Pseudomonas fluorescens and its application in the control of tobacco black shank
A technology of Pseudomonas fluorescens and tobacco black shank, applied in the field of microbiology, can solve the problems of poor control effect of tobacco black shank, and achieve the effect of active and stable, simple operation method and high activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] The screening of embodiment 1 Pseudomonas fluorescens
[0020] The screening method of Pseudomonas fluorescens of the present invention has the following steps:
[0021] 1. Isolation of soil bacteria
[0022] Take 10g of soil and add 90mL to take 10g of the collected soil sample, add it to a conical flask filled with 90mL of sterile water, place the conical flask on a shaker, shake at 180rpm for 20min, and make a soil suspension. Let the prepared soil suspension stand for 5 minutes, take the supernatant, and use the 10-fold serial dilution method to successively dilute to 10-2, 10-3, 10-4 and 10-5, and absorb 200 μL of each concentration on the NA plate On, spread evenly, repeat six times for each concentration. Then the coated NA plates were incubated in a constant temperature incubator at 28°C for 24h.
[0023] 2. Primary screening
[0024] Inoculate the bacteria cake of Geotrichum candidum (Geotrichum candidum) with a diameter of 9 mm in the center of a PDA plate...
Embodiment 2
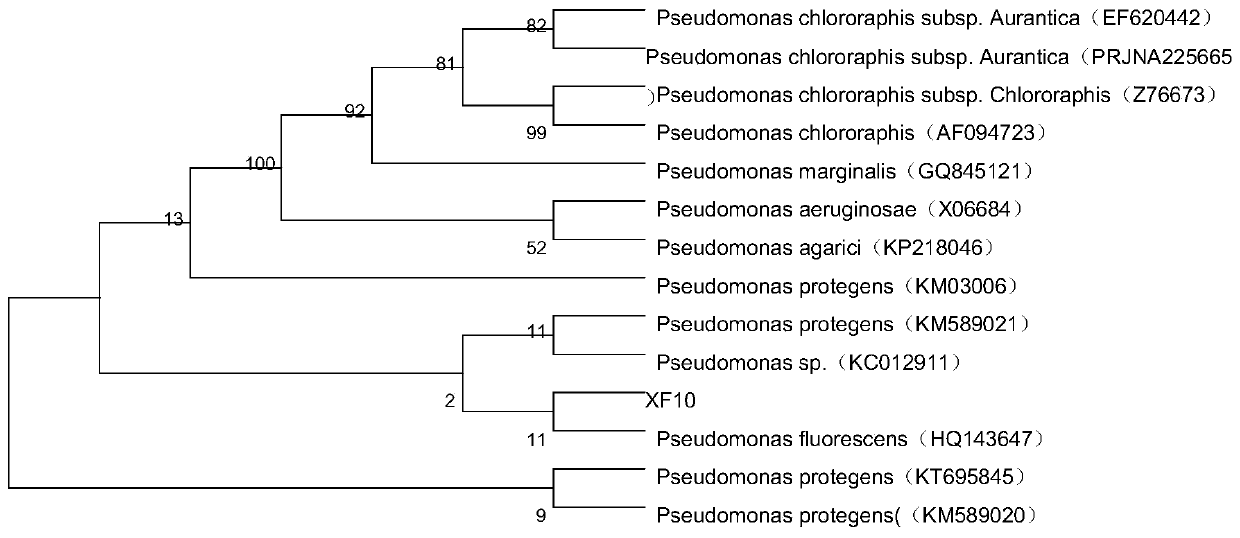
[0028] The identification of embodiment 2 Pseudomonas fluorescens
[0029] Biochemical identification was performed on the bacteria obtained above, which showed that they were Pseudomonas fluorescens.
[0030] 1. Physiological and biochemical identification
[0031] Gram staining, starch hydrolysis, oxidase, nitric acid reduction, gelatin liquefaction, etc., the determination of physiological and biochemical characteristics refers to "Plant Pathogenic Bacteria Identification Experiment Guide"
[0032] The physiological and biochemical identification of the XF10 strain is shown in Table 1. The XF10 strain is a Gram-negative bacterium that can liquefy gelatin and reduce nitrate, but cannot hydrolyze starch, and the methyl red and V-P tests are negative. The strain was preliminarily identified as Pseudomonas. The results of the salt tolerance test were positive for 1% Nacl and negative for 4% Nacl.
[0033] Table 1 Physiological and biochemical identification of strain XF10
...
Embodiment 3
[0062] The Antagonism of Example 3 Bacteria Liquid to Tobacco Black Leg Disease
[0063] 1) Cultivation of tobacco black shank: in an aseptic operating table, a 0.5 cm diameter bacterial block was taken out with a puncher, inoculated in oat medium, and cultured in the dark at 28° C. for 3-5 days.
[0064] 2) Bacteria inoculation: Insert a 5mm-diameter black shank bacterial block in the center of the oat medium plate, inoculate 10 μL of XF10 strain bacterial solution on the left and right sides 24 mm from the center, repeat 3 times, culture in dark for 72 hours, and measure the size of the inhibition zone , to calculate its inhibition rate.
[0065] Inhibition rate (%) = (CK net growth amount - treatment net growth amount) / CK net growth amount × 100
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com