A self-healing elastomer material based on reversible non-covalent bond interaction and its preparation method
An elastomer material and non-covalent bond technology, applied in the field of materials, can solve problems such as poor environmental adaptability, low mechanical strength, and low stability, and achieve the effects of low cost, high safety, and simple preparation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Measured amounts of sebacic acid and pentaethylenehexamine were placed in a reactor filled with nitrogen, and reacted at 300° C. for 1 hour to obtain an oligomer polyamide prepolymer. Add calcium hydroxide to the prepolymer, react at 300°C for 1 hour, and cool to room temperature to obtain a self-healing elastomer material. The raw material ratio of sebacic acid, pentaethylenehexamine and calcium hydroxide is measured with the molar ratio of their corresponding carboxyl groups, amino groups and basic metal compounds being 1:0.1:0.1.
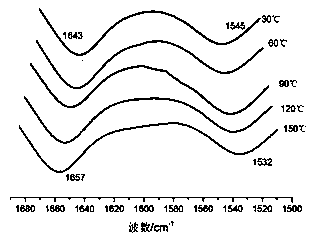
[0023] figure 1 Wavenumbers from 1500cm for elastomeric materials -1 to 1680cm -1 The variable temperature infrared spectrum, as the temperature increases from 30°C to 150°C, the stretching vibration frequency of carbonyl-C=O increases from 1643cm -1 Gradually move to 1657cm -1 ; in contrast, the in-plane bending vibration frequency of -NH- in the amide bond is from 1545cm -1 Gradually decrease to 1532cm -1 place. The increase of te...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Measured amounts of suberic acid, oleic acid and triaminobenzene were placed in a reactor filled with nitrogen, and reacted at 150° C. for 18 hours to obtain an oligomer polyamide prepolymer. Add magnesium oxide and calcium hydroxide to the prepolymer, react at 150°C for 12 hours, and cool to room temperature to obtain a self-healing elastomer material. The ratio of raw materials of suberic acid to oleic acid, triaminobenzene, magnesium oxide and calcium hydroxide is measured at a molar ratio of 1:1:1 to the corresponding carboxyl, amino, and basic metal compounds, wherein suberic acid The molar ratio of carboxyl to oleic acid is 1:0.5, and the molar ratio of magnesium oxide to calcium hydroxide is 1:1.
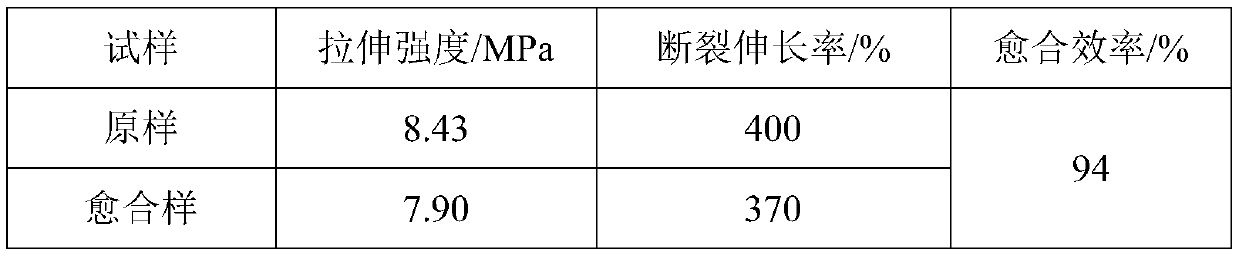
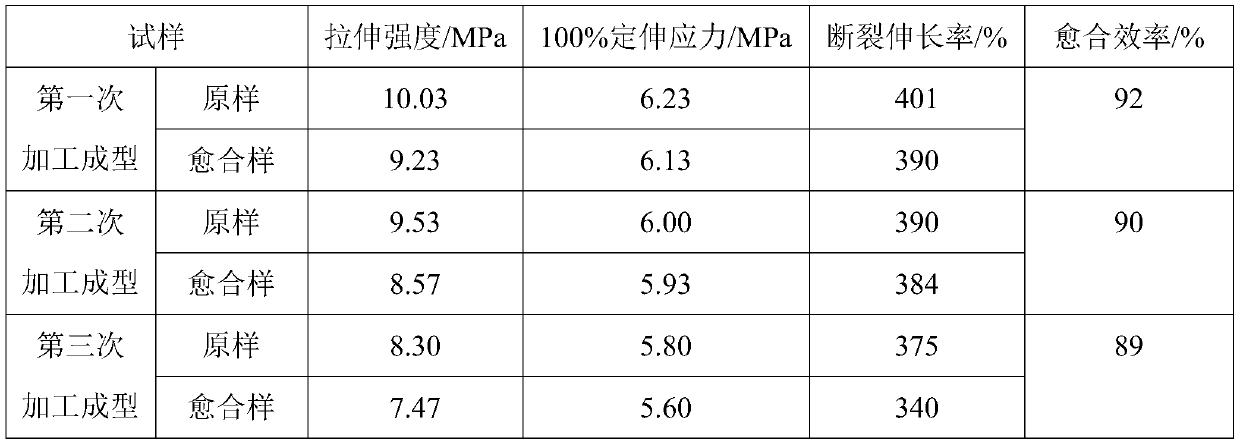
[0028] The elastic material was prepared into a standard dumbbell-shaped sample with a thickness of 1 mm, and the tensile test was performed at a tensile rate of 500 mm / min. The tensile strength of the obtained material was 7.0 MPa, and the elongation at break was 370%...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Measured amounts of pimelic acid and tetraethylenepentamine were placed in a reactor filled with nitrogen, and reacted at 250° C. for 5 hours to obtain an oligomer polyamide prepolymer. Add iron oxide to the prepolymer, react at 200°C for 4 hours, and cool to room temperature to obtain a self-healing elastomer material. The raw material ratio of pimelic acid, tetraethylenepentamine and iron oxide is measured with the molar ratio of the corresponding carboxyl groups, amino groups and basic metal compounds being 1:0.5:0.4.
[0031] Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) was performed on the prepared materials. The material is first heated from 30°C to 110°C, and kept at a constant temperature for 3 minutes to eliminate the thermal history; then the temperature is cooled to -60°C and then raised to 100°C, and the temperature change rate throughout the test is controlled at 10°C / min. The glass transition temperature of the material obtained from the DSC test curve is -5.5...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com