Treatment method of Cu-EDTA heavy metal complex wastewater
A treatment method and technology for heavy metals, which are used in metallurgical wastewater treatment, processing wastewater treatment, textile industry wastewater treatment, etc., to achieve the effects of no secondary pollution, low energy consumption, and enrichment and recovery.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1 Preparation of barium titanate / graphene composite piezoelectric material
[0026] (1) Preparation of precursor H 2 TiO 3 .
[0027] Prepare 10 M NaOH solution, add 1.88g titanium dioxide (anatase) into 80mL prepared NaOH solution, stir evenly, transfer to 100mL polytetrafluoroethylene liner, and put it into a stainless steel reaction kettle. React at 180°C for 24h, take it out, and cool to room temperature to obtain a sample. Washed with ultrapure water, then soaked in 0.2 M HCl for 4 h to obtain H 2 TiO 3 sample. Then, take the sample out, add 50mL of ultrapure water to stir repeatedly, centrifuge (10000 rpm for 5 min) and wash four times, and finally dry it in a vacuum oven at 60°C for 12h;
[0028] (2) The precursor prepared in step (1) was subjected to a second hydrothermal reaction to prepare BaTiO 3 Piezoelectric material.
[0029] Precursor H 2 TiO 3 with Ba(OH) 2 .8H 2 O undergoes a hydrothermal reaction at a molar ratio of Ti:Ba=1:1. Reac...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2 Heavy Metal Complex Degradation-Adsorption Experiment
[0032] Preparation of simulated heavy metal complex Cu-EDTA solution: Weigh 159.6mg of anhydrous copper sulfate, dissolve it in 1L of ultrapure water, and wait until it is completely dissolved; weigh 372mg of disodium edetate, dissolve it in 1L of ultrapure water in, until completely dissolved. Mix anhydrous copper sulfate and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium solution at a ratio of 1:1 and let it stand for more than 48 hours. Then the pH of the solution was adjusted to pH=5; the concentration of Cu-EDTA was 0.05 mmol / L.
[0033] Degradation experiment process:
[0034] (1) The barium titanate / graphene composite piezoelectric material (catalyst) prepared in Example 1 was added to 50 mL, 0.05 mmol / L Cu-EDTA solution, and the material dosage was 50 mg.
[0035] (2) Put the mixed solution in step (1) into a tank-type ultrasonic cleaning machine (power 100W, frequency 40kHz), take samples every 30mi...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Example 3 Heavy metal ion removal experiment
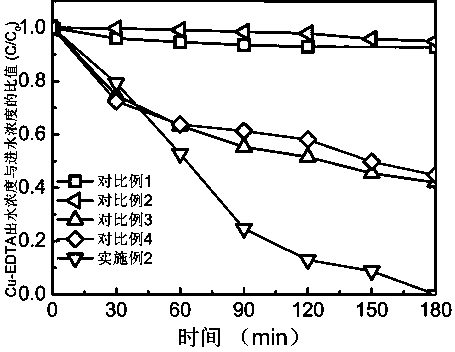
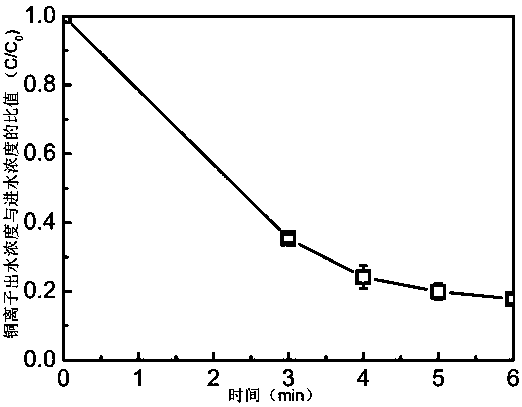
[0049] The experimental procedure of the degradation experiment is the same as that of the implementation case 2, and only the degradation experiment is extended to 3h, 4h, 5h and 6h. The adsorption experiment is consistent with the implementation case 2. After the experiment is completed, the Cu in the solution is detected. 2+ To determine the recovery rate of copper, the recovery rate is calculated as: the content of Cu in the effluent / the content of Cu in the influent. The relationship between different degradation experiment time and the recovery rate of Cu is as attached image 3 shown.
[0050] Depend on image 3 Visible: Prolonged reaction time, Cu 2+ The recovery rate was not significantly improved.
[0051] Depend on figure 2 image 3 It can be seen that the technology of the present application can realize the effective removal of Cu-EDTA heavy metal complexes and the recovery of heavy metal ions at the sam...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com