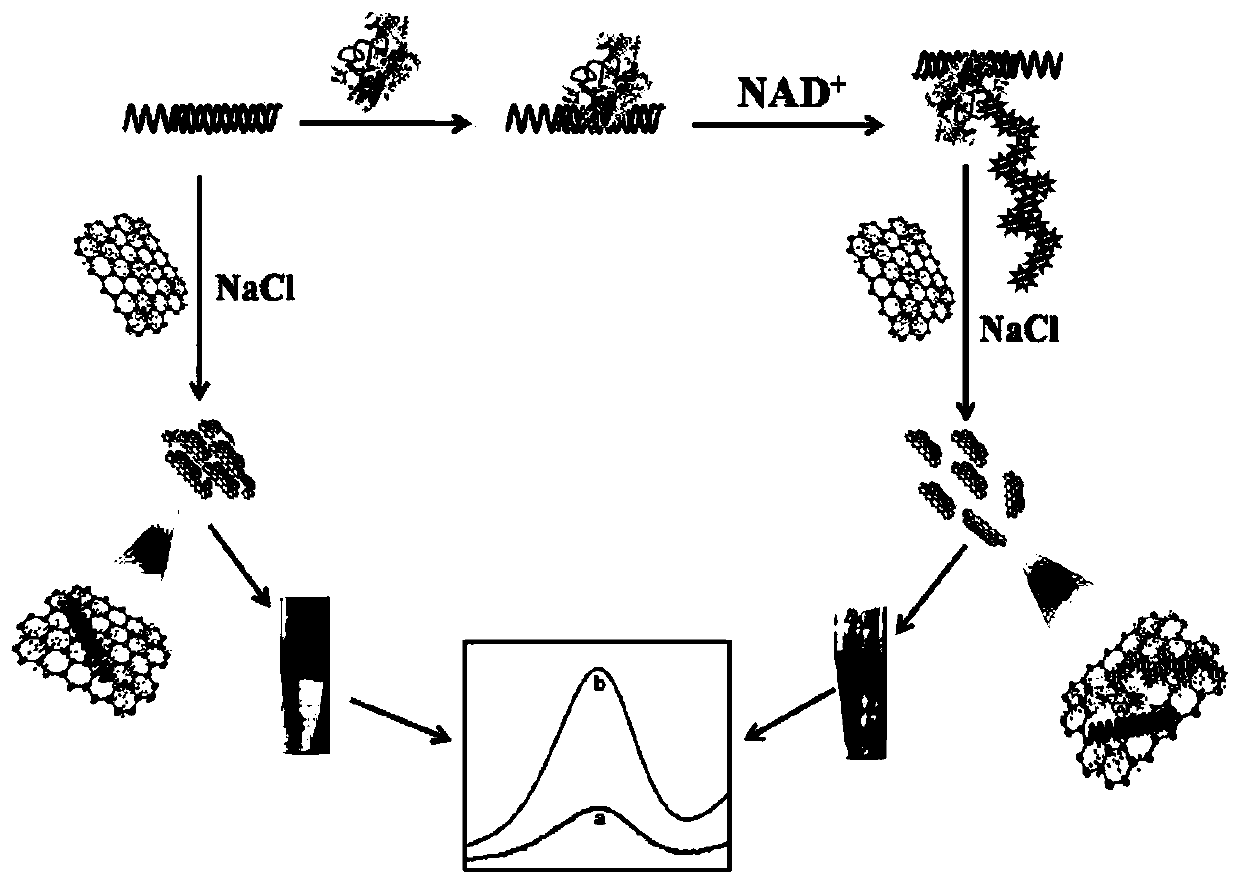
[0041] Based on the analytical method for analyzing and detecting PARP activity based on H-GNs composite material, the detection steps are:
[0042] Synthesis steps of H-GNs composite material: Weigh 10 mg of graphite oxide and dissolve it in 20 mL of secondary water (0.5 mg / mL), ultrasonically disperse for 2 h for mechanical exfoliation, centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 30 min to remove unexfoliated graphite oxide, and take the supernatant in dialysis The bag (MW:8000-12000) was dialyzed for one week to remove impurities and small molecules to obtain uniformly dispersed graphene oxide. The resulting graphene oxide solution was thoroughly mixed with 20 mL of hemin (0.5 mg / mL) dissolved in 0.1 M NaOH solution in a flask. After completion, slowly add 200 μL of ammonia solution and finally 30 μL of hydrazine hydrate. The mixed solution was vigorously stirred for 60 minutes, and the flask was placed in a water bath (60° C.) for 20 hours to obtain a stable and dispersed black solution. ...
Embodiment 2
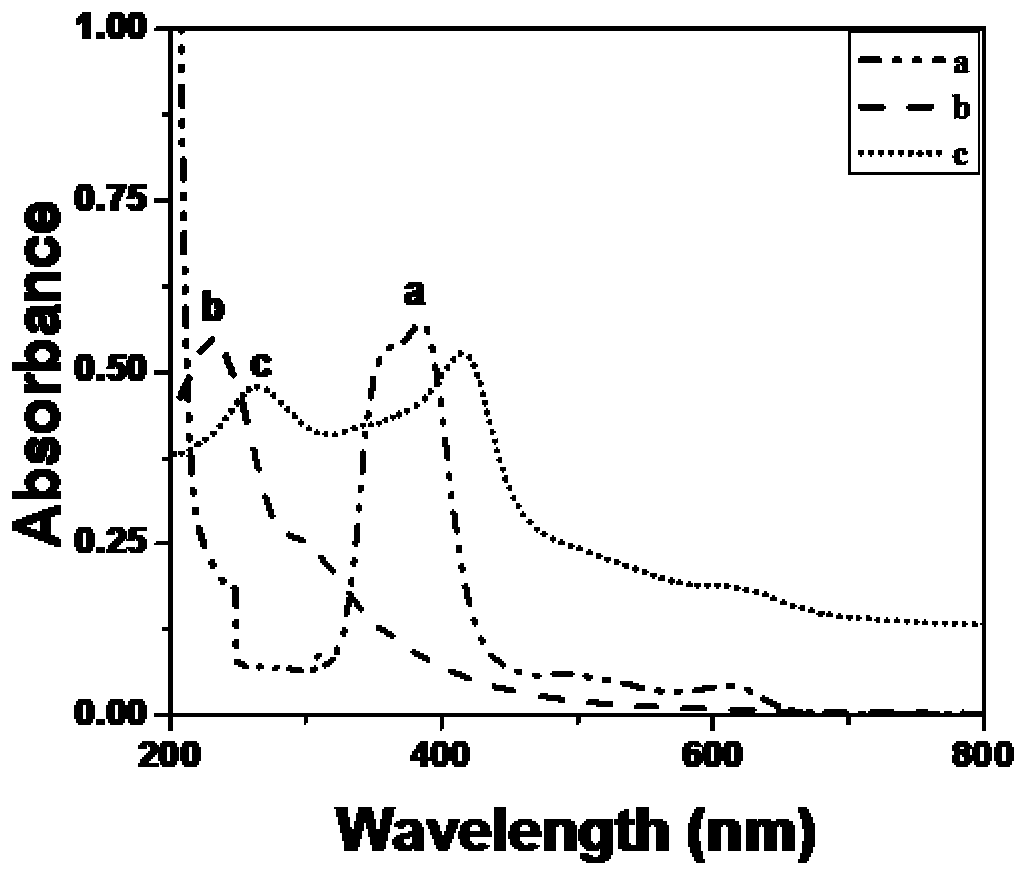
[0053] The difference from Example 1 is: select different concentrations of PARP (U, 1U=45ng): (a) 0 (b) 0.05 (c) 0.1 (d) 0.3 (e) 0.5 (f) 0.75 (g) 1 ( h)2(i)3, the obtained UV-visible light curve is as follows Figure 5 As shown, it can be seen that PARP has a good linear relationship between 0.05U and 1U in the range of 0-3U.
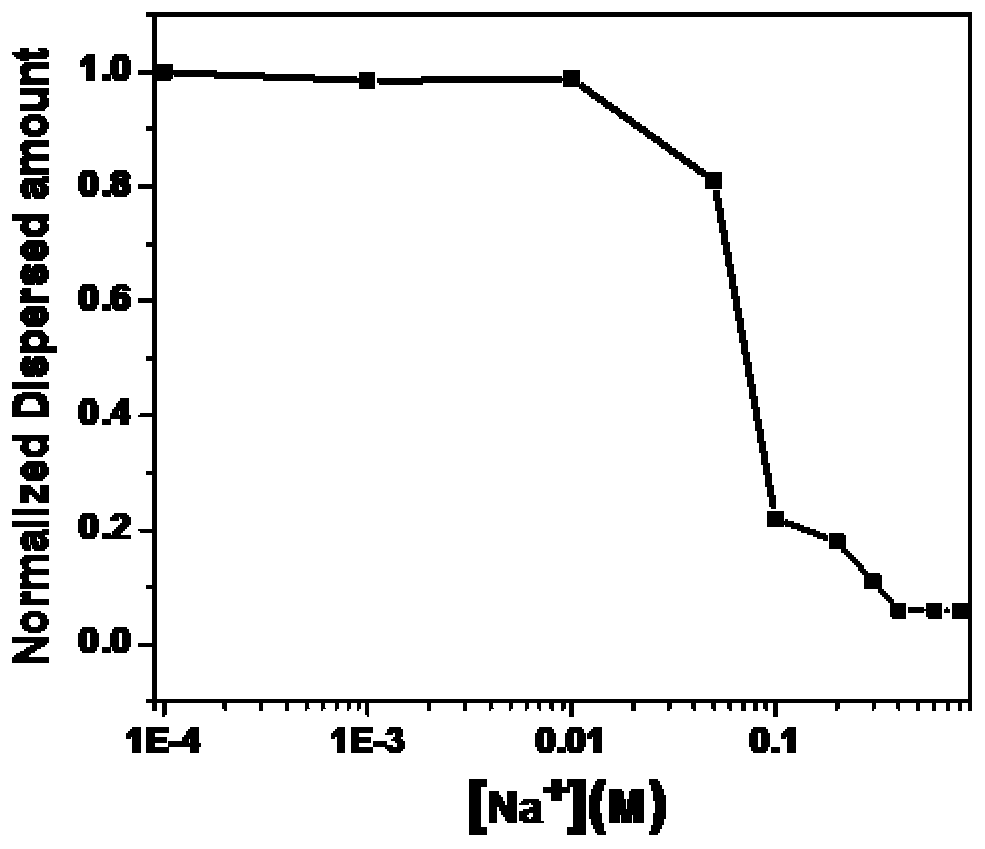
[0054] In summary, H-GNs composites can quantitatively detect PARP, due to the intrinsic catalase-like activity of H-GNs composites, adjustable dispersion in saline solution, and effective use of the characteristics of nanomaterials, The detection method does not need to be detected by precision instruments, the detection method is simplified, and the cost of virus detection is greatly reduced. The invention can successfully detect the activity of PARP added in serum, and has good clinical significance.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com