Starch-based carbon fiber and preparation method thereof
A starch-based, carbon fiber technology, applied in the direction of fiber chemical characteristics, conjugated artificial filaments, conjugated synthetic polymer artificial filaments, etc., can solve the restrictions on the popularization and application of starch-based carbon fibers, high porosity of starch-based carbon fibers, melting , flow, expansion and other problems, to achieve the effect of wide source of raw materials, simple preparation method, and reduce damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
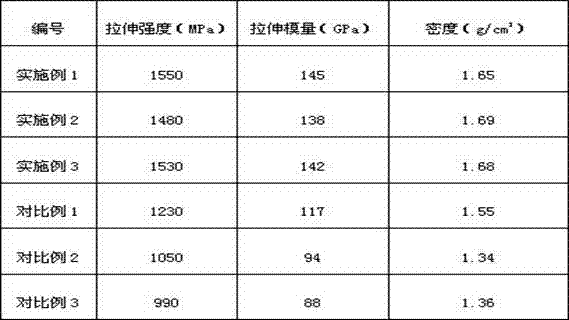
Embodiment 1
[0030] (1) Degrade and isomerize 100g of starch with 0.02g of glucose isomerase and 0.01g of amylase at 25°C for 4 hours to obtain product A;
[0031] (2) Add 1g of ferric chloride and 1g of copper chloride to product A, dehydrate at 105°C for 3 hours, separate and dry to obtain product B;
[0032] (3) Mix the product B with 8g of paraffin, 8g of phthalic acid, and 15g of polyacrylonitrile evenly, and carry out cross-linking polymerization with a twin-screw extruder; obtain product C; the twin-screw extrusion The maximum temperature of the working area in the machine is set to 330°C, and the minimum temperature is set to 280°C; the residence time of the material in the extruder is controlled at 90s;
[0033] (4) Melt spinning the product C at a temperature of 330°C to obtain starch-based carbon fiber precursors;
[0034] (5) The starch-based carbon fiber precursors were subjected to the first pre-oxidation at 200°C for 3 hours, and the second pre-oxidation at 370°C for 3 hour...
Embodiment 2
[0036] (1) Degrade and isomerize 100g of starch with 0.01g of glucose isomerase and 0.01g of amylase at 35°C for 5h to obtain product A;
[0037] (2) Add 1 g of ferrous chloride to product A, dehydrate at 85°C for 5 hours, separate and dry to obtain product B;
[0038] (3) Mix the product B with 5g of paraffin, 10g of phthalic acid, and 20g of polyacrylonitrile evenly, then carry out a cross-linking polymerization reaction at 320°C for 2 hours; obtain product C;
[0039] (4) Melt spinning the product C at a temperature of 350°C to obtain starch-based carbon fiber precursors;
[0040] (5) Carry out the first pre-oxidation of the starch-based carbon fiber precursor at a temperature of 220°C for 3 hours, and perform the second pre-oxidation at a temperature of 350°C for 5 hours, and then perform carbonization treatment at a temperature of 1250°C to obtain starch-based carbon fibers .
Embodiment 3
[0042](1) Degrade and isomerize 100g of starch with 0.03g of glucose isomerase and 0.02g of amylase at 35°C for 2 hours to obtain product A;
[0043] (2) Add 1g of ferric chloride, 1g of ferrous chloride, and 1g of hydrochloric acid to product A, dehydrate at 120°C for 1 hour, separate and dry to obtain product B;
[0044] (3) Mix the product B with 10g of paraffin, 5g of phthalic acid, and 10g of polyacrylonitrile evenly, and conduct a cross-linking polymerization reaction at a temperature of 340°C for 1 hour to obtain product C;
[0045] (4) Melt spinning the product C at a temperature of 310°C to obtain starch-based carbon fiber precursors;
[0046] (5) Carry out the first pre-oxidation of the starch-based carbon fiber precursors at a temperature of 180°C for 3 hours, and perform the second pre-oxidation at a temperature of 390°C for 2 hours, and then perform carbonization treatment at a temperature of 1050°C to obtain starch-based carbon fibers .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com