Super-paramagnetic nanoparticle for capturing exosomes and preparation method thereof as well as specific exosome luminescence immune quantitative detection kit
A nanoparticle, luminescent immune technology, applied in biological testing, measuring devices, material testing products, etc., can solve the problems of inconvenience, time-consuming, and unfavorable clinical routine development, and achieve simple operation, high sensitivity, and short detection time. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0028] The present invention also provides a method for preparing the superparamagnetic nanoparticles for capturing exosomes, which includes the following steps: 1) oxidizing the coupling unit, iron oxide nanoparticles and chloroform under ultrasonic conditions to obtain The carboxyl-modified iron oxide nanoparticles are a superparamagnetic nanoparticle matrix; 2) condensation coupling the superparamagnetic nanoparticle matrix with an exosome common marker antibody to obtain superparamagnetic nanoparticles capturing exosomes.
[0029] In the present invention, carboxyl phospholipid polyethylene glycol and iron oxide nanoparticles are oxidized to obtain carboxyl-modified iron oxide nanoparticles, which is the superparamagnetic nanoparticle matrix. In the present invention, the particle size of the iron oxide nanoparticles is preferably 2-40 nm; the preparation method of the iron oxide nanoparticles preferably includes: mixing and stirring iron, oleic acid and octadecene at 300-3...
Embodiment 1
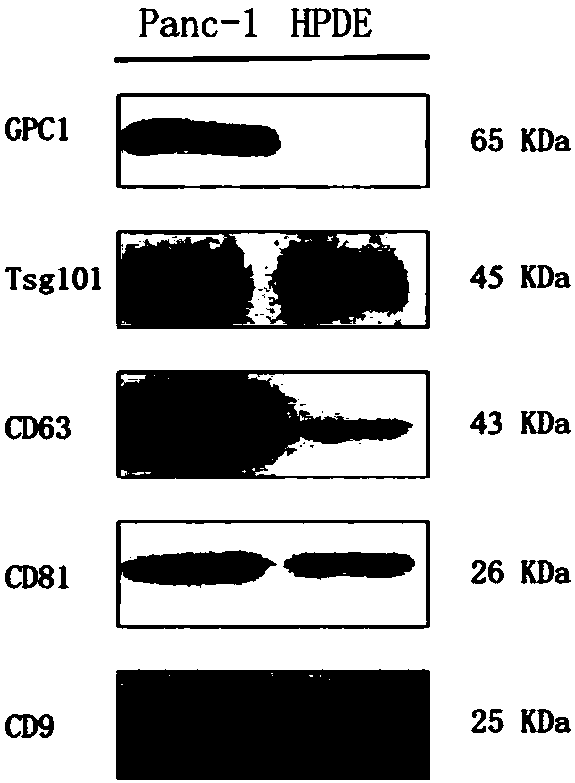
[0070] Consensus and specific marker confirmation of exosomes
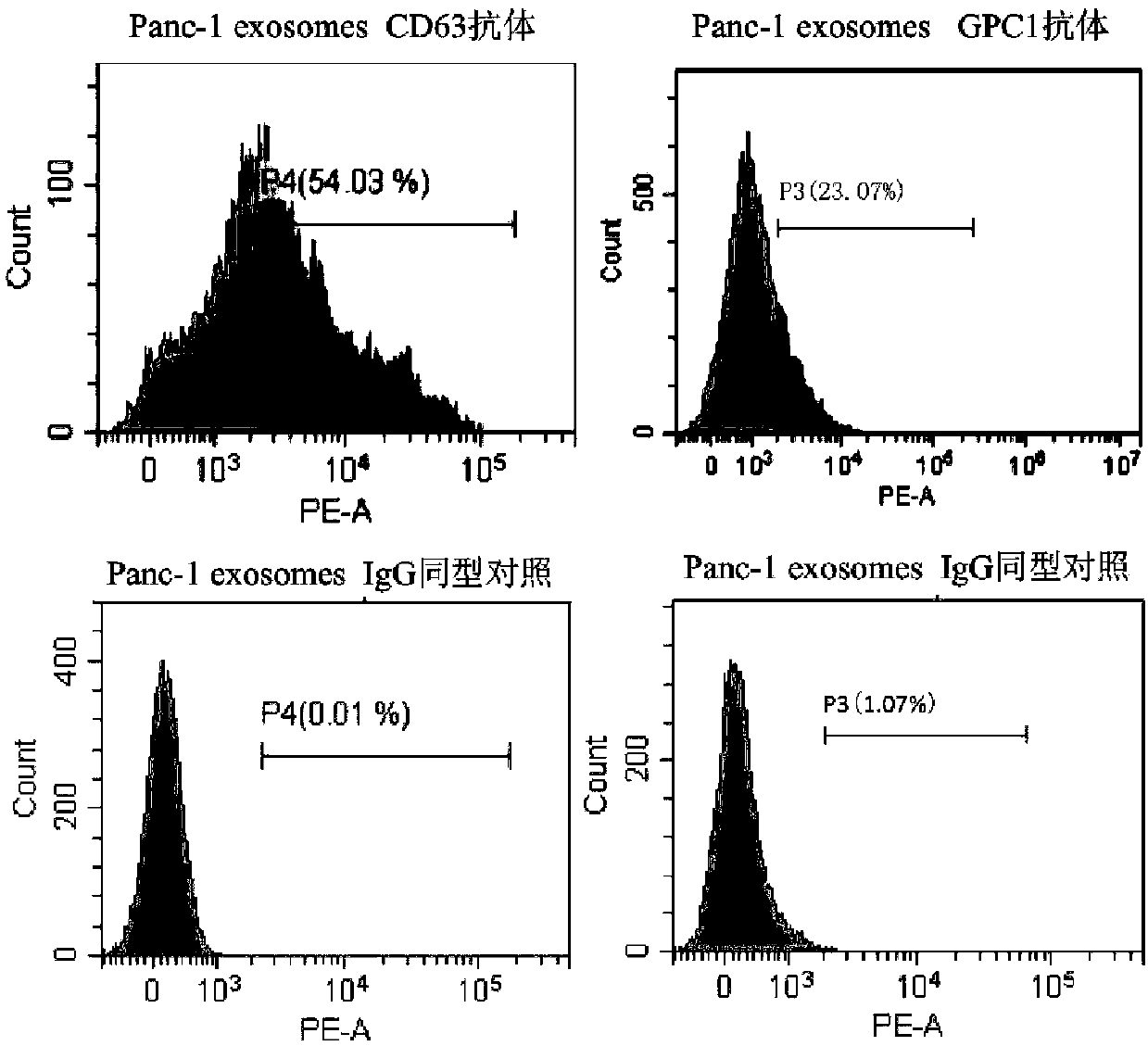
[0071] Pancreatic cancer cell line Panc-1 and pancreatic normal cell line HPDE were cultured with RPMI 1640 containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), and when the growth density reached 80%, the RPMI 1640 medium without FBS was replaced to continue culturing for 36 hours; The supernatant was used to extract exosomes. Dispense the supernatant into 50mL centrifuge tubes, centrifuge at 1000g for 10min to remove cell debris; continue to centrifuge the supernatant at 10000g for 20min to remove microvesicles and cell debris; take the supernatant and centrifuge at 110000g for 70min, remove the supernatant and resuspend the pellet with PBS buffer After the substance was centrifuged again at 110,000 g for 70 min, the precipitate (exosome) was obtained. The pellet was resuspended in 100 μL PBS buffer for subsequent experiments: the morphology of the extracted exosomes was identified by transmission electron microscopy; the ...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Screening of specific binding antibodies for exosome markers
[0074] Self-made antibodies that can bind to specific exosome surface protein markers identified by flow cytometry include GPC1, GPC3, PSMA, TMEM256 and EpCAM. Pick exosomes suspended in PBS, join Aldehyde / sulfate beads, mix at room temperature for 15 minutes. join in PBS, overnight at 4°C. join in 1M glycine, mix at room temperature for 30min. Centrifuge at 12000rpm for 1.5min. remove the supernatant, use Resuspend the pellet in 10% BSA. Mix well at room temperature and block for 1 hour. Centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 1.5 min. After removing the supernatant, add GPC3, PSMA, TMEM256 or EpCAM, etc., the corresponding antibody was diluted with 2% BSA Mix well at room temperature for 1 hour. join in 2% BSA, centrifuged at 12,000rpm for 1.5min, removed the supernatant, added 2% BSA, centrifuge at 12,000rpm for 1.5min, then discard the supernatant. join in fluorescent secondary antibo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com