A laser direct machining method for microwave substrate cavity
A processing molding and laser direct technology, applied in the direction of laser welding equipment, metal processing equipment, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of corrosion taper, low corrosion rate and cavity size consistency, etc., to achieve good compatibility, high control precision, good verticality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Take the machining of a cavity with a plane size of 2 mm×2 mm and a depth of 100 μm on a substrate 1 of silicon material with a thickness of 0.4 mm and a thickness of 6 inches as an example.
[0042] The specific processing steps are as follows:
[0043] (1) Pretreatment of 6-inch substrate and protection of circuit graphics
[0044] (1.1) Clean the substrate 1;
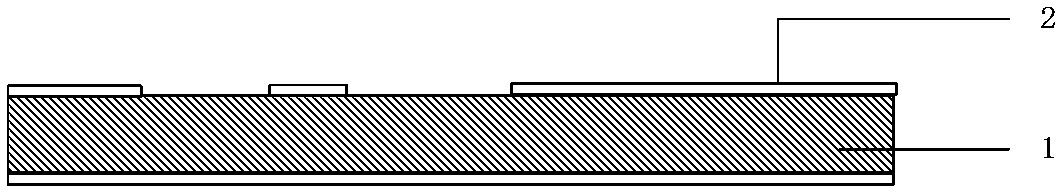
[0045] (1.2) see figure 1 and figure 2 1. Coat the surface of the cleaned substrate 1 with photoresist 2 to protect the surface circuit pattern. The thickness of the photoresist 2 is 5-10 μm, and open a window at the processing position of the cavity through photolithography and development.
[0046] (2) The laser beam etches the substrate to form a cavity
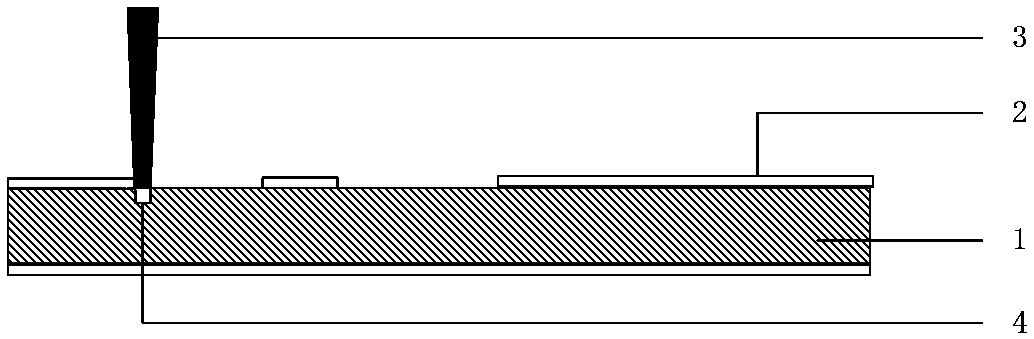
[0047] (2.1) see Figure 3-5 , at the opening position on the substrate 1, laser etching forms more than one cavity 7 on the substrate 1, and the angle between the cavity wall of the cavity 7 and the vertical direction is less than 5 degrees;
[004...
Embodiment 2
[0053] A stepped cavity with two steps is processed on a 6-inch silicon wafer with a thickness of 0.4 mm; in the stepped cavity, the large-sized cavity is located at the upper part, and the small-sized cavity is located at the lower part. The planar size of the large-size cavity is 2mm×2mm and the depth is 100μm, and the planar size of the small-size cavity is 1.5mm×1.5mm and the depth is 200μm.
[0054] The specific processing steps are as follows:
[0055] Step 1: Pre-treatment of silicon substrate and protection of circuit pattern; coat the surface of the cleaned silicon substrate with photoresist for surface circuit pattern protection, the thickness of photoresist is 5-10 μm, and pass photolithography and development in the cavity The body processing position opens the window.
[0056] Step 2: The laser beam etches the silicon substrate to form an upper cavity; select a laser with a wavelength of 355nm and a spot size of 0.015mm, and laser marking is carried out sequentia...
Embodiment 3
[0060] On a 1.2mm thick LTCC substrate, a cavity with a plane size of 2mm×5mm and a depth of 200μm is taken as an example.
[0061] The specific operation steps of LTCC substrate cavity laser processing are as follows:
[0062] Step 1: LTCC substrate pre-processing and circuit pattern protection
[0063] see figure 1 and figure 2 , Coat the surface of the cleaned LTCC substrate with photoresist to protect the surface circuit pattern, the thickness of the photoresist is 5-10 μm, and open a window at the cavity processing position through photolithography and development.
[0064] Step 2: Laser beam etching LTCC substrate to form a cavity
[0065] see Figure 3-5 , choose a laser with a wavelength of 355nm and a spot size of 0.015mm, and the laser marking is carried out in the order of crossing the number of processing passes in the horizontal and vertical directions. Laser processing parameters: laser energy 4.5W, laser spot overlap rate 75%, laser frequency 32KHz, markin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com