A processing technology of ceramic tableware body for daily use
A processing technology and a technology of blanks, which are applied in the processing technology field of daily ceramic tableware blanks, can solve problems such as the absence of daily ceramic tableware blanks, and achieve the advantages of improving thermal shock resistance, ensuring flatness and reducing economic losses. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] (1) Raw material preparation: mix 50kg of kaolin, 10kg of clay, and 15kg of feldspar powder, add 0.5kg of nano-titanium dioxide and 0.5kg of molecular sieve raw powder, fully mix, and use a pulverizer to make coarse powder and fine powder into a particle size of 50 The target powder is then subjected to dry magnetic separation using a magnetic separator to remove iron, and the billet powder is obtained;
[0028] (2) Slurry preparation: add 60kg of billet powder into 300kg of water, make a slurry with a particle size of 100 mesh after refining, and use a magnetic separator to further remove iron through wet magnetic separation;
[0029] (3) Mud filtration and dehydration: the above-mentioned prepared mud is passed through a 120-mesh vibrating screen, and the resulting filtrate is sent into a bag filter press for dehydration through pressure filtration, and the water content of the gained mud after dehydration is controlled at 18-23%;
[0030] (4) Vacuum mud refining: the...
Embodiment 2
[0035] (1) Raw material preparation: mix 55kg of kaolin, 15kg of clay, and 10kg of feldspar powder, add 1kg of nano-titanium dioxide and 0.5kg of molecular sieve raw powder, fully mix, and use a pulverizer to make coarse powder and fine powder into a particle size of 50 mesh powder, and then use a magnetic separator to go through dry magnetic separation to remove iron, that is, the green powder;
[0036] (2) Slurry preparation: add 70kg of billet powder into 400kg of water, make a slurry with a particle size of 100 mesh after refining, and use a magnetic separator to further remove iron through wet magnetic separation;
[0037] (3) Mud filtration and dehydration: the above-mentioned prepared mud is passed through a 120-mesh vibrating screen, and the resulting filtrate is sent into a bag filter press for dehydration through pressure filtration, and the water content of the gained mud after dehydration is controlled at 18-23%;
[0038] (4) Vacuum mud refining: the obtained mud i...
Embodiment 3
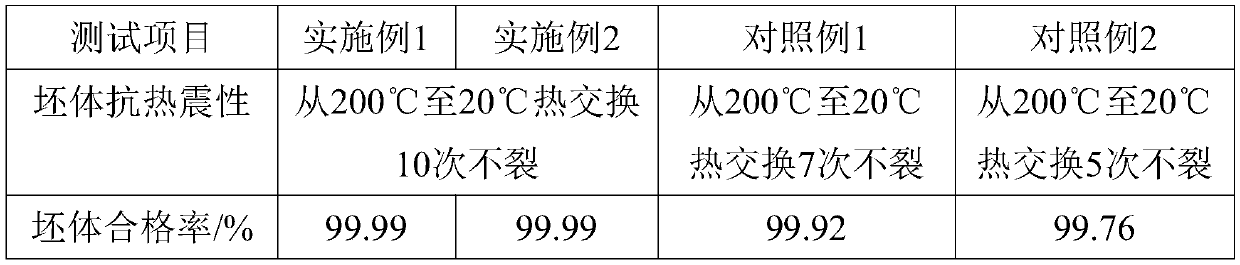
[0058] Use the methods described in Example 1, Example 2, Comparative Example 1, and Comparative Example 2 to process the ceramic tableware body, and test the thermal shock resistance of the processed body, and then send the body into the same kiln The furnace was fired under the same firing conditions, and the pass rate of the green body after firing was measured. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0059] Table 1 The thermal shock resistance of the green body made by processing and the pass rate of the green body after firing
[0060]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com