Codon optimized recombinant human lysozyme gene and application thereof
A technology of codon optimization and human lysozyme, which is applied in the fields of cell engineering and molecular biology, can solve the problems of low recombinant protein expression, affecting mRNA stability and translation efficiency, and high purification and production costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Example 1: Codon usage bias analysis of bovine dominant milk protein
[0046] The codon usage bias analysis of bovine dominant milk protein gene using CodonW and EMBOSS software showed that the codon preference of bovine milk protein gene ended with GC, while the codon preference of human lysozyme gene ended with AT.
[0047] In this example, the applicant selected αs1, αs2, β, K casein, β-lactoglobulin, whey albumin, and lactoferrin according to the content of various proteins in the mammary gland. High dominant milk protein was used as the analysis object, and the sequence of the CDS region of the protein-coding gene above was obtained by searching NCBI. For the specific milk protein gene name, GenBank accession number, and CDS sequence length, please refer to Attached Table 1.
[0048] Attached Table 1: Sequence information of bovine dominant milk protein gene
[0049]
[0050] The relative probability of codon usage (RSCU) analysis was carried out on 59 codons ...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Embodiment 2: Codon optimization design of human lysozyme gene
[0056] According to the analysis results of the above-mentioned CodonW software, the third base of the codon of human lysozyme ends with AT (the average content of the third base GC3s is 0.41), while the third codon of the bovine dominant milk protein gene ends with GC (The average content of the third base GC3s is 0.54). According to the use of high-frequency codons and low-frequency codons of milk protein in the attached table 2, the inventors optimized the codon design of human lysozyme. Among them, lyzop optimized all the codons of the human lysozyme gene, while Lyzop23 only optimized the first 23 codons of the human lysozyme gene (Supplementary Table 3).
[0057] Attached Table 3: Codon Optimization of Human Lysozyme Gene
[0058]
[0059] Note: The bold italic part indicates the optimized codons of the recombinant human lysozyme gene according to the cow milk protein preference codons.
[0060]...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Example 3: Detection of impact of codon optimization design on human lysozyme mRNA transcription level
[0064] Lyzcw, Lyzop23, and Lyzop were synthesized according to the sequence in Appendix 3, and HindIII and XhoI restriction sites were added.
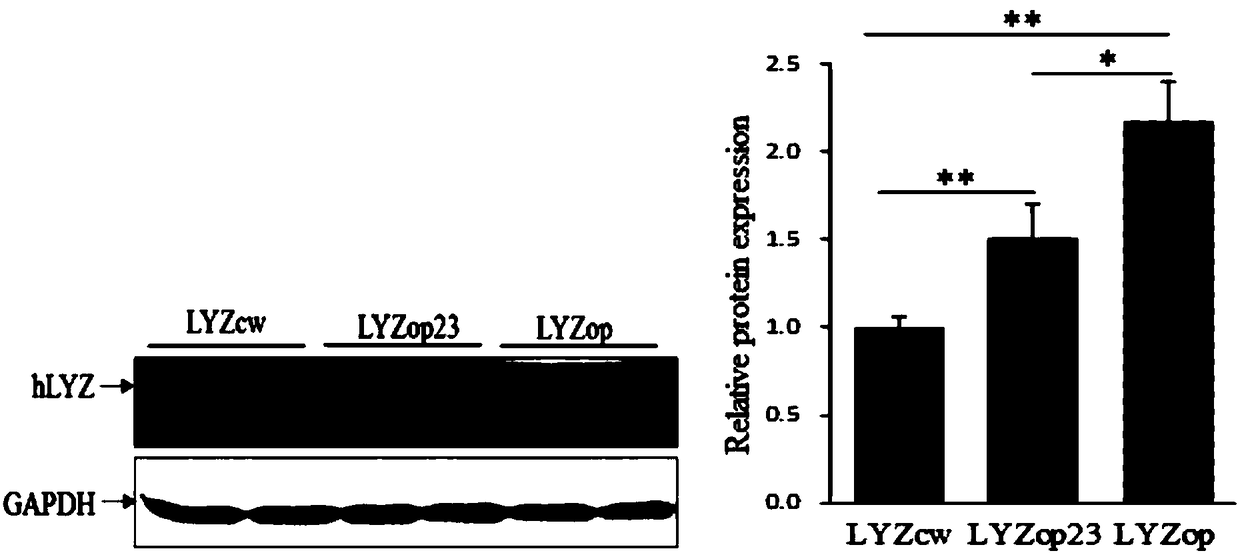
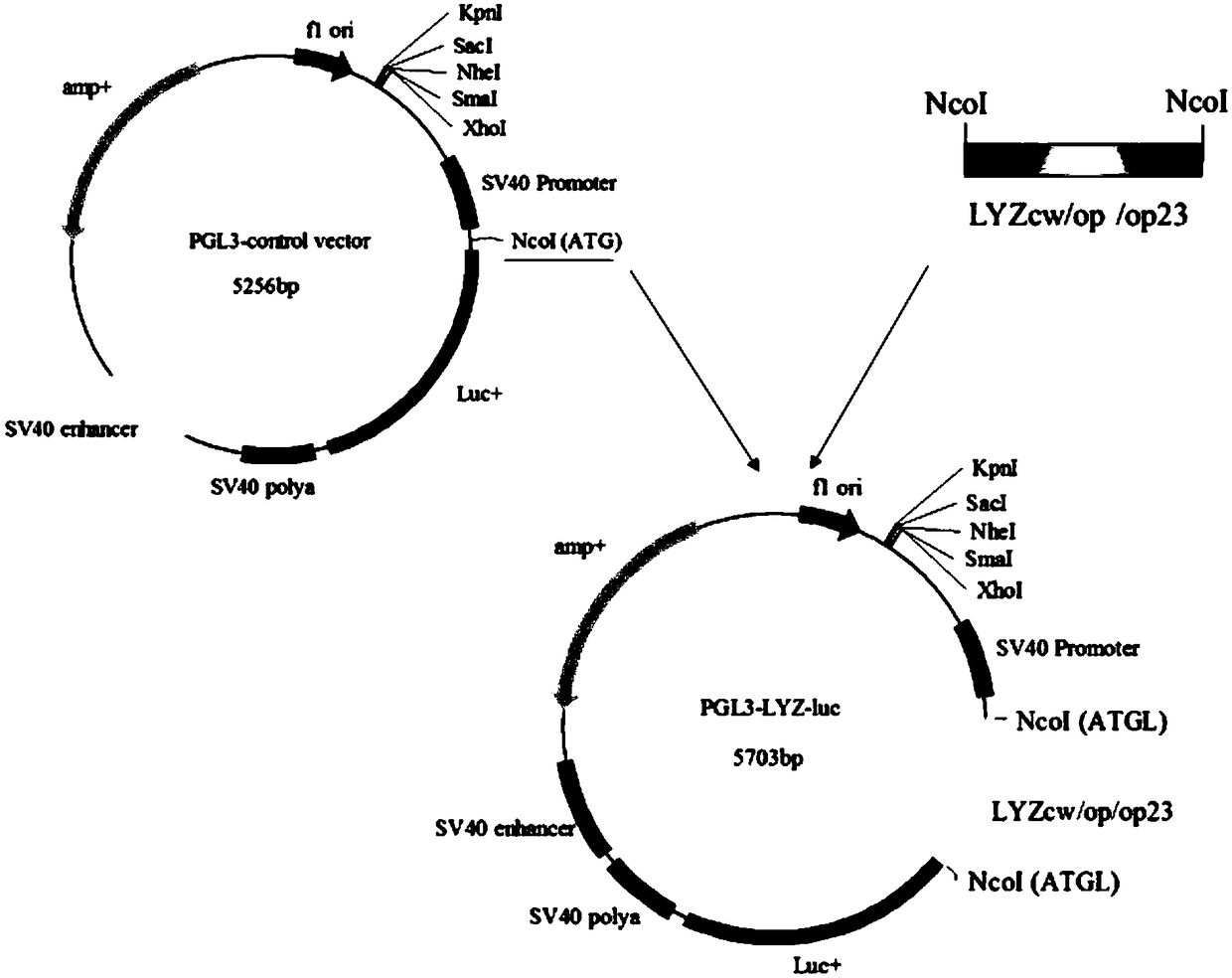
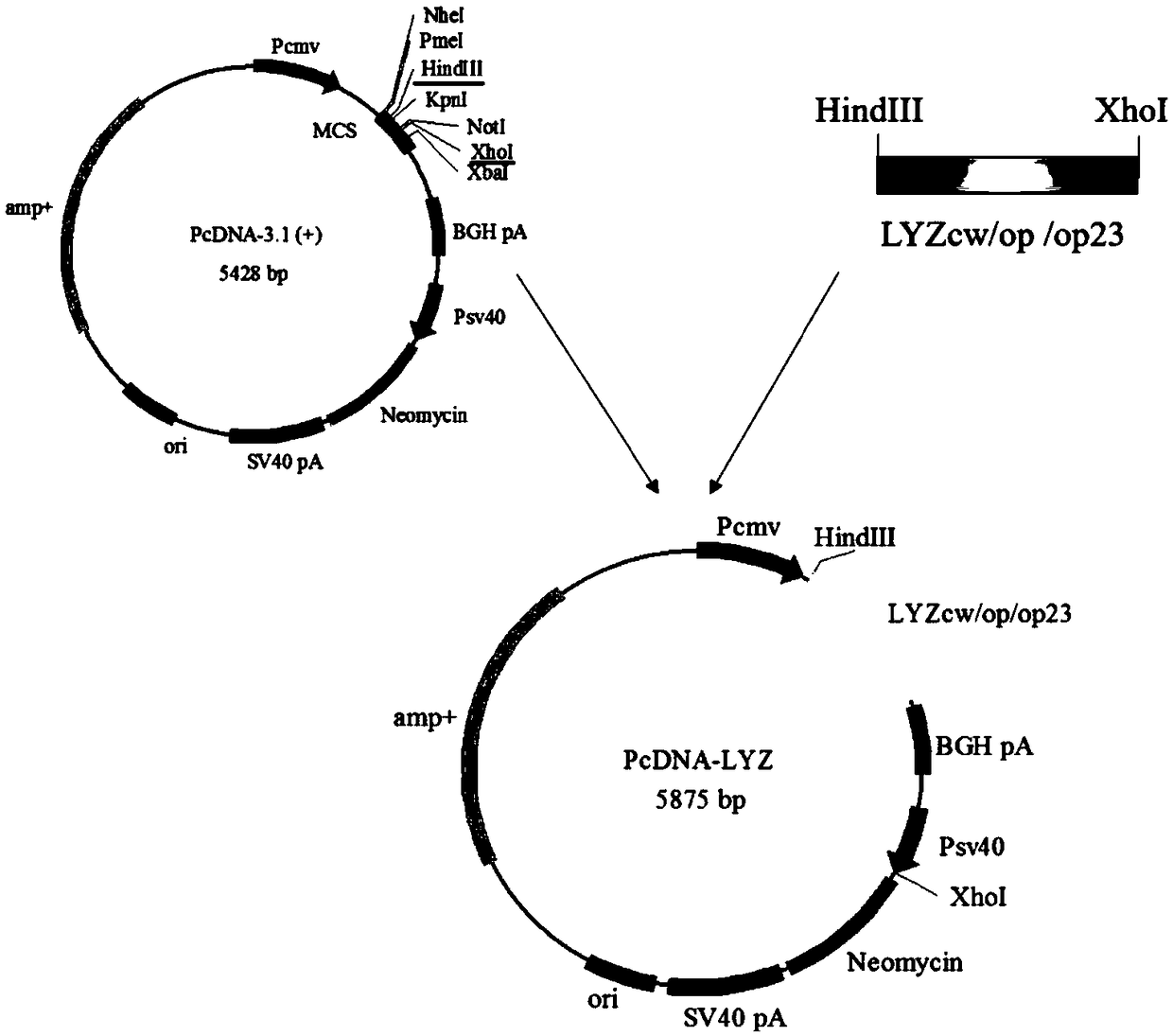
[0065] Further, HindIII and XhoI digested Lyzcw, Lyzop23, Lyzop and PcDNA3.1 (+) vectors respectively, recovered the above fragments by gel, and used T4 DNA enzyme to connect and construct three human lysozymes: PcDNA-Lyzcw, PcDNA-Lyzop23 and PcDNA-Lyzop respectively expression plasmid (see figure 1 ).
[0066] After the above three plasmids were transfected with DH5α, single-clonal shaking bacteria, extracted plasmids, HindIII and XhoI double enzyme digestion and identification, the successfully constructed PcDNA-Lyzcw, PcDNA-Lyzop23 and PcDNA-Lyzop plasmids were selected for cell transfection.
[0067] When the confluence of cultured bovine fetal fibroblasts (BFFC), bovine mammary epithelial cells (BMEC), and mouse mammar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com