Derivative of selenole and application of derivative
A technology of benzoselenodiazole and derivatives, which is applied in the field of chemical synthesis of drugs, can solve the problems of reproductive function impact, high toxicity and side effects, bone marrow suppression, etc., and achieve the effect of expanding the synthesis scale, reducing toxicity and side effects, and optimizing the process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
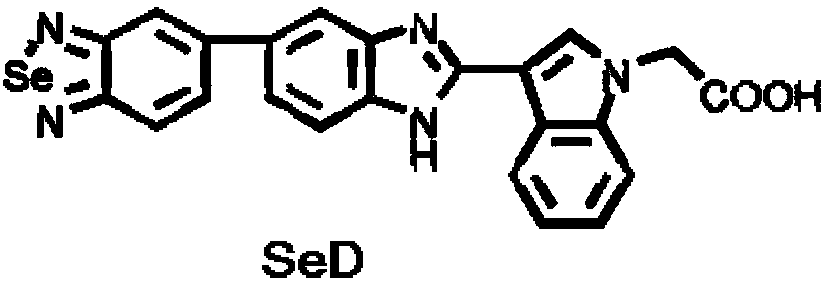
[0038] Synthesis and Characterization of 5-(2-Substituted Indolylbenzimidazole) Benzo[1,2,5]Selenadiazole Derivatives
[0039] (1) Weigh 30mmol of 3,3'-diaminobenzidine into a 1L flask, and fully dissolve it with 600ml of pure water (with an appropriate amount of HCl added). Weigh 30mmol selenium dioxide (SeO 2 ) was dissolved in 30mL hot water, and after dissolving, it was transferred to a constant pressure dropping funnel and slowly dropped into the flask. The reaction was stirred at room temperature for 1.5h. A large amount of yellow solids were precipitated. After the reaction was completed, suction filtration was performed. The filter residue was redissolved with sodium hydroxide solution to make it neutral, and the target product was obtained by suction filtration again. After drying, it was a reddish-brown solid powder with a yield of 95%.
[0040] (2) Weigh 3mmol of the product of step (1) (4-(benzo[c][1,2,5]selenadiazol-6-yl)benzene-1,2-diamino) in a 100mL flask, ad...
Embodiment 2
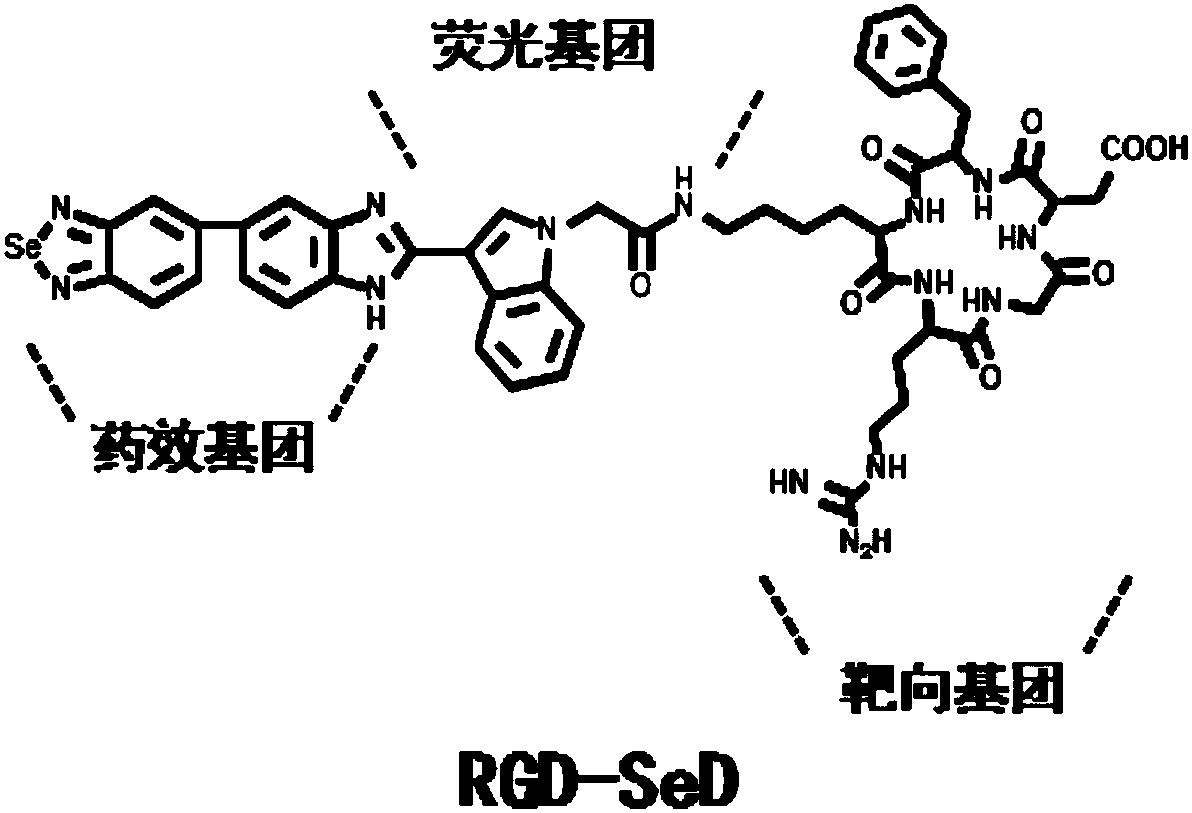
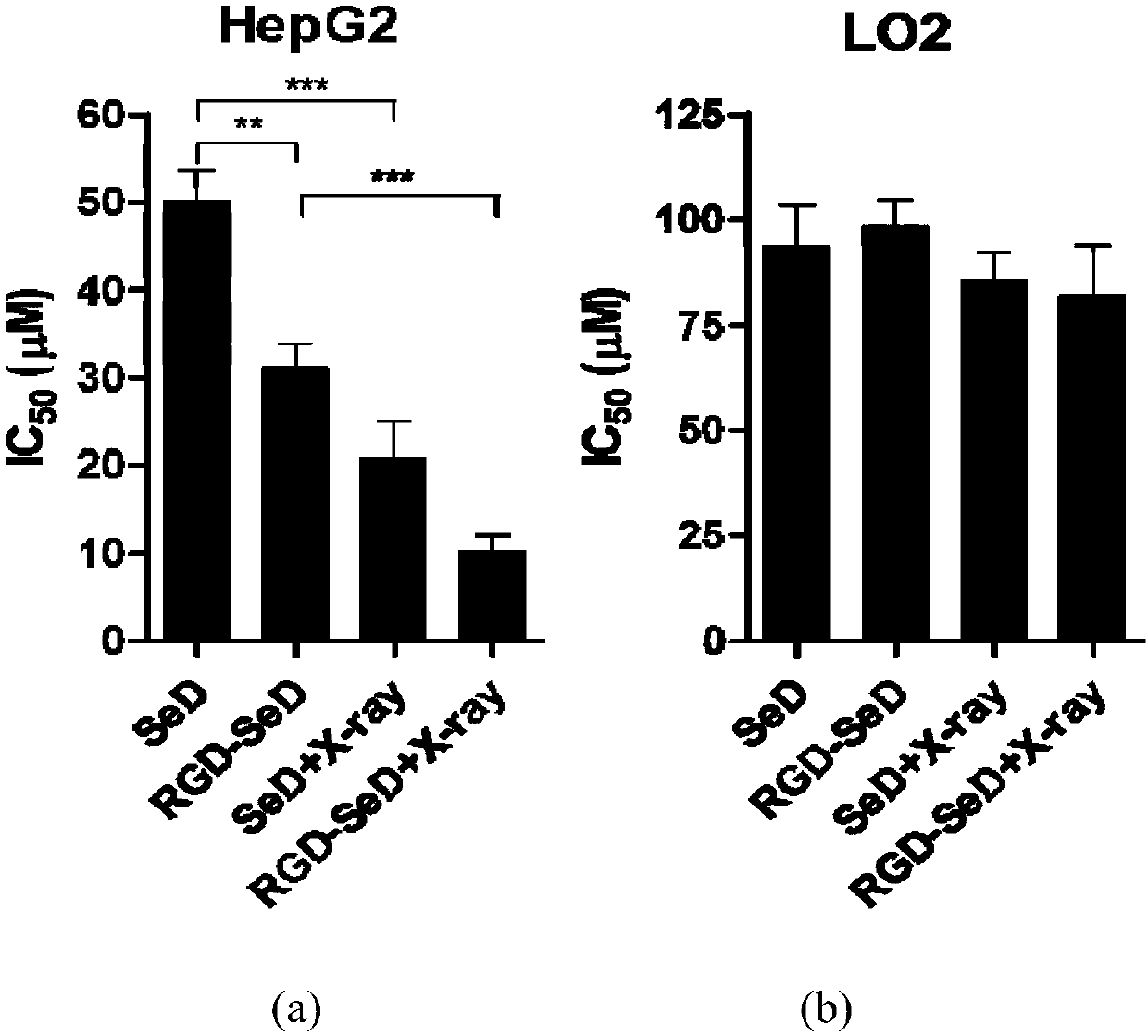
[0048] RGD-5-(2-substituted indolylbenzimidazole)benzo[1,2,5]selenadiazole RGD-SeD and SeD have antitumor activity and radiosensitization activity
[0049] In this example, the in vitro antitumor activity and radiosensitivity of SeD and RGD-SeD synthesized in Example 1 were evaluated by the MTT (thiazolium blue) method.
[0050] The human liver cancer cells HepG2 and human normal liver tissue L02 cells used in the experiment were respectively purchased from the American ATCC and the Cell Bank of the Type Culture Collection Committee of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Cultured in DMEM medium (Gibco, Life technology) containing 10% FBS (Gibco, Life technology) in 5% CO 2 , 37°C cell culture incubator.
[0051] HepG2 and L02 cells were cultured to the logarithmic growth phase, digested with 0.25% trypsin (containing 0.02% EDTA), counted, and inoculated into 96-well plates, with 2000 cells per well, and the medium volume was 100 μL. Place in the incubator for 24 hours until the...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Cell uptake and localization of RGD-5-(2-substituted indolylbenzimidazole)benzo[1,2,5]selenadiazole
[0058] This example is to detect whether RGD-SeD improves its selective killing effect on tumor cells by increasing its uptake by tumor cells.
[0059] HepG2 and L02 cells were cultured to logarithmic growth phase, digested with 0.25% trypsin (containing 0.02% EDTA), counted, spread in 10cm culture dishes, each dish spread 1.5×10 6 cells. After the cells adhered to the wall, 50 μM (final concentration) of SeD or RGD-SeD were added respectively. Discard the medium at 0, 2, 4, and 8 hours, wash with PBS three times, digest with 0.25% trypsin, and collect the cells; mix with 5ml concentrated nitric acid:perchloric acid (volume ratio 3:1), and put in the nitration furnace Nitrate at 180°C for 2h, add 6mol / L hydrochloric acid for reduction for 30min, and finally detect the content of selenium with an atomic fluorescence spectrometer. Experimental results such as Figure ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Cell density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com