Porous ceramic as well as preparation method thereof, air-floating bearing and application
A technology of porous ceramics and green bodies, applied in the field of ceramic materials, can solve the problems of reducing the permeability of porous materials, the hardness of porous stainless steel is small, and the air bearing is easy to be worn, so as to avoid the reduction of porosity, good wear resistance, The effect of reducing the amount of grinding debris
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
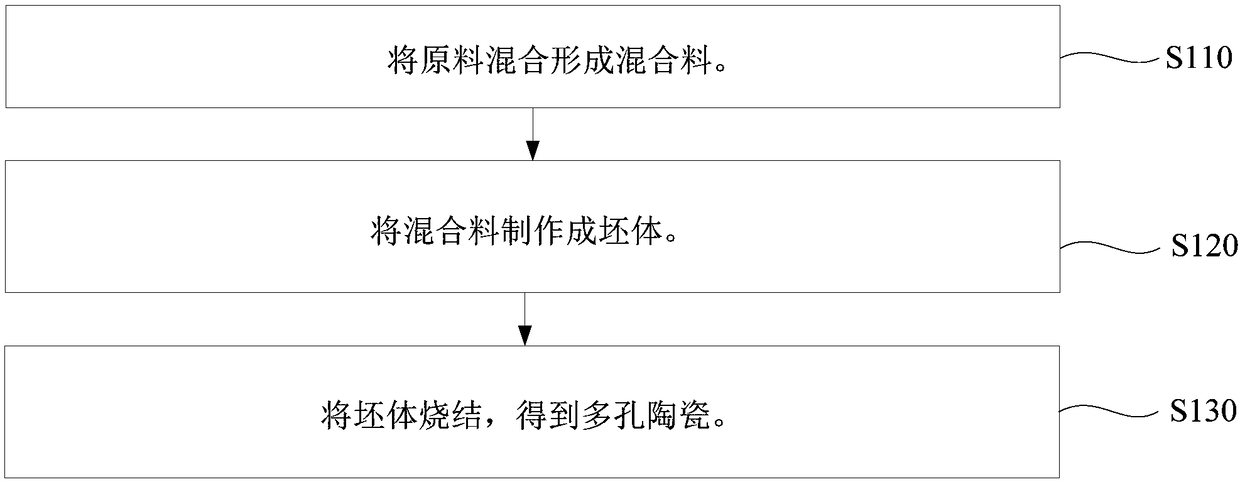
[0023] Such as figure 1 As shown, a method for preparing a porous ceramic according to an embodiment, the porous ceramic prepared by the method is a silicon carbide porous ceramic. The preparation method of the porous ceramic comprises the following steps:
[0024] Step 110: Mix the raw materials to form a compound.
[0025] Wherein, in terms of mass percentage, the raw materials include: 55% to 70% of silicon carbide, 5% to 15% of seaweed mud, 10% to 20% of additives and 10% to 15% of lubricant.
[0026] The main component of diatom mud is silicon dioxide. There are many pores in the structure of diatom mud, which is conducive to increasing the porosity of porous ceramics and improving the permeability of ceramics.
[0027] The additive is at least one selected from bauxite, industrial alumina and activated alumina. The aluminum oxide in the above additives can form mullite with the silicon dioxide component in the diatom ooze, so as to improve the strength, hardness and ...
Embodiment 1
[0057] The preparation process of the porous ceramic of the present embodiment is as follows:
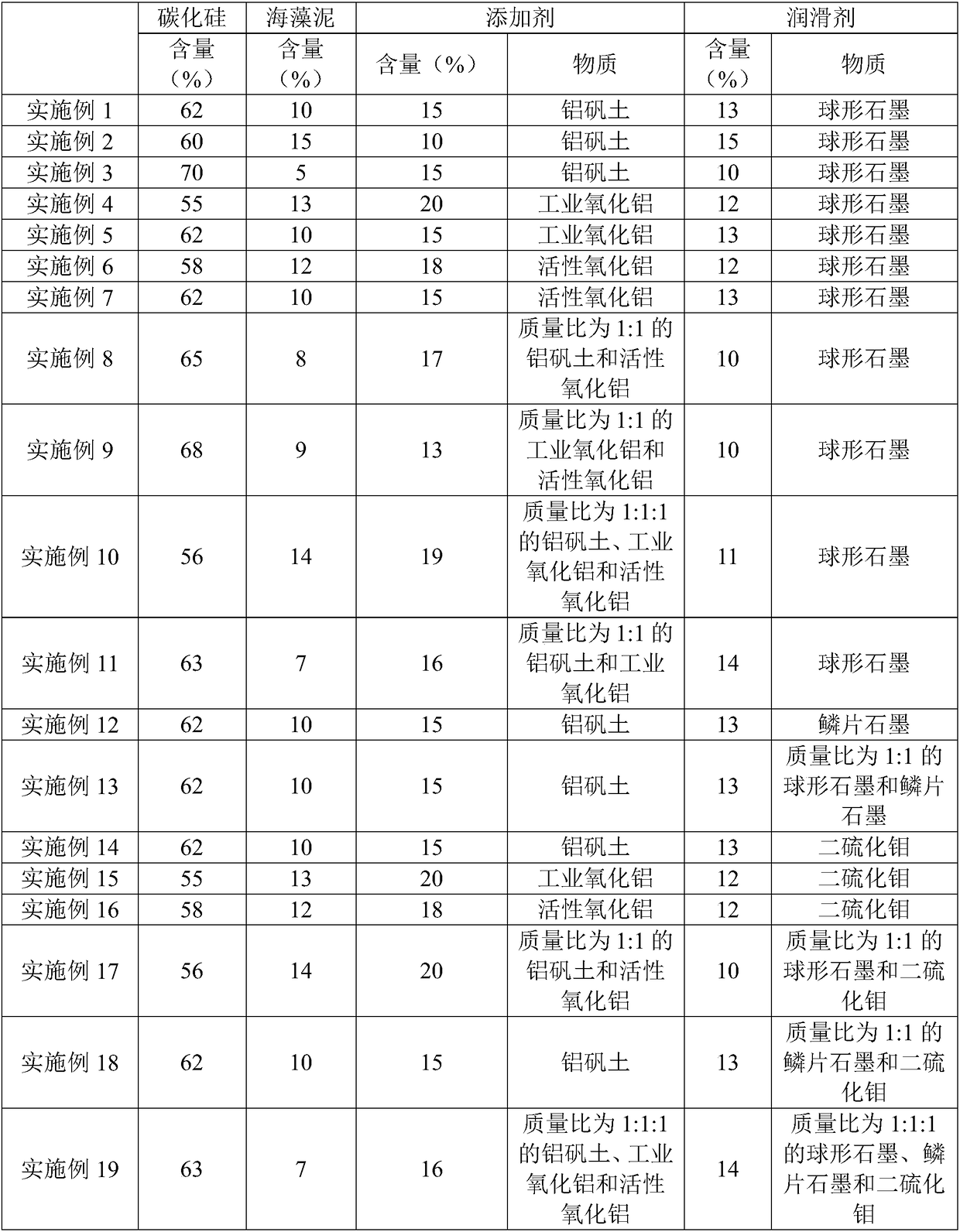
[0058] (1) According to Table 1, each component was weighed according to the mass percentage (referred to as content in the table) to obtain raw materials. Among them, the median particle size of silicon carbide is 10 microns, the median particle size of seaweed mud is 15 microns, the median particle size of additives is 15 microns, and the median particle size of lubricant is 20 microns. Among them, in bauxite, the mass percentage of aluminum oxide is 89%, the mass percentage of ferric oxide is 1.2%, the mass percentage of titanium oxide is 1.8%, calcium oxide, magnesium oxide The total mass percentage of sodium oxide and potassium oxide is 1%.
[0059] (2) Mix the dispersant and distilled water for 2 hours to form a premix; mix the raw materials with the premix to form a slurry, and when the ball mill is mixed, the mass ratio of the raw material to the grinding medium is 1:2, and...
Embodiment 2
[0066] The preparation process of the porous ceramic of the present embodiment is as follows:
[0067] (1) According to Table 1, each component was weighed according to the mass percentage (referred to as content in the table) to obtain raw materials. Among them, the median particle size of silicon carbide is 5 microns, the median particle size of seaweed mud is 20 microns, the median particle size of additives is 20 microns, and the median particle size of lubricant is 15 microns. In bauxite, the mass percentage of aluminum oxide is 88%, the mass percentage of ferric oxide is 1.5%, the mass percentage of titanium oxide is 2%, calcium oxide, magnesium oxide, oxide The total mass percentage of sodium and potassium oxide is 1.5%.
[0068] (2) Mix the dispersant and distilled water for 2 hours to form a premix; mix the raw materials with the premix to form a slurry, and when the ball mill is mixed, the mass ratio of the raw material to the grinding medium is 1:1, and the mixing ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Median particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Median particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Median particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com