Method for utilizing chrome-vanadium solution to produce vanadium product and chromium sulfate basic
A chromium sulfate solution technology, applied in the field of vanadium chemical metallurgy, can solve the problems of easy accumulation of impurity elements, high equipment requirements, harsh operating conditions, etc., and achieve the effect of good application prospects, feasible technology, and simple equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
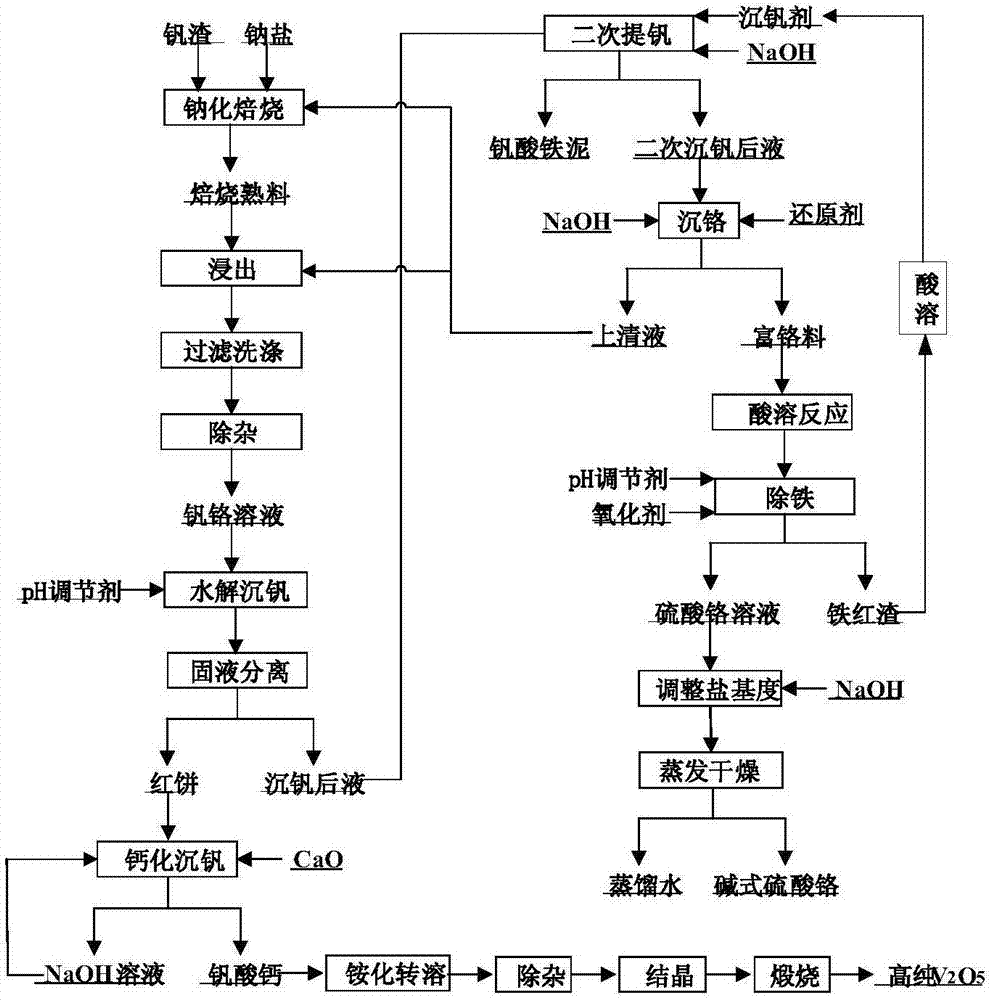
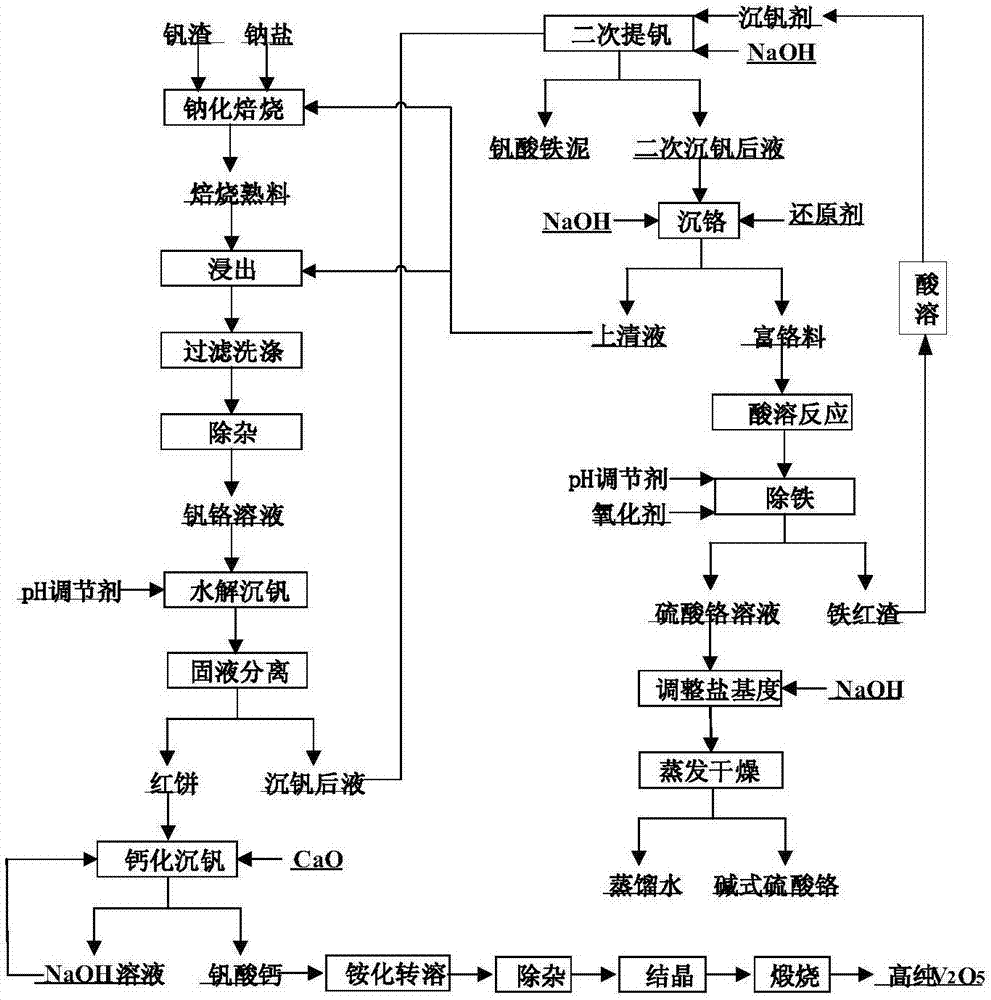
[0058] (1) Hydrolysis of vanadium precipitation: Add hydrochloric acid to the vanadium-chromium solution containing 24.5g / L of vanadium and 568.2mg / L of chromium to adjust the pH to 1.8, and then filter after hydrolysis of the vanadium precipitation to obtain solid-phase red cakes and precipitates containing vanadium and chromium. Vanadium after solution;
[0059] (2) Calcification reaction: According to the molar ratio of Ca / V of 1.5, mix the red cake obtained in step (1) and calcium oxide into water for calcification reaction, control the reaction temperature to 95°C, and the reaction time to 1h, after filtration Obtain solid-phase calcium vanadate, and obtain vanadium pentoxide through ammonification, transsolution, impurity removal, crystallization and calcination of the obtained calcium vanadate;
[0060] (3) Enrichment of chromium: add polyferric chloride to the liquid after the vanadium precipitation obtained in step (1), adjust the pH to be 5 and carry out the secondar...
Embodiment 2
[0064] (1) Hydrolysis of vanadium precipitation: Add hydrochloric acid to the vanadium-chromium solution containing 24.5g / L of vanadium and 568.2mg / L of chromium to adjust the pH to 1.9, and then filter after hydrolysis of the precipitation of vanadium to obtain solid-phase red cake and precipitation of vanadium and chromium. Vanadium after solution;
[0065] (2) Calcification reaction: According to the molar ratio of Ca / V being 1.9, mix the red cake and calcium oxide obtained in step (1) into water for calcification reaction, control the reaction temperature to 85°C, and the reaction time to 1.5h, filter Finally, solid-phase calcium vanadate is obtained, and the obtained calcium vanadate is converted into ammonium, impurity removal, crystallization, and calcined to obtain vanadium pentoxide;
[0066] (3) Enrichment of chromium: add polyferric chloride to the solution after the vanadium precipitation obtained in step (1), adjust the pH to 4.5 to carry out the secondary vanadiu...
Embodiment 3
[0070] (1) Hydrolysis of vanadium precipitation: add hydrochloric acid to the vanadium-chromium solution containing 24.5g / L of vanadium and 568.2mg / L of chromium to adjust the pH to 1.6, and then filter after hydrolysis of the precipitation of vanadium to obtain solid-phase red cake and precipitation of vanadium and chromium. Vanadium after solution;
[0071] (2) Calcification reaction: According to the molar ratio of Ca / V of 1.3, mix the red cake obtained in step (1) and calcium oxide into water for calcification reaction, control the reaction temperature to 75°C, and the reaction time to 2h, after filtration Obtain solid-phase calcium vanadate, and obtain vanadium pentoxide through ammonification, transsolution, impurity removal, crystallization and calcination of the obtained calcium vanadate;
[0072](3) Enrichment of chromium: add polyferric chloride to the liquid after the vanadium precipitation obtained in step (1), adjust the pH to be 5.2 and carry out the secondary va...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com