A method for studying photodissociation at low temperature
A photo-separation and low-temperature technology, which is applied to the parts of particle separator tubes, particle separation tubes, dynamic spectrometers, etc., can solve problems affecting experimental accuracy, broadening, long data acquisition time, etc., to improve energy accuracy and structure Compact and simple, the effect of increasing energy resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
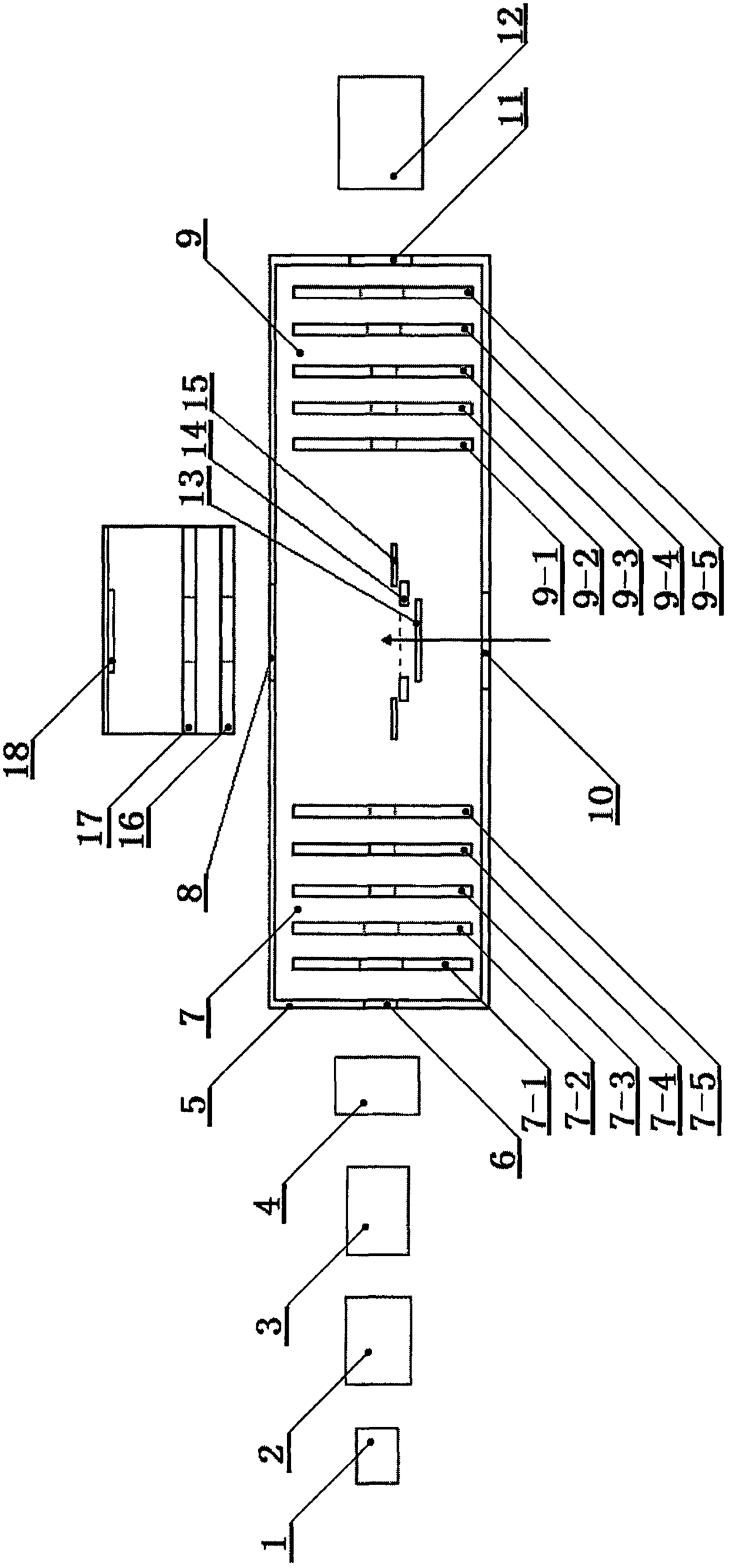
[0020] Such as figure 1It is a schematic diagram of the structure of the present invention. The device for studying photo-induced separation at low temperature is located in an ultra-high vacuum environment, and mainly includes an ion source (1), an accelerator (2), a time-of-flight mass spectrometer (3), a particle mass selector (4), a magnetic Shielding cover (5), ion beam entrance (6), electrode I (7-1), electrode II (7-2), electrode III (7-3), electrode IV (7-4), electrode V (7 -5) Focusing electrode group (7), photoelectron outlet (8), composed of electrode VI (9-1), electrode VII (9-2), electrode VIII (9-3), electrode IX (9-4) , mass selection electrode group (9) composed of electrode X (9-5), laser entrance (10), ion exit (11), ion detector (12), electronic background reduction plate (13), reflection plate (14) , ion correction plate (15), extraction electrode (16), beam focusing electrode (17) and electron detector (18), described focusing electrode group (7), mass se...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com