Low-melting-point porous foam stone and preparation method thereof
A technology with porous foam and low melting point, which can be used in chemical instruments and methods, ceramic products, and other household appliances, and can solve problems such as low strength, high energy consumption, and high temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
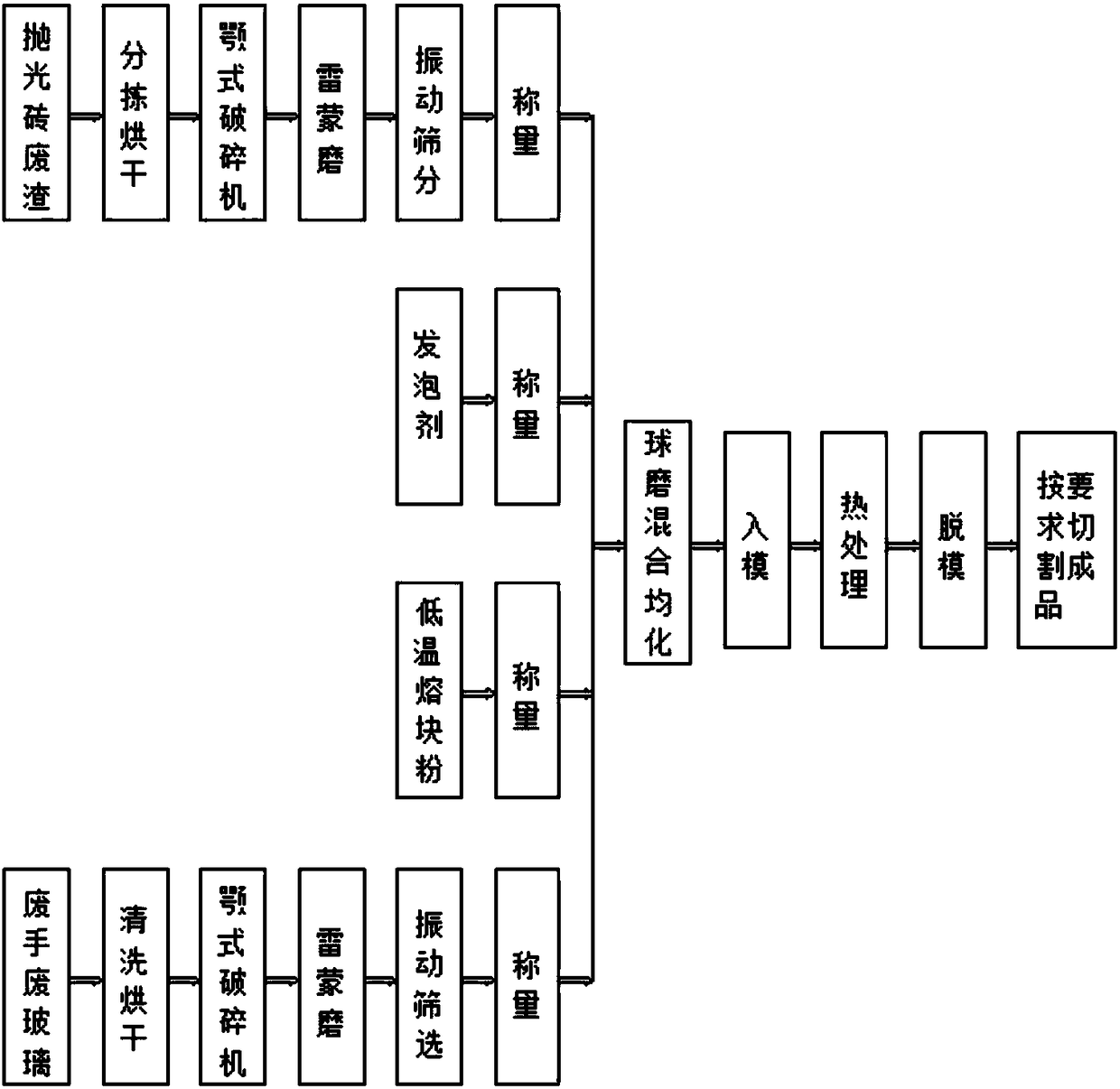
[0029] The invention relates to a low melting point porous foam stone and a preparation method thereof. The two major solid wastes in the water glass ceramics industry that will destroy the ecological environment, pollute the groundwater quality and occupy a large amount of land resources - waste glass and polished brick waste are cleaned, dried, crushed, ground, and screened to obtain two corresponding types. powder, then the above two powders are proportioned according to different mass fractions, and then a small amount of low-temperature frit powder and industrial starch (or materials such as carbon powder, ammonium bicarbonate, PMMA microspheres) are added. The low-temperature frit powder plays the role of fluxing and reducing the sintering temperature during the sintering process; the polymer flocculant and industrial starch contained in the waste slag of polished bricks are easy to foam under high-temperature calcination and can play the role of foaming agent. Add the a...
Embodiment 1
[0034] (1) Material preparation: dehydrate and air-dry the discarded polishing waste slag from the ceramic factory, crush it with a jaw crusher, send it to the Raymond mill for grinding to obtain 20-50um polished brick waste powder, and then send it to a special ash storage tank for standby; After the waste glass is cleaned and dried, use the same process to obtain 50-100um waste glass powder, which is also sent to a special ash storage tank for standby.
[0035] (2) Ingredients: the weight percentages of various raw materials are as follows: 20% of polished brick waste slag powder, 55% of waste glass powder; 20% of low-temperature frit powder, and 5% of industrial starch.
[0036] (3) Mixing: Send the above prepared materials to the ball mill and mix for 30 minutes to obtain the batch materials.
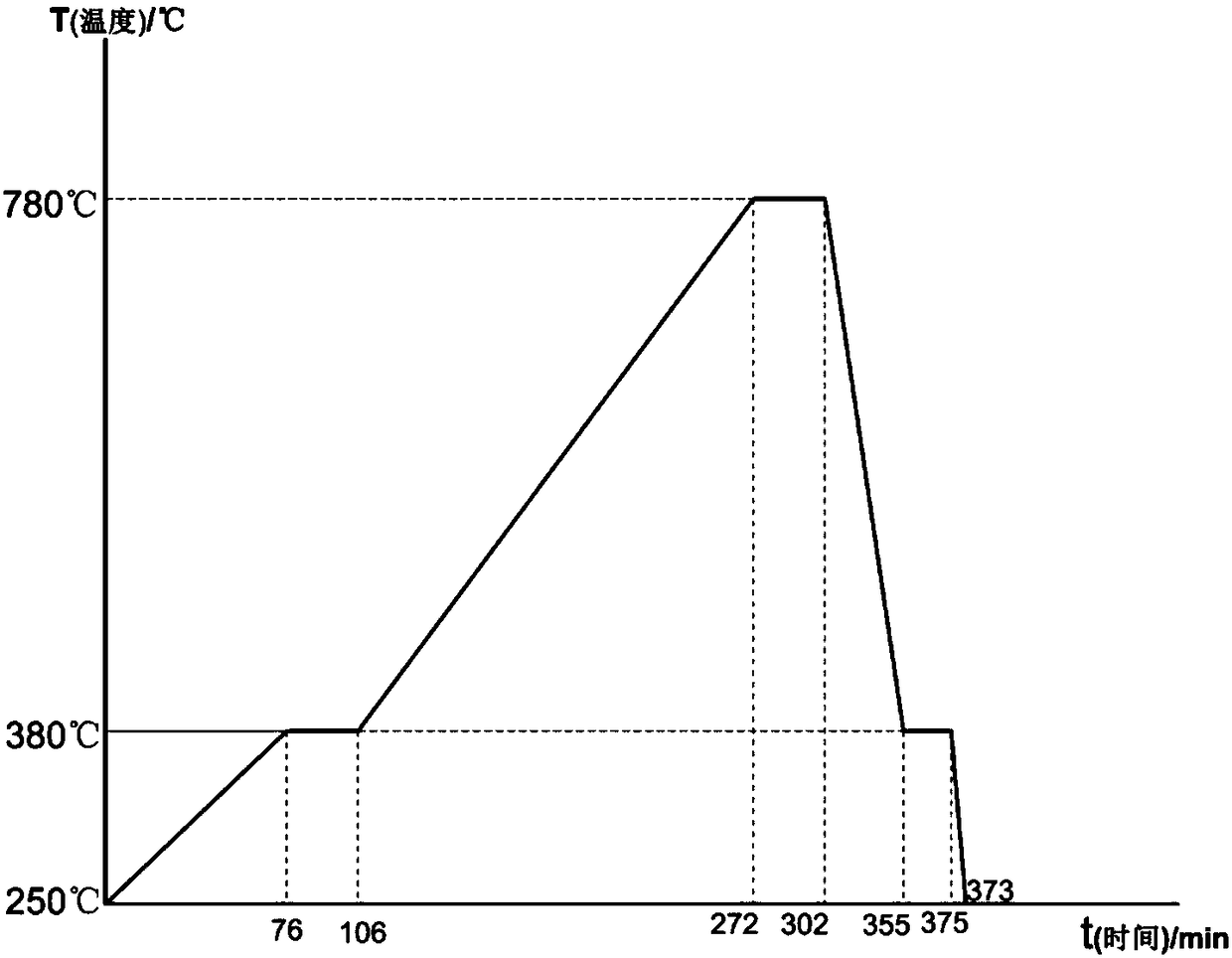
[0037] (4) Sintering: Add the batch material to a heat-resistant steel mold with a refractoriness greater than 1000°C and coated with a release agent, and burn it in a muffle furnac...
Embodiment 2
[0040](1) Material preparation: dehydrate and air-dry the discarded polishing waste slag from the ceramic factory, crush it with a jaw crusher, send it to the Raymond mill for grinding to obtain 20-50um polished brick waste powder, and then send it to a special ash storage tank for standby; After the waste glass is cleaned and dried, use the same process to obtain 50-100um waste glass powder, which is also sent to a special ash storage tank for standby.
[0041] (2) Ingredients: the weight percentages of various raw materials are as follows: 30% of polished brick waste slag powder, 45% of waste glass powder; 15% of low-temperature frit powder, and 10% of a mixture of carbon powder and foamable resin.
[0042] (3) Mixing: Send the above prepared materials to the ball mill and mix for 25 minutes to obtain the batch materials.
[0043] (4) Sintering: Add the batch material to a heat-resistant steel mold with a refractoriness greater than 1000°C and coated with a release agent, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com