Bacillus subtilis and application thereof to degradation of aspergillus ochraceus A (OTA) in post-fermented tea pile fermentation
A Bacillus subtilis, fermented tea technology, applied in bacteria, pre-extraction tea treatment, microorganism-based methods, etc., can solve the destruction of nutrients and functional components, can not effectively control the total amount of OTA, ochratoxin A biodegradation research Issues that have not been reported
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] The screening of embodiment 1 bacterial strain DTMo1
[0034] (1) The bacterial strain DTMo1, which was isolated and purified from the piled tea sample during the post-fermentation tea pile process, was activated and made into a bacterial suspension with a concentration of about 10 6 CFU / ml.
[0035] (2) After the prepared LB liquid medium is sterilized at high temperature, it is divided into 200ml Erlenmeyer flasks, each bottle has a volume of 50ml, and then 20ml of 10μg / ml OTA solution and 100μL of bacterial suspension are added to the Erlenmeyer flask liquid, sealed and cultured in a shaker at 28-35°C, with a shaker speed of 200r / min. Set up a control group, the blank control system does not add OTA, adds an equal volume of distilled water, and other conditions are the same.
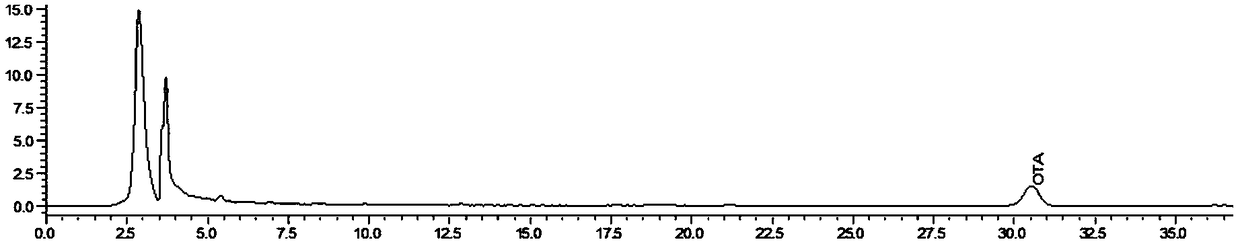
[0036] (3) After 3 days of bacterial culture, extract OTA in 5 mL of medium every 2 days, measure the content of OTA by HPLC, and detect the ability of the strain to degrade OTA by HPLC.
[...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment 2, identification of bacterial strain DTMo1
[0045] The 16S rRNA sequence of the strain DTMo1 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and the 16S rRNA gene of the strain was amplified by PCR using primers 27F (5'-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3') and 1492R (5'-TAC GGCTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3'). Sequence analysis and homology comparison of 16S rRNA sequence in GenBank, GenBank accession number is MG256170, and the similarity between strain DTMo1 and Bacillus subtilis strain NBRC 13719 is 99%. Strain DTMo1, after the morphological identification of the strain, physiological and biochemical experiments, 16S rRNA sequence analysis and homology comparison, the similarity between the strain DTMo1 and Bacillus subtilis strain NBRC 13719 is 99%, so the strain Bacillus subtilis DTMo1 is determined for Bacillus subtilis.
[0046] The microbiological characteristics of the strain DTMo1 are as follows: it is a species of Bacillus. Single cell 0.7~0.8×2~3 microns, evenly colored. Uncapsulated, wi...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Embodiment 3, the cultivation of Bacillus subtilis
[0050] The Bacillus subtilis strain DTMo1 was inoculated in LB liquid medium, the shaker speed was 200r / min, the temperature was 28-35°C, and the fermentation broth of Bacillus subtilis DTMo1 was obtained after 72 hours of cultivation. The fermentation broth was centrifuged to remove the supernatant, and the precipitate was repeatedly washed with distilled water to obtain fermentation strains. Bacillus subtilis DTMo1 was diluted with distilled water to prepare bacterial suspensions containing different numbers of bacteria per unit volume, which were used for inoculation of subsequent tea pile fermentation.
[0051] The formula of the LB medium is: tryptone 10g, yeast powder 5g, sodium chloride 10g (solid medium plus 1.5% agar), add distilled water to 1L, and sterilize at 121° C. for 20 minutes.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com