Method of packaging CRISPR-Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat-associated 9) system by using temperate phage vector
A bacteriophage, mild technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, other methods of inserting foreign genetic material, stably introducing foreign DNA into chromosomes, etc. The effect of slowing transmission, blocking horizontal transfer, and reducing drug resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
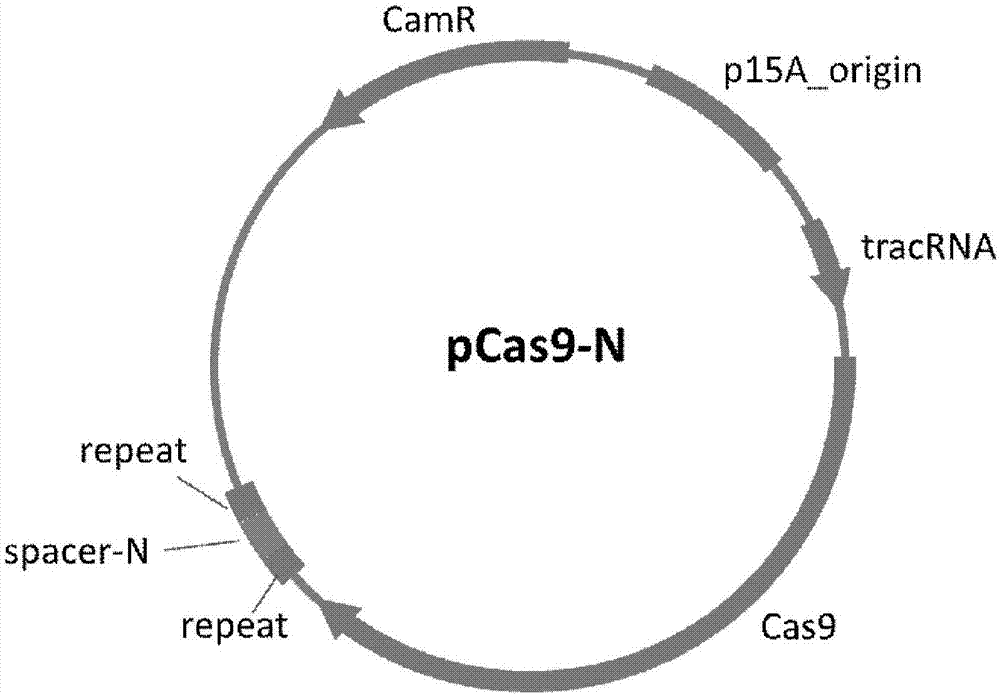
[0049] Example 1: Construction and screening of a CRISPR-Cas9 system targeting NDM-1 and MCR-1 drug resistance genes using pCas9 as a carrier
[0050] 1. Design of target sequences
[0051] (1) The design of the NDM-1 target sequence, according to the PAM principle in the design requirements of sgRNA, select the 30bp base sequence upstream of the NGG trinucleotide in the blaNDM-1 sequence as the target sequence, that is, the spacer in the CRISPR sequence sequence, which can be transcribed into sgRNA in bacterial cells.
[0052] A high-efficiency and specific target T1 sequence was screened from the twenty initially designed target sequences: SEQ ID NO: 1 (5'-ACCGCATTAGCCGCTGCATTGATGCTGAGC-3').
[0053] (2) Design of MCR-1 drug resistance gene sequence target
[0054] According to the colistin resistance gene MCR-1 sequence, according to the PAM principle, a 30bp base sequence was selected as the target of the gene, SEQ ID NO.2 (5'-atgccctacagaccgaccaagccgagacca-3').
[0055...
Embodiment 2
[0093] Example 2: CRISPR-Cas9 system targeted removal of NDM-1 drug-resistant plasmids
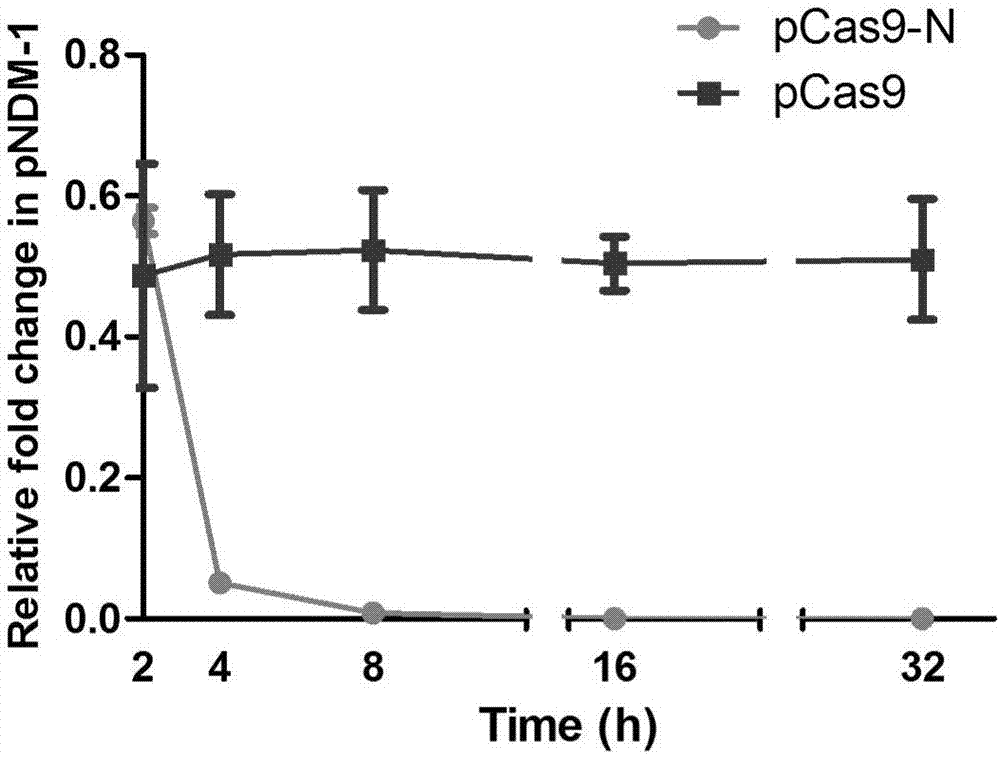
[0094] 1. The CRISPR-Cas9 system plasmid pCas9-N targeting NDM-1 was transformed into a drug-resistant bacterial model containing the pNDM-1 plasmid. Efficient removal of high-copy NDM-1 cloning plasmids (see image 3 ). The removal efficiencies are all greater than 99.9%. Figure 4 Confocal scanning photos of the removal effect of NDM-1 recombinant EGFP high-copy plasmid, NDM-1 plasmid contains a gene capable of expressing enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP), from Figure 4 It can be seen that the efficient clearance of NDM-1 by pCas9-N leads to the extreme reduction or even disappearance of EGFP. Figure 5 is the columnar control graph of the fluorescence intensity of the NDM-1 plasmid clearance rate; Figure 5 It can be seen that after pCas9-N plasmid removal, the fluorescence intensity decreased by more than 600 times.
Embodiment 3
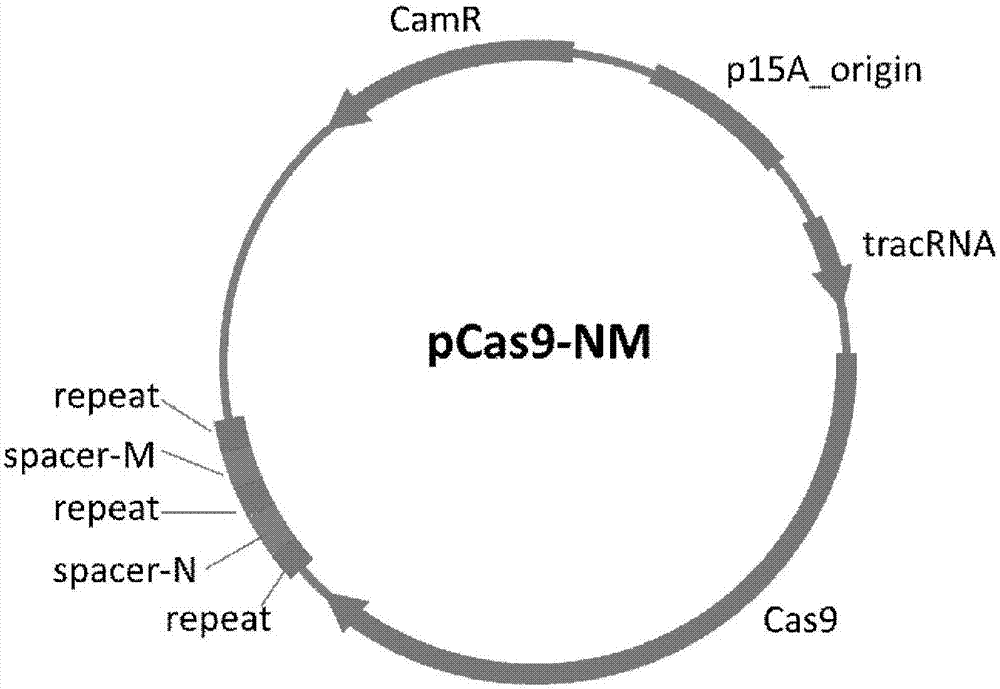
[0095] Example 3: CRISPR-Cas9 system pCas9-NM simultaneously targets and eliminates NDM-1 and MCR-1 drug-resistant plasmids
[0096] The NDM-1 and MCR-1 drug-resistant plasmids were cleared by pCas9-NM respectively, and the drug-resistant plasmids of the two drug-resistant bacterial models transformed with the pCas9-NM plasmid were detected. After shearing by pCas9-NM, both drug-resistant plasmids were eliminated and could not be detected by PCR (see Figure 6 ).
[0097] Detect changes in bacterial antibiotic sensitivity after pCas9-NM action. Etest drug-sensitive paper strip quantitatively detects the MIC value of the NDM-1 drug-resistant bacteria model to imipenem (thiamycin antibiotic with a carbapenem ring). / ml is reduced to 0.38ug / ml (see Figure 7 ).
[0098] The plate method was used to qualitatively analyze the changes in the bacterial drug sensitivity results after the MCR-1 plasmid was cleared by pCas9-NM. On the LB plates containing 0.5ug / ml colistin, there w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com