Method for in-situ preparation of nickel-iron bimetallic materials by repairing nickel ion polluted wastewater
An in-situ preparation, bimetallic technology, applied in water pollutants, metal processing equipment, water/sewage treatment, etc., to achieve the effects of low energy consumption, fast speed, and mild reaction conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] (1) in N 2 Under protection, 0.5g / L sodium bentonite, 0.05mol / L FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O and 0.1mol / L NaBH 4 Mix and stir for 2 hours, wash with deoxygenated water and ethanol, and vacuum freeze-dry to prepare bentonite-supported nanometer zero-valent iron.
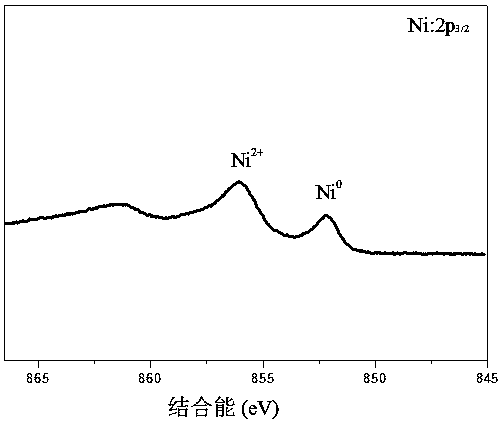
[0030] (2) Weigh the bentonite loaded with zero-valent iron (25 mg iron content) prepared in step (1) and add it to the wastewater containing 200 mg / L Ni(II) (adjust the pH to 6). in N 2 Under protection, shake the reaction for 2 hours (150 rpm, 25°C). After the reaction, the solid was obtained by centrifugation, and the residual Ni(II) in the supernatant was determined to be zero, and the removal rate of Ni(II) was 100%. The solid was washed, vacuum freeze-dried, and determined by XPS to contain zero-valent nickel active components such as figure 1 As shown, the results confirm that the Fe / Ni(II) bimetal was indeed formed during the treatment of Ni(II) with zero-valent iron loaded on bentonite.
[0031] (3) Add the N...
Embodiment 2
[0033] (1) Bentonite loaded with zero-valent iron was prepared according to the method of step (1) in Example (1).
[0034](2) Weigh the bentonite loaded with zero-valent iron (15 mg iron content) prepared in step (1) and add it to the waste water containing 100 mg / L Ni(II) (adjust the pH to 5). 2 Under protection, shake the reaction for 2 hours (150 rpm, 25°C). After the reaction, the Ni / Fe bimetallic material was obtained by centrifugation, and the residual Ni(II) in the supernatant was determined to be zero, and the removal rate of Ni(II) was 100%.
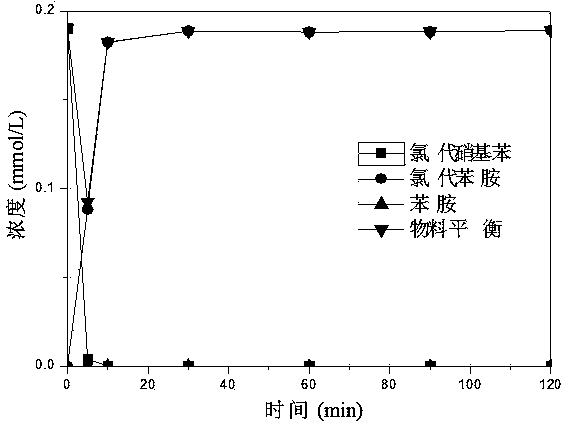
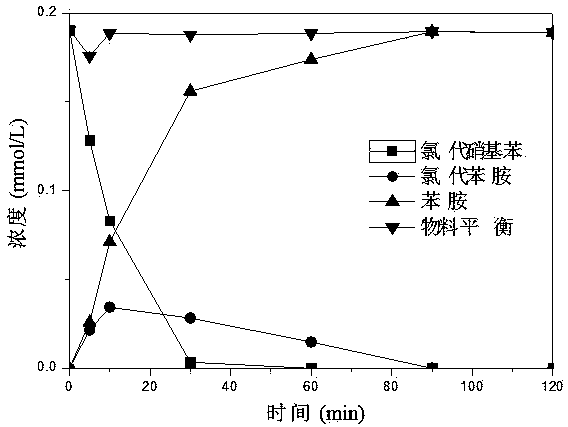
[0035] (3) Add the Ni / Fe bimetallic material obtained in step (2) and the Ni / Fe bimetallic material prepared by conventional methods (the iron content of the two materials are the same), respectively, into Benzene wastewater (pH 6), N 2 Shake the reaction under protection for 2 hours (150 rpm, 25°C). After the reaction, the products and their concentrations in the wastewater were measured respectively. The results showed th...
Embodiment 3
[0037] (1) Bentonite loaded with zero-valent iron was prepared according to the method of step (1) in Example (1).
[0038] (2) Weigh the bentonite loaded with zero-valent iron (10 mg iron content) prepared in step (1) and add it to the wastewater containing 50 mg / L Ni(II) (adjust the pH to 6.5). 2 Under protection, shake the reaction for 1 hour (150 rpm, 25°C). After the reaction, the Ni / Fe bimetallic material was obtained by centrifugation, and the residual Ni(II) in the supernatant was determined to be zero, and the removal rate of Ni(II) was 100%.
[0039] (3) Add the Ni / Fe bimetallic material obtained in step (2) to the wastewater containing 20 mg / L p-chlorophenol (pH 6), N 2 Shake the reaction under protection for 2 hours (150 rpm, 25°C). After the reaction, the products and their concentrations in the wastewater were measured respectively. The results show that the Ni / Fe bimetallic material has completely reduced p-chlorophenol to phenol, indicating that the chlorine...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com