Method for improving cell compatibility of bio-derived hydroxyapatite
A hydroxyapatite and compatibility technology, applied in tissue regeneration, medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems of loss of cytocompatibility, affecting the speed of osteogenesis, transplantation failure, etc., to improve biocompatibility , improve cell compatibility, improve the effect of impact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
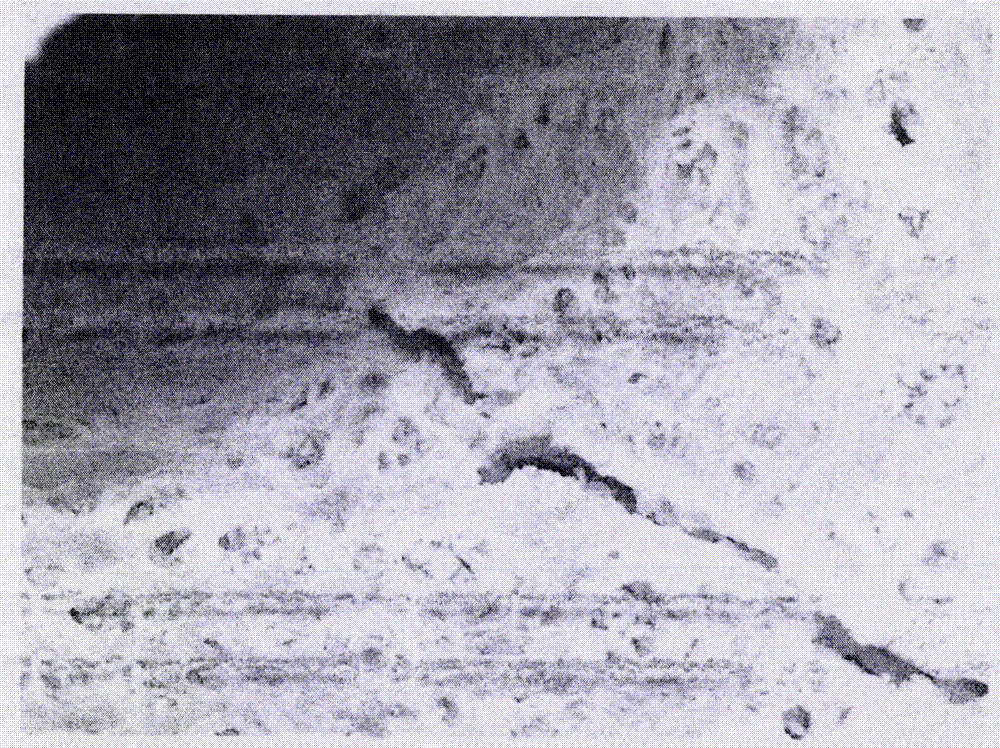
[0030] Observation of supercritical carbon dioxide degreasing effect, scanning electron microscope observation of bone materials that have undergone supercritical carbon dioxide degreasing and non-degreasing bone materials. , Fat is removed thoroughly, and cell components can be removed at the same time.
[0031] Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that there are a large number of fat droplets in the material without degreasing, and the fat cleaning is not thorough; figure 2 It can be seen that there are no fat particles on the surface of supercritical carbon dioxide degreased bone tissue, and cell lacuna after cell removal can be seen.
Embodiment 2
[0033] The biologically derived hydroxyapatite-like material prepared by the present invention was observed with the naked eye and a scanning electron microscope, and the results showed that the color of the material without supercritical carbon dioxide degreasing was yellowish-white after calcining, indicating that the fat removal in the early stage was not complete, and the subsequent hydroxyapatite The preparation of the material has a significant impact; the color of the calcined material degreased by supercritical carbon dioxide is ivory white, and the observation of the microstructure shows that the traditional calcined method is prone to produce a large number of microcracks on the surface of the calcined bone, while the calcined bone prepared by this method has basically no cracks on the surface. microcracks occur.
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3 In order to show the biomechanical properties of the bio-derived hydroxyapatite-like material prepared by the present invention, the biomechanical properties of hydroxyapatite prepared by traditional methods and hydroxyapatite prepared by this method were measured, as follows:
[0035] The prepared composite material was trimmed into 5×5×5mm cubes, 5 pieces in each group, and its compressive strength was measured by RGT-20A microcomputer-controlled universal testing machine, the loading rate was 1mm / s, and the elastic modulus was calculated. The specific results are shown in Table 1. It shows that the hydroxyapatite prepared by this method can effectively improve the biomechanical properties of the material due to the reduction of microcracks generated during calcination.
[0036] Table 1 Compressive strength and elastic modulus of bio-derived hydroxyapatite-like materials prepared by traditional calcination method and this method
[0037]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com