Flexible organic solar cell and full-printing preparation method thereof
A solar cell and full printing technology, applied in the field of solar cells, can solve problems such as expensive equipment, unfavorable industrial preparation, and reduced yield of organic solar cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
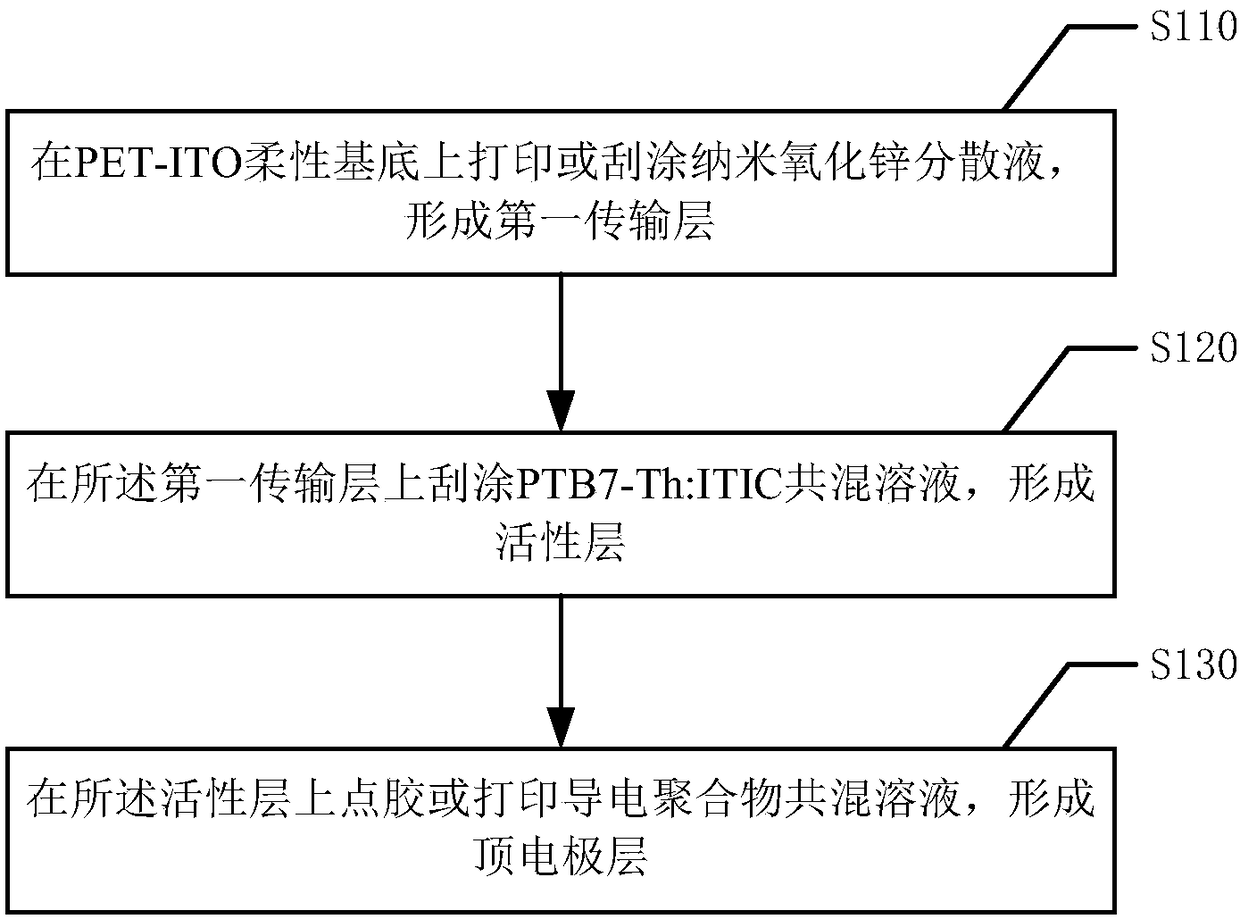
[0091] figure 1 is a schematic structural view of the flexible organic solar cell according to the first embodiment of the present invention. Such as figure 1 As shown, the flexible organic solar cell includes a polyethylene terephthalate-indium tin oxide (Polyethylene terephthalate-ITO, PET-ITO) flexible base electrode 1, a first transport layer 2, an active layer 3 and a top electrode layer 4 . After the organic solar cell absorbs light, the light passes through the first transport layer 2, and the material in the active layer 3 absorbs light to generate excitons (electron-hole pairs), and then the excitons diffuse into the active layer material. The interface of the bulk material is split into free carriers, namely electrons and holes. Subsequently, the electrons and holes are transported to the electrode through the transport layer in their respective host phases (the donor phase of the donor material and the acceptor phase of the acceptor material), that is, the electr...
Embodiment 2
[0104] Figure 4 It is a schematic structural diagram of a flexible organic solar cell according to the second embodiment of the present invention. Such as Figure 4 As shown, the flexible organic solar cell includes a polyethylene terephthalate-indium tin oxide (Polyethylene terephthalate-ITO, PET-ITO) flexible base electrode 1, a first transport layer 2, an active layer 3 and a top electrode layer 4 . After the organic solar cell absorbs light, the light passes through the first transport layer 2, and the material in the active layer 3 absorbs light to generate excitons (electron-hole pairs), and then the excitons diffuse into the active layer material. The interface of the bulk material is split into free carriers, namely electrons and holes. Subsequently, the electrons and holes are transported to the electrode through the transport layer in their respective host phases (the donor phase of the donor material and the acceptor phase of the acceptor material), that is, the...
Embodiment 3
[0117] Figure 7 is a schematic structural view of a flexible organic solar cell according to the third embodiment of the present invention. Such as Figure 7As shown, the flexible organic solar cell includes a flexible substrate 1 , a bottom electrode 2 , a first transport layer 3 , an active layer 4 and a top electrode layer 5 . After the organic solar cell absorbs light, the light passes through the flexible substrate 1 and the first transport layer 3, and the material in the active layer 4 absorbs the light to generate excitons (electron-hole pairs), and then the excitons diffuse into the active layer material to give The interface between the bulk material and the acceptor material is split into free carriers, namely electrons and holes. Subsequently, the electrons and holes are transported to the electrode through the transport layer in their respective host phases (the donor phase of the donor material and the acceptor phase of the acceptor material), that is, the ele...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
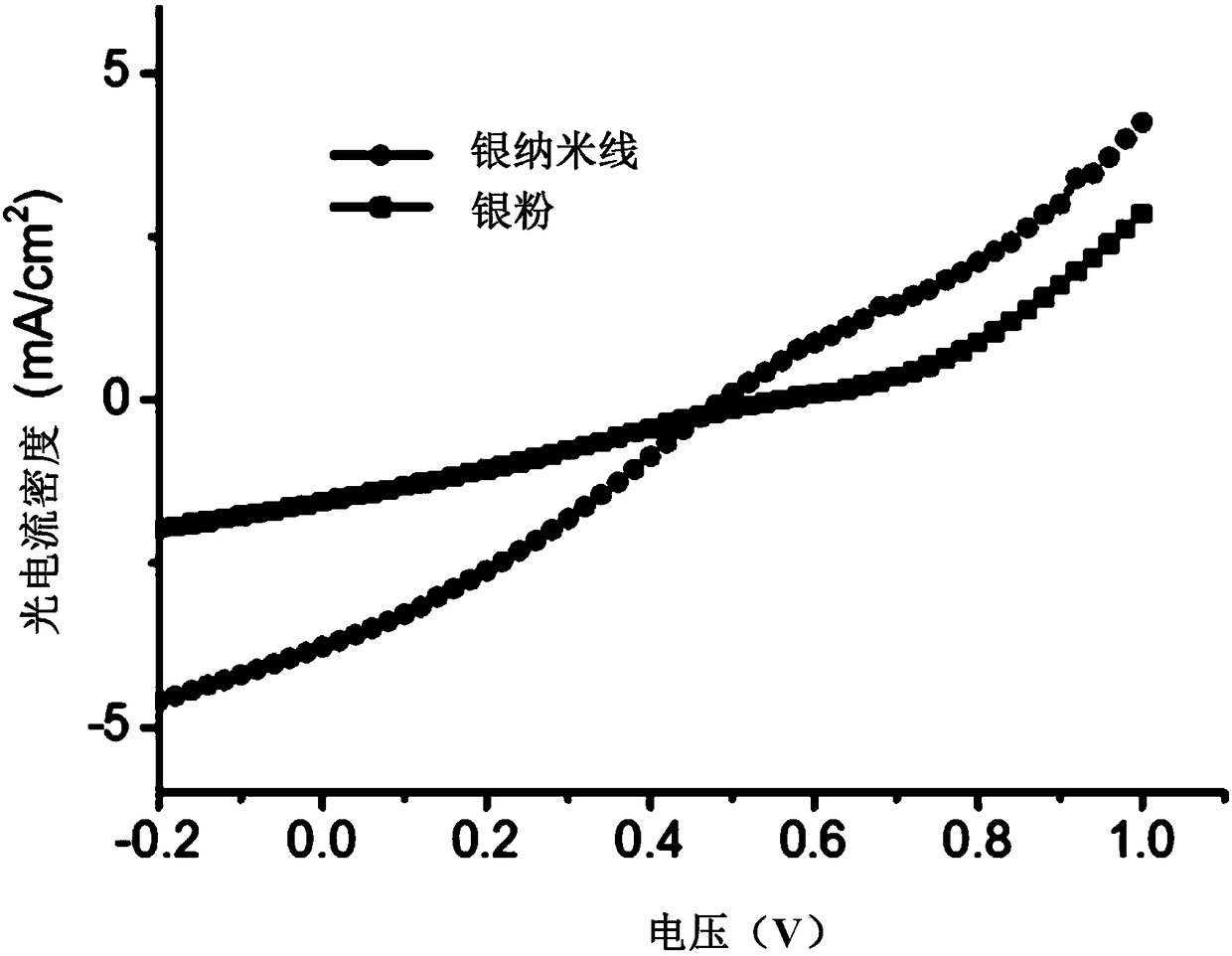
| Short circuit current density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com