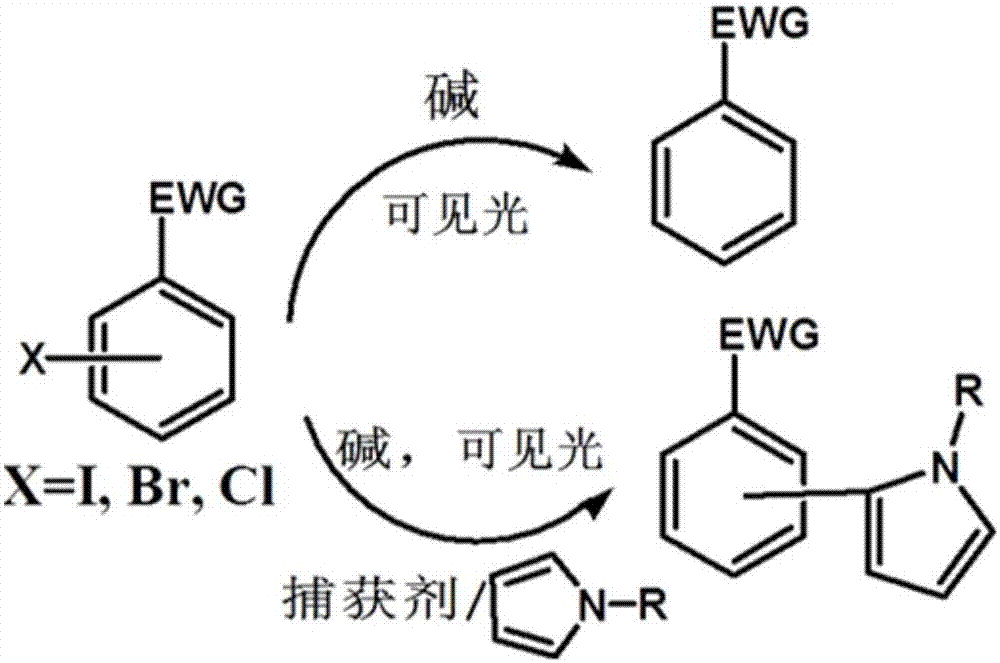
Visible light catalysis method for dehalogenation of aryl halide without need of photooxidation reduction catalyst
A halogenated aromatic hydrocarbon and catalyst technology, applied in the field of visible light catalysis organic synthesis, can solve the problems of affecting the actual yield of the reaction, increase the difficulty of operation, complex synthesis, etc., and achieve the effects of low cost, easy availability of raw materials and high reaction efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
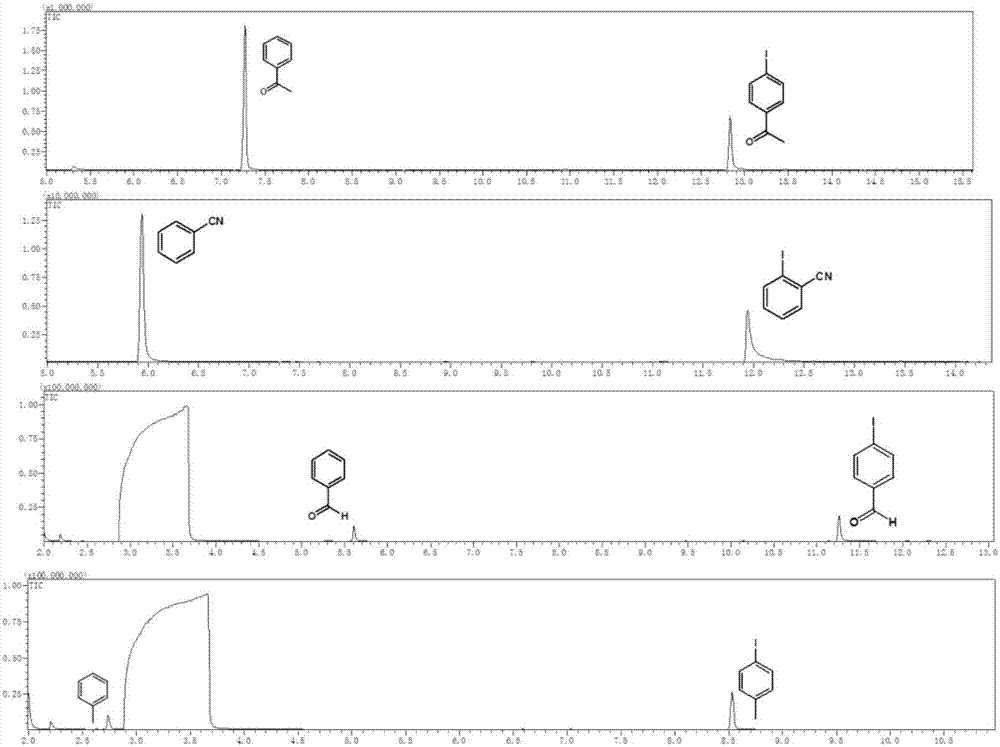
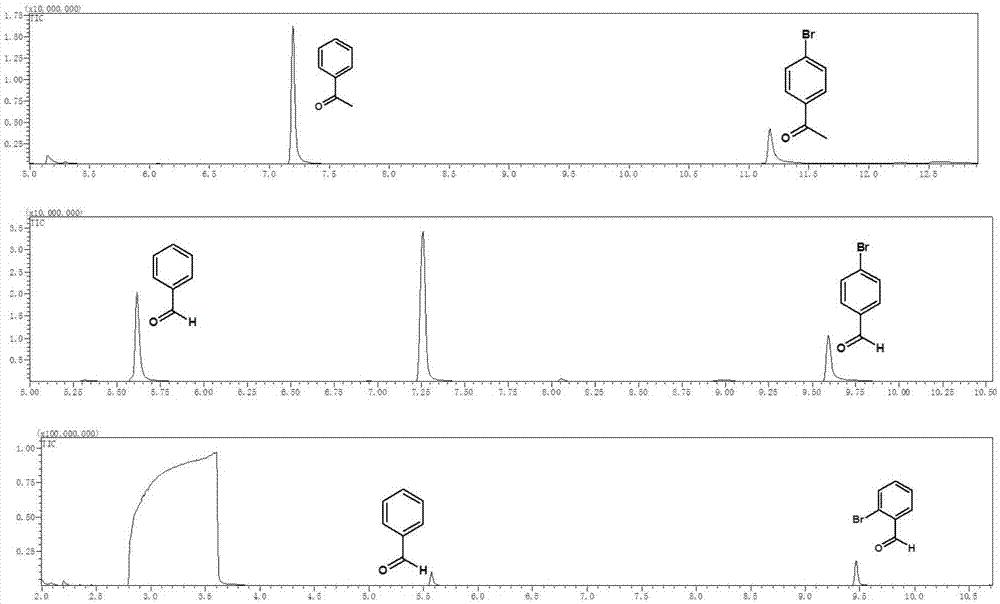
[0047]Example 1 Weigh 0.05 mM halogenated aromatic hydrocarbon into a reaction flask, add 2 mL of solvent, fill the reaction flask with nitrogen gas for deoxygenation for 20 minutes, and add 30 μL of triethylamine during deoxygenation. Afterwards, the reaction container was sealed, placed above a light-emitting diode (LED) with a wavelength of 400 nm and a power of 2 W for irradiation, and the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 24 hours. Afterwards, utilize gas chromatography-mass spectrometry to characterize the yield of dehalogenation reaction, and the productive rate of acetophenone is 83.4%, and the characterization result of gas chromatography-mass spectrometry is as follows: figure 2 Shown; Wherein halogenated arene is iodoacetophenone, solvent is toluene.
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2 Weigh 0.02 mM halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons into a reaction flask, add 1 mL of solvent, fill the reaction flask with nitrogen gas for deoxygenation for 10 minutes, and add 15 μL of triethylamine during deoxygenation. Afterwards, the reaction container was sealed, placed above a light-emitting diode (LED) with a wavelength of 400 nm and a power of 0.5 W for irradiation, and the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 12 hours. Afterwards, the yield of the dehalogenation reaction was characterized by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, and the yield of o-phenylacetonitrile was 80.7%. Tetrahydrofuran.
Embodiment 3
[0049] Example 3 Weigh 0.1 mM halogenated aromatic hydrocarbon into a reaction flask, add 2 mL of solvent, fill the reaction flask with nitrogen gas for deoxygenation for 25 minutes, and add 30 μL of potassium tert-butoxide during deoxygenation. Afterwards, the reaction vessel was sealed, placed above a light-emitting diode (LED) with a wavelength of 450 nm and a power of 30 W for irradiation, and the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 18 hours. Afterwards, utilize gas chromatography-mass spectrometry to characterize the yield of dehalogenation reaction, and the productive rate of benzaldehyde is 51.5%, and the gas chromatography-mass spectrometry characterization result is as follows figure 2 Shown; Among them, the halogenated aromatic hydrocarbon is p-iodobenzaldehyde, and the solvent is N,N-dimethylformamide.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com