A nickel-cobalt synergistic extractant and its method for extracting and separating nickel-cobalt from impurities
An extractant, nickel-cobalt technology, applied in the field of metal extractant, nickel-cobalt synergistic extractant, can solve the problems of poor selectivity and achieve the effects of short phase separation time, clear oil-water interface, and good solubility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Synthesis of intermediate product p-pyridinecarboxaldehyde 2-ethylhexyleneamine
[0055] In a 250ml round bottom flask, dissolve pyridine-4-carbaldehyde (21.38g, 0.2mol), 2-ethylhexylamine (25.90g, 0.2mol) and 1.0g p-toluenesulfonic acid in absolute ethanol (150mL) , Stirring and refluxing in 80℃ oil bath for 8h, TLC tracking and detecting until the reaction is complete, adding 1.54g anhydrous K 2 CO 3 , Continue the reaction for 30 minutes, cool to room temperature, concentrate under reduced pressure, wash with water, and extract three times with 100 ml of ethyl acetate. Collect the organic phase, dry with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filter, remove the organic solvent by vacuum rotary evaporation, and dry in vacuum. Yield: 41.24g. The yield was 94.50%.
Embodiment 2
[0057] Synthesis of extractant α-phosphoramidate (abbreviated as EHPMPD)
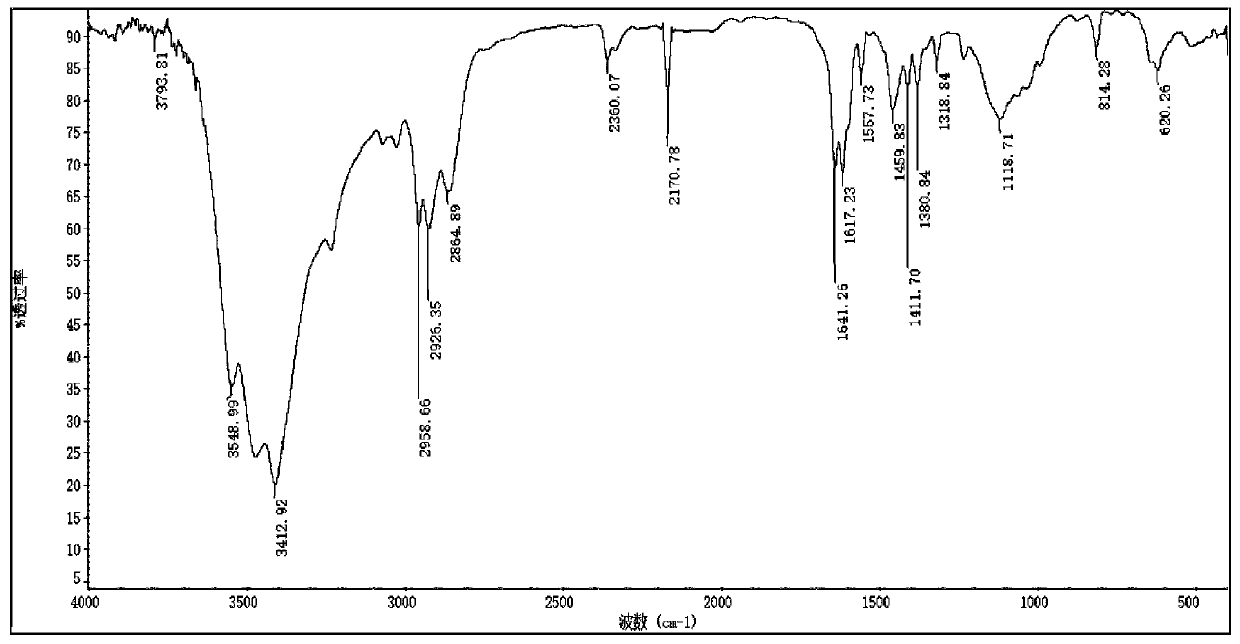
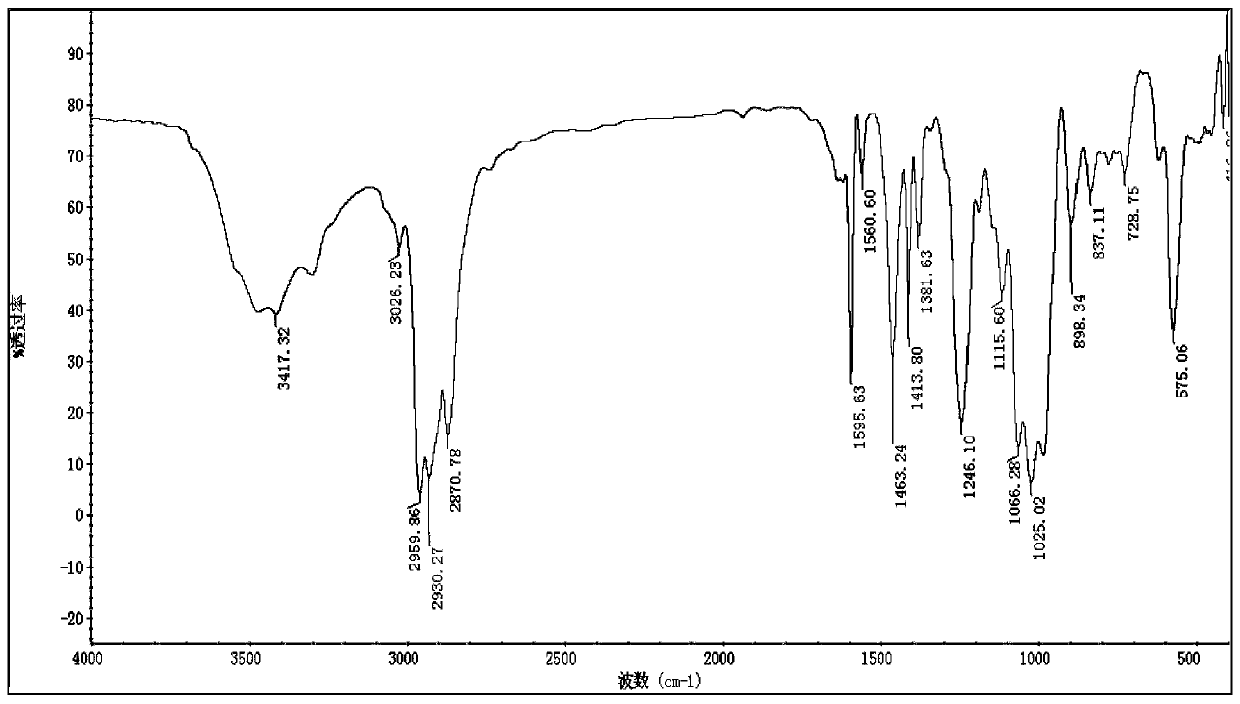
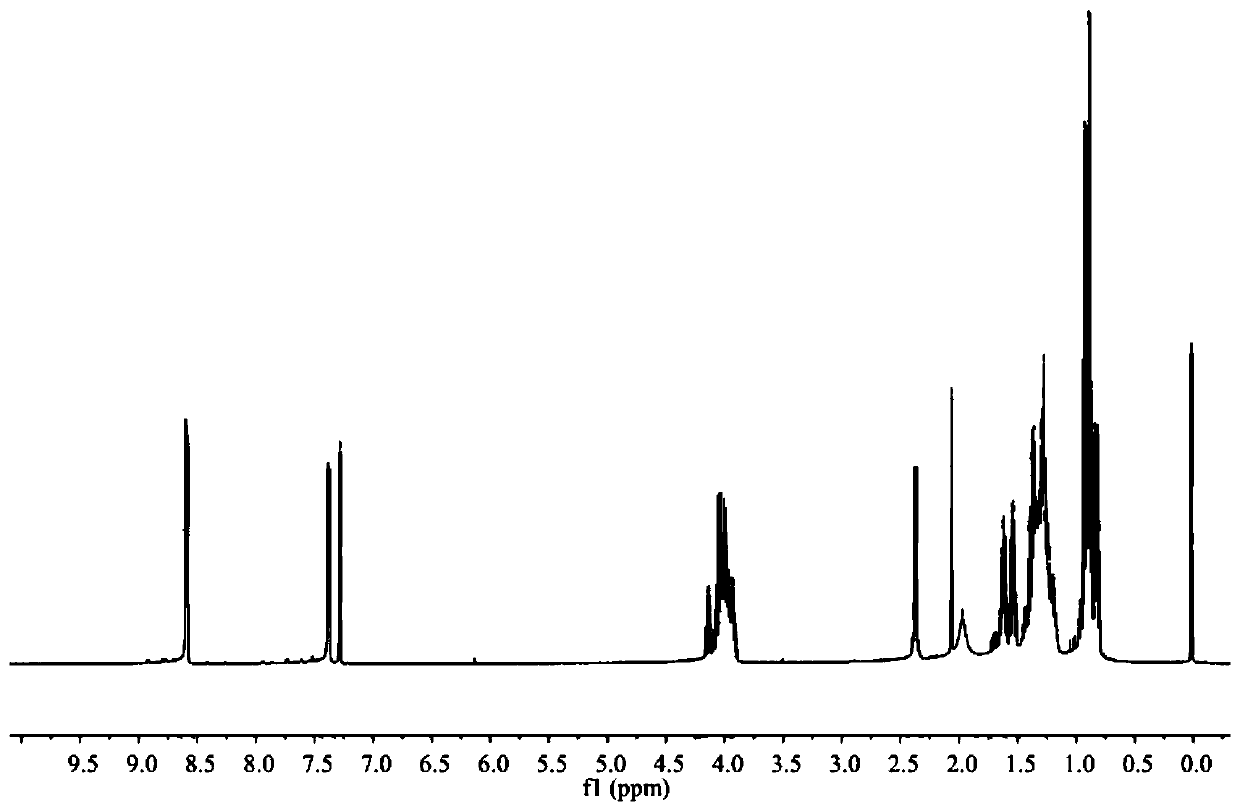
[0058] In a 500ml round-bottomed flask, the product obtained in the previous step (182.85g, 0.84mol), diethyl phosphite (162.77g, 0.84mol) were reacted in an oil bath at 80°C without solvent for 5h, followed by TLC to check whether the reaction was complete , Cooled to room temperature, transferred to a 1000ml separatory funnel, acid washed 3 times, alkaline washed 3 times, washed with water to neutral, extracted with ethyl acetate, dried with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered, combined the organic phases, vacuum rotary evaporated to remove acetic acid The ethyl ester was dried under vacuum overnight to obtain a wine-red liquid. Yield: 326.56g. The yield was 94.52%. The structure is characterized as follows: IR (KBr) ν / cm-1: 3417, 3026, 2930, 1596, 1561, 1463, 1382, 1246, 1025, 898, 575; 1H NMR (500MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.59 (d, J =5.4Hz, 2H), 7.38 (d, J = 4.1 Hz, 2H), 4.14 (dd, J = 14.3, 7.1 Hz, 1H), 4.06–...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Aqueous material liquid: simulated material liquid, the material liquid contains Ni 1.187g / L, Co 1.163g / L, Mg 1.309g / L, Mn1.204g / L, Ca 0.463g / L, pH 5.81;
[0061] Organic phase: Use sulfonated kerosene as the diluent, and the extraction agent is the single extractant EHPMPD, and the concentration is set to: 0.10, 0.15, 0.20, 0.25mol / L.
[0062] Extraction: The above-mentioned organic phase and the feed liquid are compared (O / A) 2:1, the mixing time is 5 min, the shaking frequency is 200 r / min, and the extraction is performed at room temperature. The experimental results are shown in Table 1 below.
[0063] It can be seen from Table 1 that the single extractant EHPMPD has very poor ability to extract nickel, cobalt, magnesium, manganese and calcium, and there is almost no extraction effect.
[0064] Table 1 Extraction effect of single extractant EHPMPD
[0065]
[0066]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com