Application and method of pslg protein or its coding sequence in detecting the number of microorganisms
A microbial and protein technology, applied in the field of extracellular polymer degrading enzymes, can solve the problem of not being able to accurately reflect the real bacterial amount of the sample, and achieve the effect of accurate measurement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0046] The preparation of LBNS solid medium used 5g yeast extract, 10g tryptone, 15g agar powder and 1000ml distilled water.
[0047] LBNS liquid medium was prepared using 5 g of yeast extract, 10 g of tryptone and 1000 ml of distilled water.
[0048] The preparation of LD solid medium used 5g yeast extract, 10g tryptone, 2.5g NaCl, 15g agar powder and 1000ml distilled water.
[0049] 5 g of yeast extract, 10 g of tryptone, 2.5 g of NaCl and 1000 ml of distilled water were used for the preparation of LD liquid medium.
[0050] Jensen broth (pH 7.3) was prepared using 5 g NaCl, 2.51 g K 2 HPO 4 , 15.56g L-glutamic acid monosodium salt, 2.81g valine, 1.32g phenylalanine, 13.87g glucose, 0.165g MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 0.105 mg CaCl 2 2H 2 O, 5.5 μg FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 12 μg ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O and 1000ml distilled water.
[0051] KLG liquid medium (pH6.8) contains 0.87g / L KH 2 PO 4 , 1.67g / L K 2 HPO 4 , 0.48g / L NaCl, 0.29g / L MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 0.005g / L Na 2 MoO 4 ·H 2 O, 0.072g / L...
Embodiment 1
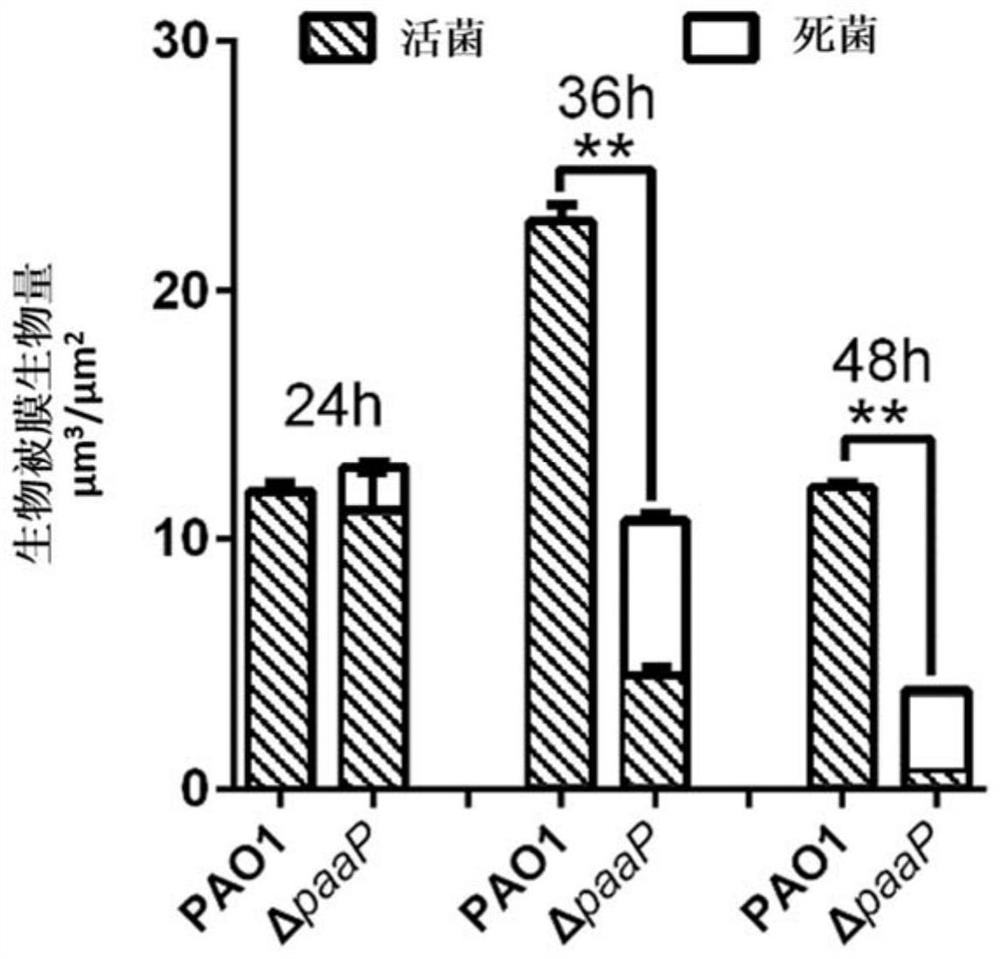
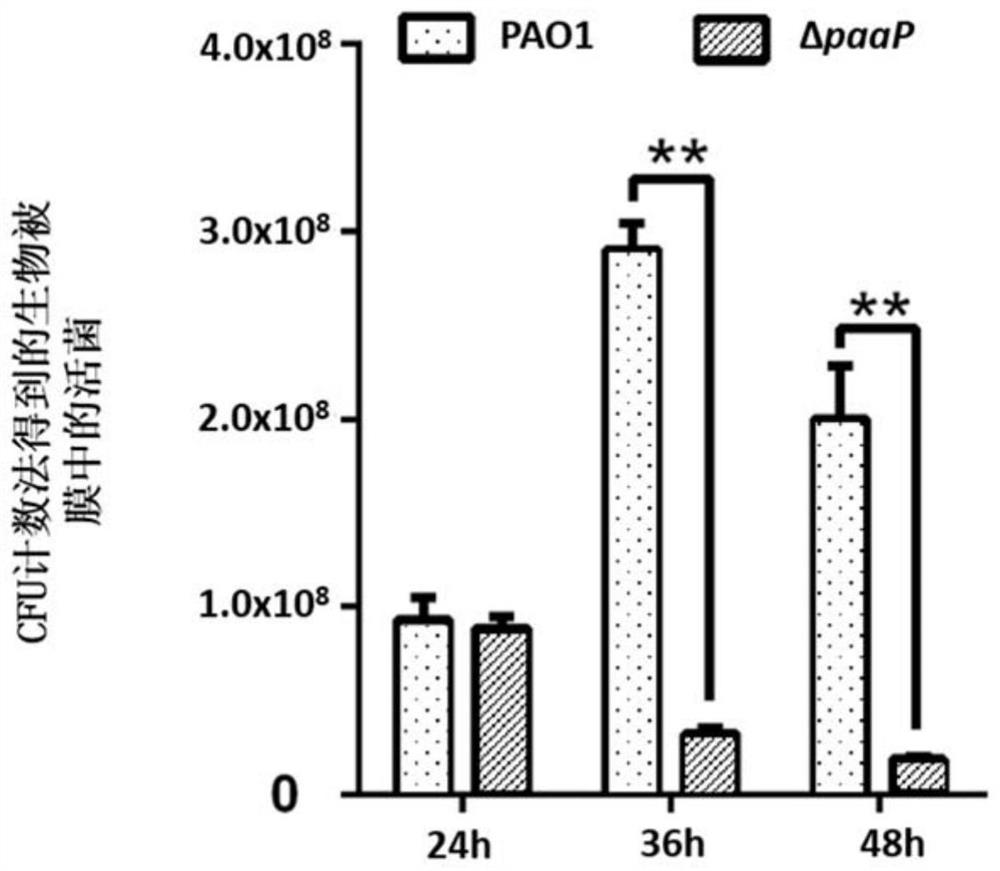
[0052] Embodiment 1, polysaccharide hydrolase PslG can be used for the quantitative calculation of living bacteria in biofilm
[0053]Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 and PaAP deletion mutant strain ΔpaaP were inoculated on LB solid medium plate, and cultured overnight at 37°C; single clones of PAO1 and ΔpaaP were picked from the plate that completed the above steps and inoculated to LB liquid culture medium, shaking culture at 200rpm at 37°C overnight; take 10μl of PAO1 and ΔpaaP overnight bacterial solution to inoculate 1ml into Jensen medium, add to 1×1×4cm four-hole glass chamber (Chambered#1.5 German CoverglassSystem , Nunc Inc.) at 30°C for 24h, 36h and 48h.
[0054] The steps for staining PAO1 and ΔpaaP biofilm dead bacteria are as follows: Before staining, gently suck out the culture solution in the chamber to make the biofilm slowly fall on the cover glass at the bottom of the chamber, and wash the biofilm once with phosphate buffered saline (PBS); LIVE / DEAD TM BacLight...
Embodiment 2
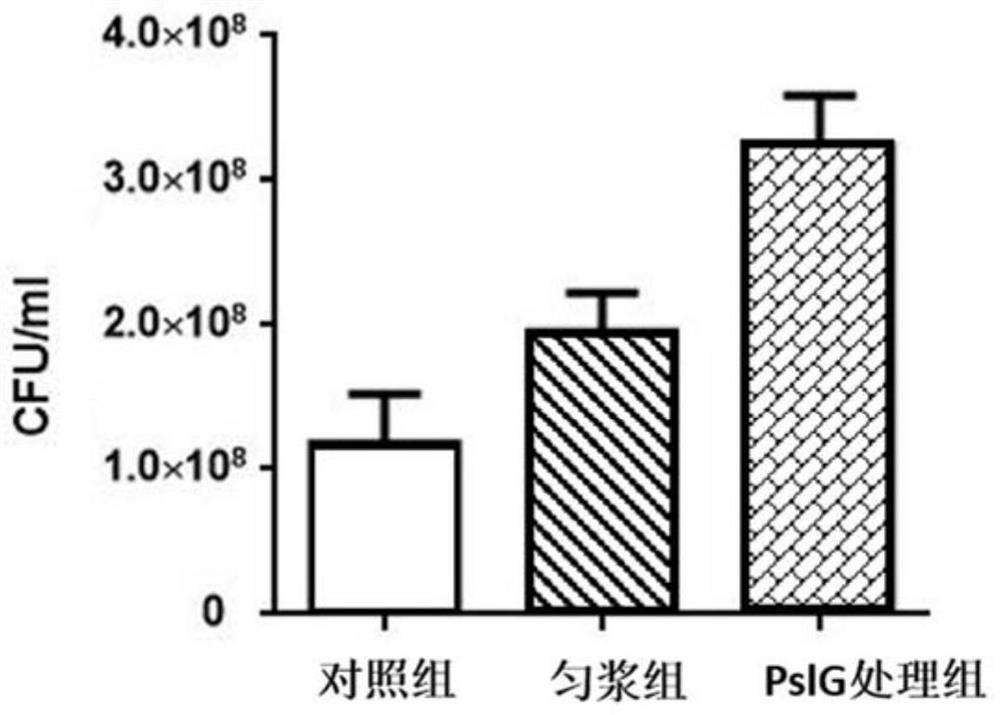
[0059] Embodiment 2, PslG processing and the comparison of counting biofilm live bacteria number after tissue homogenate processing
[0060] Inoculate Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 on the LBNS solid medium plate and culture it overnight at 37°C; pick a single clone of PAO1 from the plate that has completed the above steps, inoculate it into the LBNS liquid medium, and culture it overnight at 37°C Shake culture at 200rpm overnight; wash the overnight culture medium once with PBS, then inoculate it in Jensen liquid medium at an inoculum size of 1:100 (V:V), and culture it statically at 30°C for 24 hours in a 24-well culture plate To form a biofilm at the gas-liquid interface; use a pipette to suck up the bacterial solution under the biofilm, wash the biofilm twice with PBS, remove the bacteria in the floating state, and obtain a sample of biofilm bacteria; resuspend the biofilm in In PBS buffer, they were divided into control group, homogenate group and PslG treatment group. The ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com