Multilayer composite thermal conductive film and preparation method thereof
A thermally conductive thin film, multi-layer composite technology, applied in coatings and other directions, can solve the problems that the thermal conductivity cannot meet higher demands, cannot be applied in the field of thermal conductivity and insulation, and the operation process is cumbersome, etc., to achieve excellent mechanical properties, wide sources, and operation simple effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
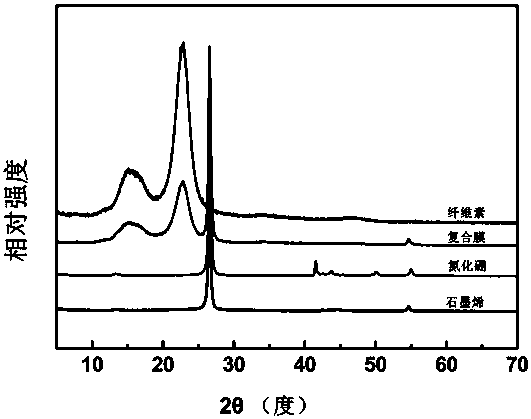
[0038] (1). Obtain 20 mg of nanocellulose / boron nitride dispersion (concentration 2-2.5 mg / mL) by magnetic stirring and ultrasonic dispersion for 30 minutes, in which the mass of filler (boron nitride) accounts for the total mass 6wt% of
[0039] (2). Pour 20 mg of nanocellulose / boron nitride dispersion onto the filter membrane until drained.
[0040] (3). Pour 20 mg nanocellulose dispersion (concentration: 2 mg / mL) on the pumped film until it is drained.
[0041] (4). On the basis of operation (3), repeat operation step (2) (pour on (3)) until it is drained.
[0042] (5). Compress the film with two parallel steel plates and place it in a vacuum oven at 40 °C overnight to obtain a symmetrical three-layer biomimetic composite heat-conducting film.
Embodiment 2
[0044] (1). Obtain 25 mg of nanocellulose / boron nitride dispersion (concentration 2-2.5 mg / mL) by magnetic stirring and ultrasonic dispersion for 50 min, in which the mass of filler (boron nitride) accounts for 1% of the total mass 10wt%
[0045] (2). Pour 25 mg of nanocellulose / boron nitride dispersion onto the filter membrane until drained.
[0046] (3). Pour 25 mg nanocellulose dispersion (concentration: 2 mg / mL) on the film that has been pumped until it is dry.
[0047] (4). On the basis of operation (3), repeat operation step (2) (pour on (3)) until it is drained.
[0048] (5). Compress the film with two parallel steel plates and place it in a vacuum oven at 60 °C overnight to obtain a symmetrical three-layer biomimetic composite heat-conducting film.
[0049]When the amount of filler accounts for 10wt% of the mass of each film (8wt% of the total film weight), the thermal conductivity of the three-layer biomimetic composite heat-conducting film is 5.61W·m −1 • K −1 Co...
Embodiment 3
[0051] (1). Obtain 20 mg of nanocellulose / graphene dispersion (concentration 1.5-2 mg / mL) by magnetic stirring and ultrasonic dispersion for 30 minutes, in which the mass of filler (graphene) accounts for 6wt of the total mass %
[0052] (2). The dispersion liquid of 20 mg nanocellulose / graphene is poured on the filter membrane until it is sucked dry.
[0053] (3). Pour 20 mg nanocellulose dispersion (concentration: 2 mg / mL) on the pumped film until it is drained.
[0054] (4). On the basis of operation (3), repeat operation step (2) (pour on (3)) until it is drained.
[0055] (5). Compress the film with two parallel steel plates and place it in a vacuum oven at 40 °C overnight to obtain a symmetrical three-layer biomimetic composite heat-conducting film.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com