Low-cost method for preparing starch bioplastic
A bioplastic and low-cost technology, applied in the field of low-cost preparation of starch bioplastics, can solve the problems of complex preparation process, poor environmental protection, high energy consumption, etc., and achieve the effect of simple process, low cost and low viscosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Mix 18kg of butyl acrylate, 25kg of methyl methacrylate, 12kg of acrylic acid, 2kg of octylphenol polyoxyethylene ether and 43kg of deionized water, heat to 48°C and keep stirring, then add ammonia water to adjust the pH to 7 , to obtain the polyacrylate precursor solution, and then add 35kg of starch ultrafine particles, using an ultrasonic frequency of 40kHz and a power density of 0.7W / cm 2 Ultrasonic assisted dispersion is uniform; then add 1.7kg of dibenzoyl peroxide to form a hyperbranched macromolecule that coats starch ultrafine particles to obtain a composite starch filler; then take 25kg of composite starch filler and 60kg of poly Premix ethylene and 15kg of processing aids in a high-speed mixer, knead, extrude, and granulate with an extruder, and then cool and dry to obtain starch bioplastics;
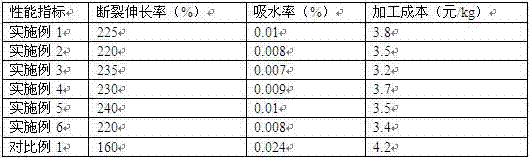
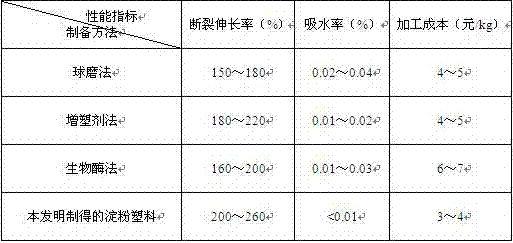
[0033] The starch bioplastic prepared in Example 1 was tested for elongation at break, water absorption and processing cost, and the obtained data are shown in Table 2...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Mix 15kg of butyl acrylate, 20kg of methyl methacrylate, 10kg of acrylic acid, 1kg of glyceryl monostearate and 54kg of deionized, heated to 45°C and keep stirring, then add ammonia water to adjust the pH to 6, Obtain the polyacrylate precursor solution, then add 30kg of starch ultrafine particles, using an ultrasonic frequency of 38kHz and a power density of 0.6W / cm 2Ultrasonic assisted dispersion is uniform; then add 1.3kg of tertiary butyl peroxide to form a hyperbranched macromolecule that coats starch ultrafine particles in it to obtain a composite starch filler; then take 20kg of composite starch filler and 70kg 10kg of polyethylene and 10kg of processing aids are pre-mixed in a high-speed mixer, mixed, extruded, and granulated by an extruder, and cooled and dried to obtain starch bioplastics;
[0036] The starch bioplastic prepared in Example 2 was tested for elongation at break, water absorption and processing cost, and the obtained data are shown in Table 2.
Embodiment 3
[0038] Mix 20kg of butyl acrylate, 30kg of methyl methacrylate, 15kg of acrylic acid, 3kg of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate and 32kg of deionized water, heat to 50°C and keep stirring, then add ammonia water to adjust the pH to 8. Obtain the polyacrylate precursor solution, then add 40kg of starch ultrafine particles, using an ultrasonic frequency of 45kHz and a power density of 0.8W / cm 2 Ultrasonic assisted dispersion is uniform; then add 2.1kg of diisopropyl peroxydicarbonate to form a hyperbranched macromolecule that coats starch ultrafine particles in it to obtain a composite starch filler; then take 30kg of composite starch filler and 50kg The polyethylene and 20kg of processing aids are pre-mixed in a high-speed mixer, mixed, extruded, and granulated by an extruder, and cooled and dried to obtain starch bioplastics;
[0039] The starch bioplastic prepared in Example 3 was tested for elongation at break, water absorption and processing cost, and the obtained data are show...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com