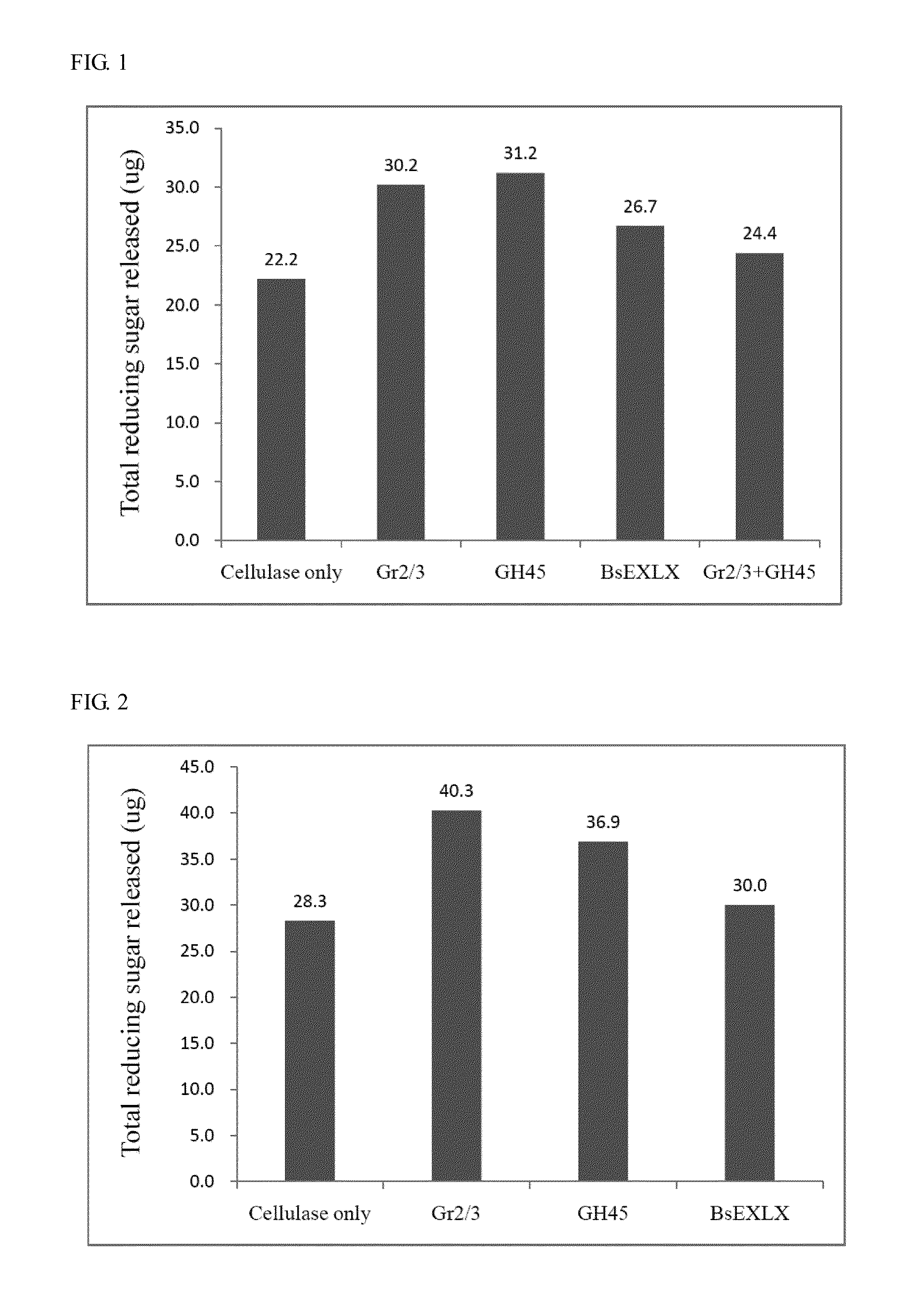
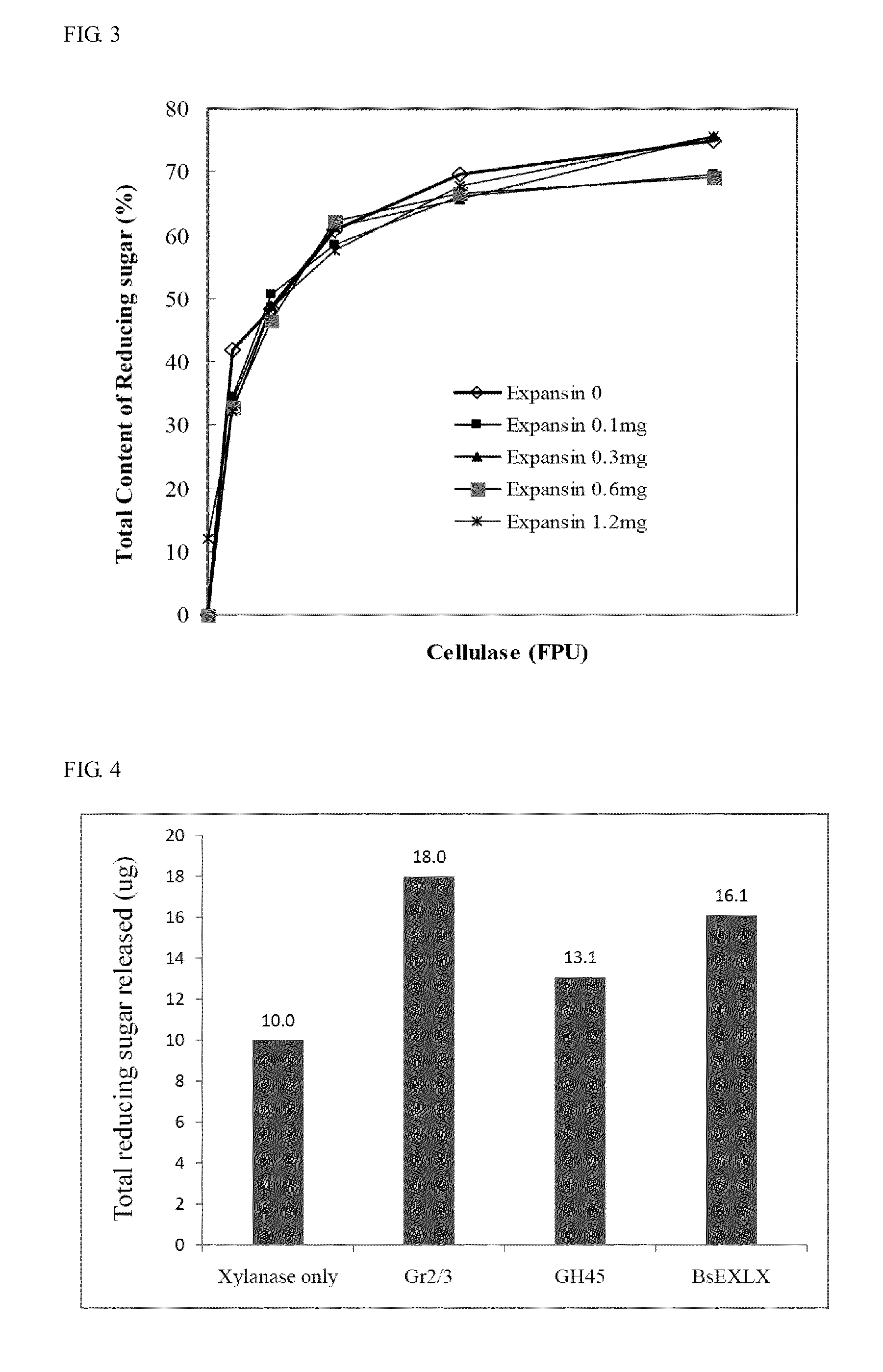
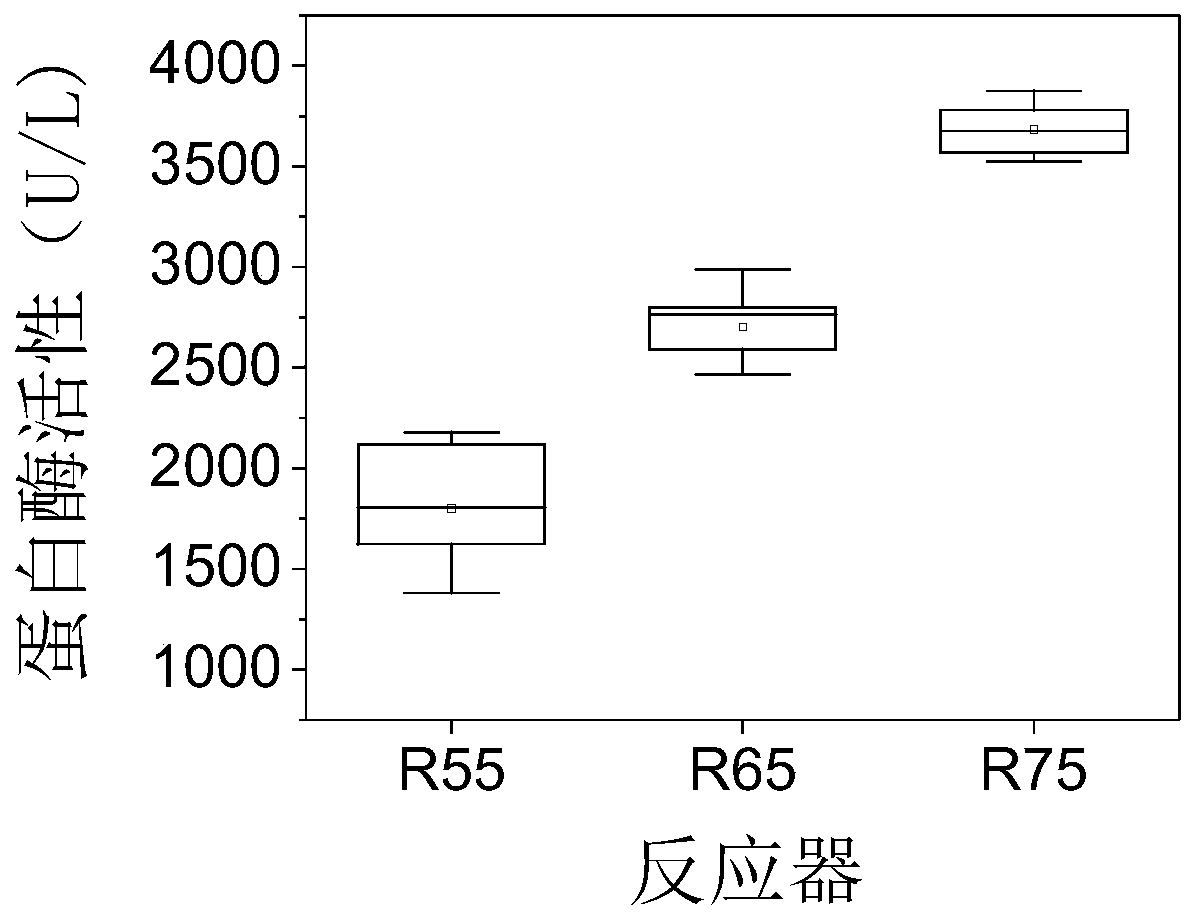
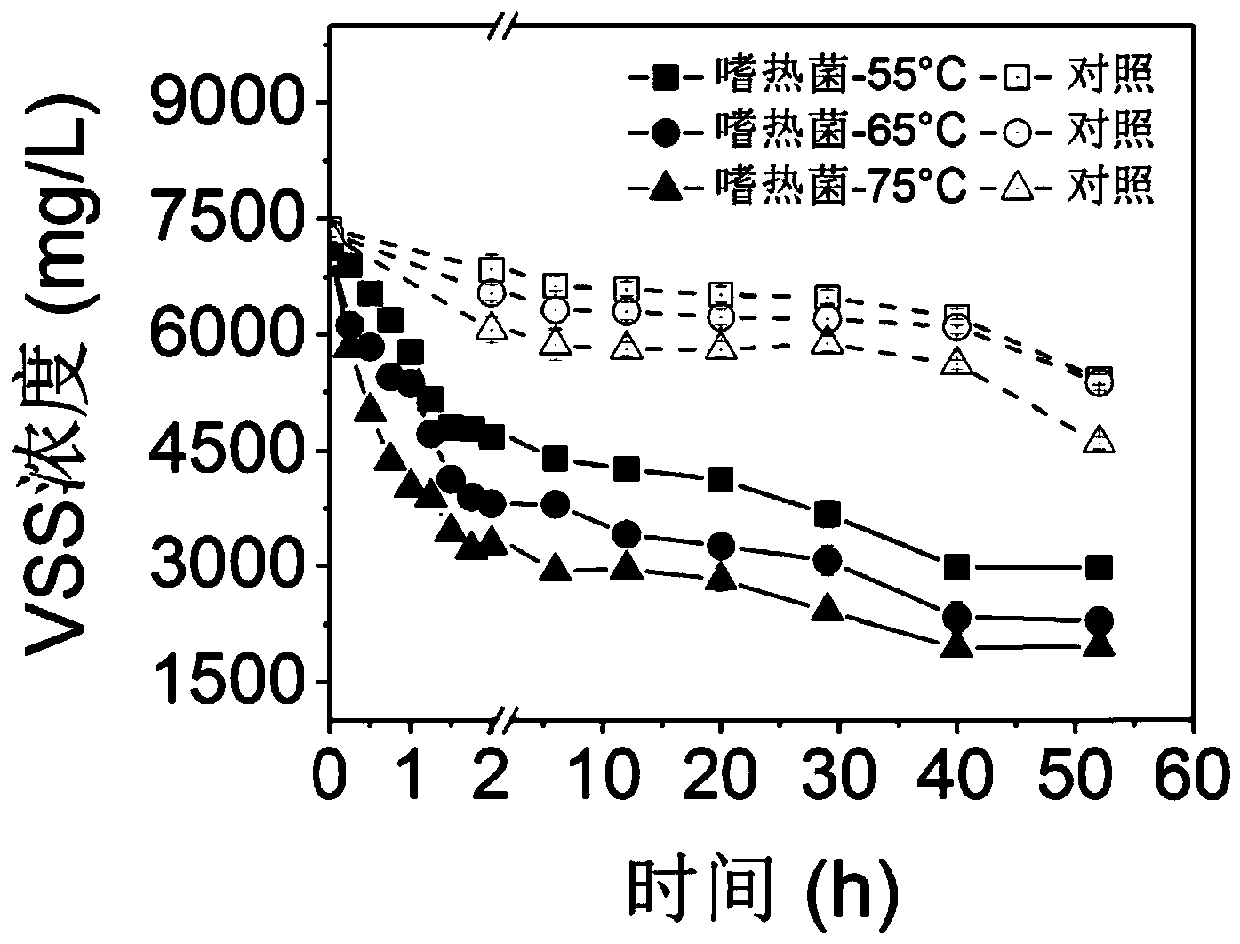
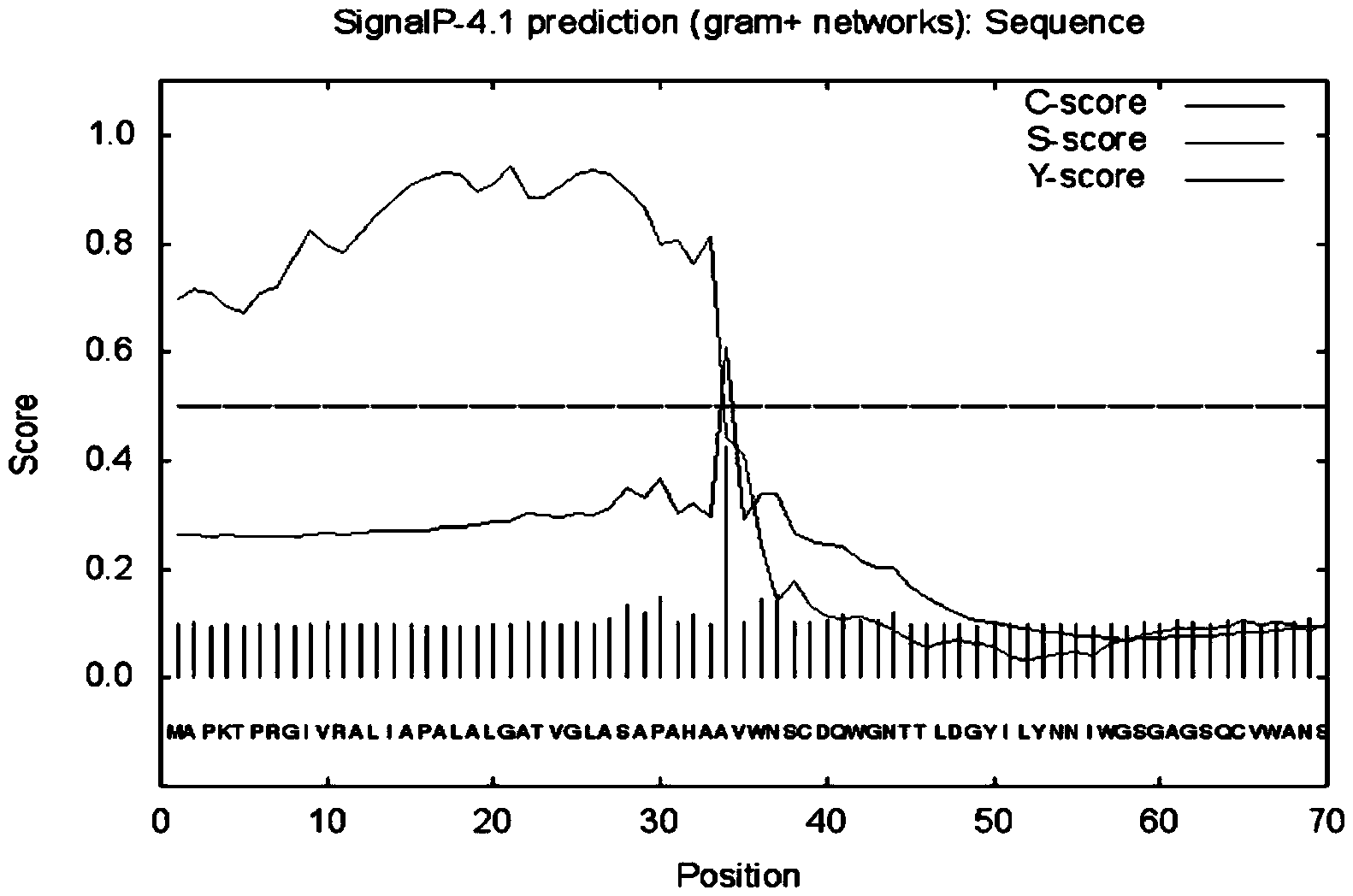
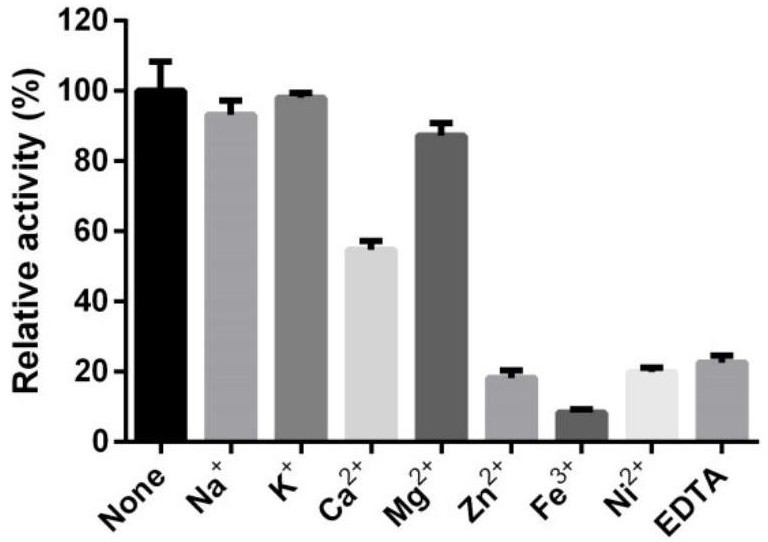
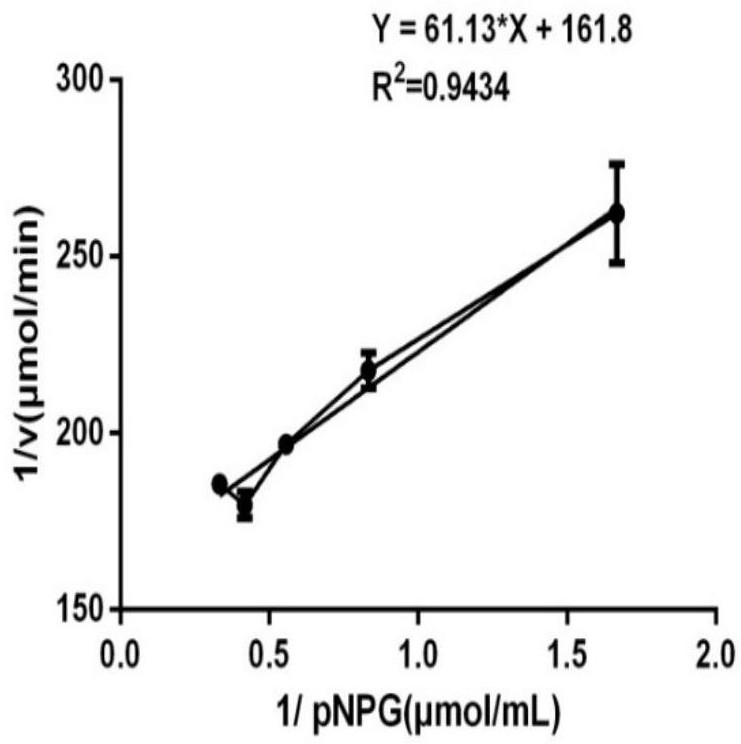
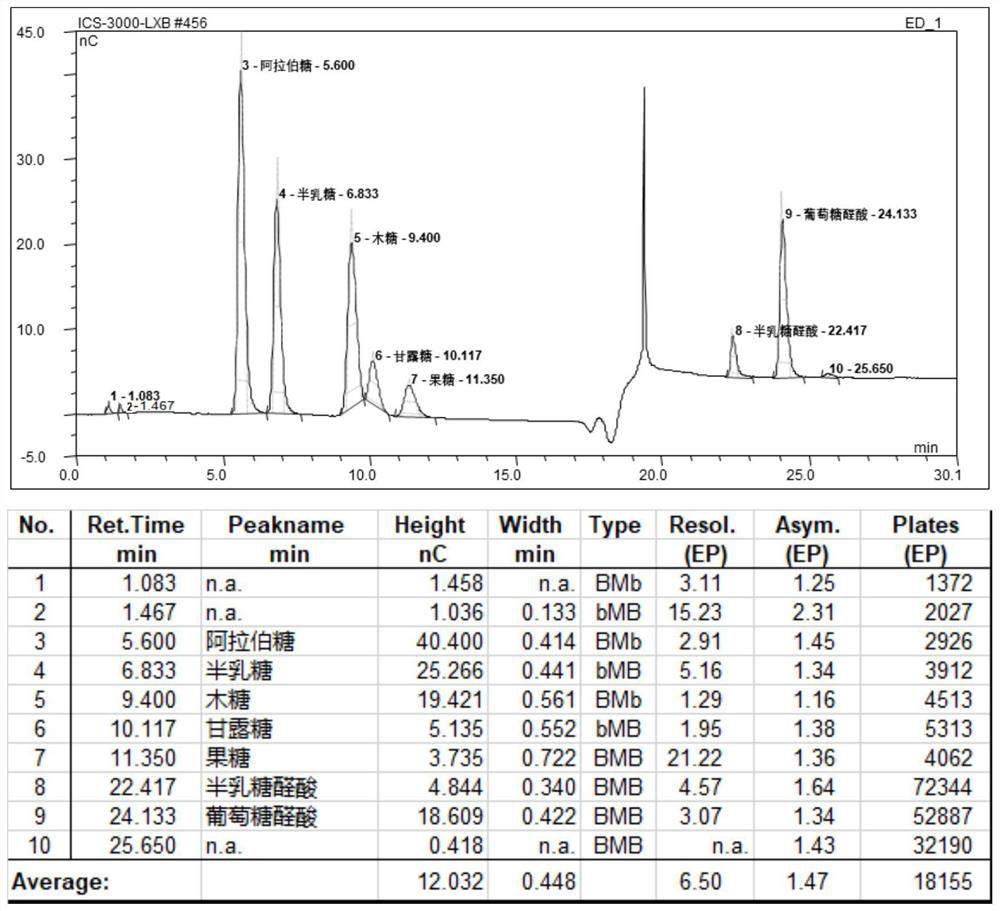
Patents
Literature
39 results about "Polysaccharide Hydrolase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An enzyme that hydrolyzes the breakdown of a polysaccharide to simple sugars.
Method for extracting protein and phytic acid from rapeseed meal
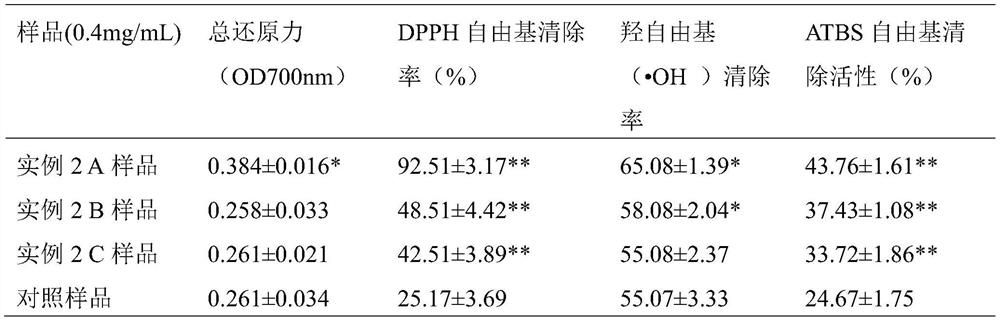
InactiveCN102296099AResidue reductionEliminate residueGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPeptide preparation methodsHydrolysatePolysaccharide Hydrolase
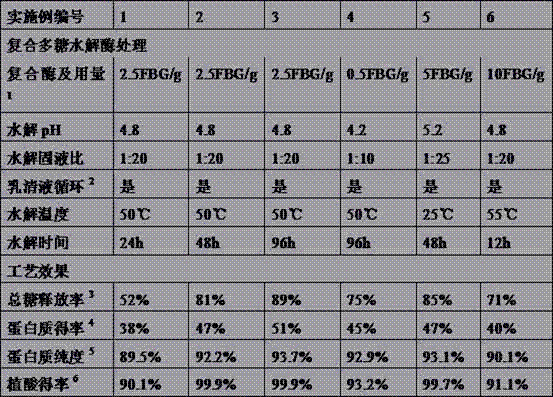
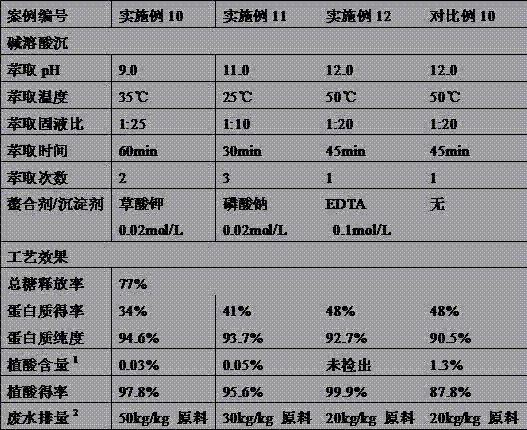
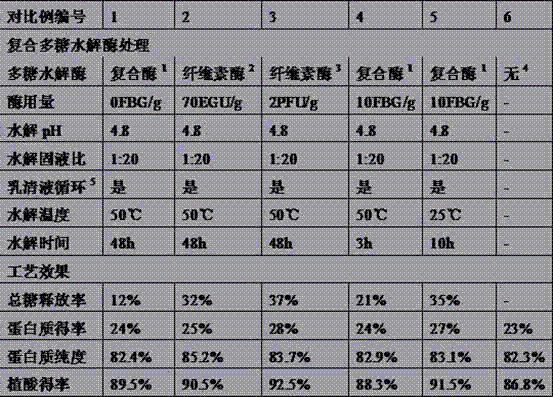
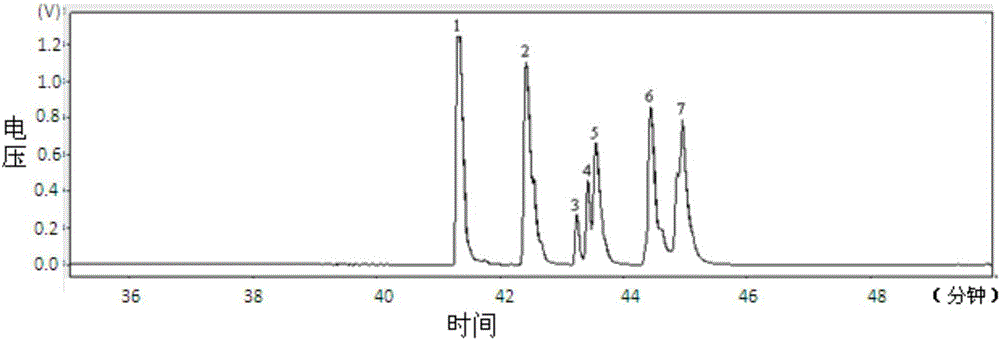
The method for extracting protein and phytic acid from rapeseed cake includes: using a compound of two or more polysaccharide hydrolytic enzymes to hydrolyze the rapeseed cake so that the ratio of the total sugar of the rapeseed cake released into the hydrolyzate liquid phase is greater than 50% ; Adjust the obtained hydrolyzate to pH 3-6 to extract phytic acid, and then separate solid-liquid to obtain phytic acid extract and hydrolyzed cake; use alkaline solution to extract protein in hydrolyzed cake at pH 9-12; use acid precipitation method Or membrane separation method to separate protein from alkaline extract. Improve the extraction efficiency of rapeseed protein and phytic acid, and improve the purity and quality of rapeseed protein products (reduce phytic acid residue).
Owner:刘晔
Nucleotide sequence of encoded fucoidin glucoside hydrolase and application thereof
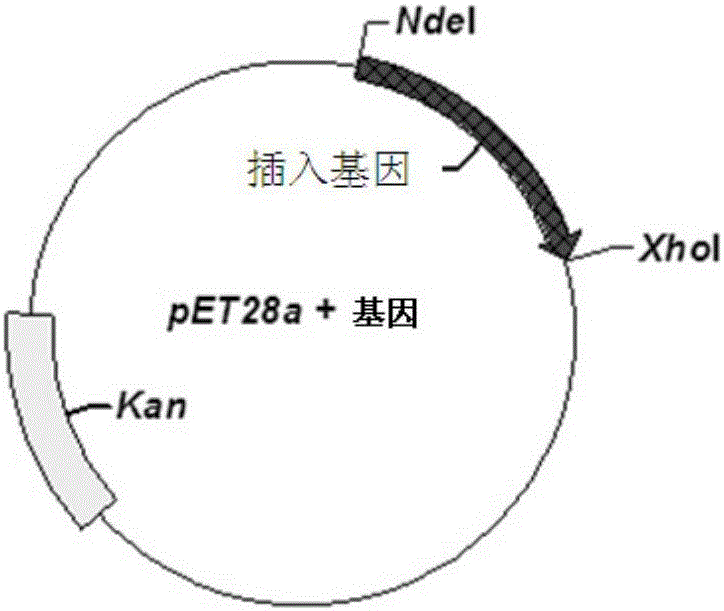
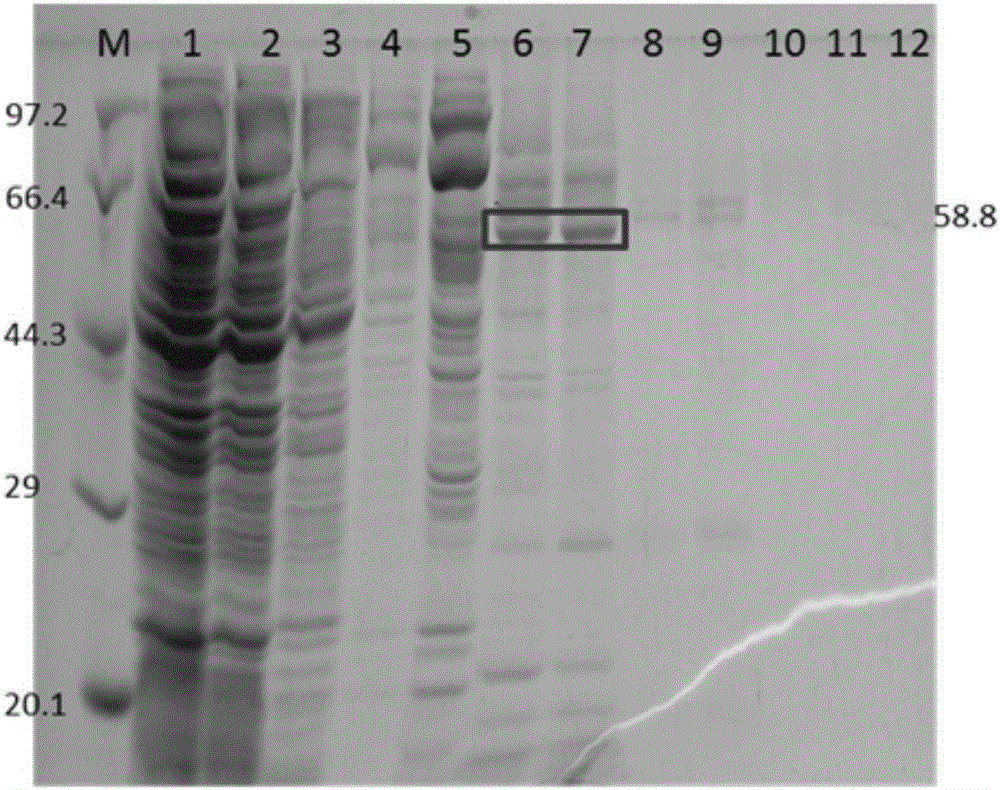
The invention relates to a nucleotide sequence of encoded fucoidin glucoside hydrolase and an application thereof. The nucleotide sequence is SEQ ID NO.1, encoded protein contains 529 amino acids, the nucleotide sequence is SEQ ID NO.2, and the predicted molecular mass of protein is 58.8 kDa. According to the nucleotide sequence and the application thereof, the gene GenBank No:AJ877239 of the encoded fucoidin hydrolase is subjected to codon optimization, 1599bp basic groups exist after optimization, and are loaded into a cloning vector pET28a, genes of the optimized fucoidin hydrolase can be expressed in escherichia coli BL21, glucoside hydrolase capable of efficiently and exclusively hydrolyzing fucoidin is obtained, and a biological degrading enzyme is provided for fucoidin hydrolysis.
Owner:SHANDONG JIEJING GROUP CORP
Method for extracting mulberry leaf polysaccharide by utilizing microbial fermentation method
ActiveCN112481134AHigh extraction yieldPromote hydrolysisFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMucor racemosus
The invention discloses a method for extracting mulberry leaf polysaccharide by using a microbial fermentation method, which comprises the following steps: adding sterile normal saline into mulberry leaf powder, inoculating spores of Mucor racemosum SY5-47, fermenting at 28-30 DEG C for 3-4 days, carrying out ultrasonic water extraction on the fermented product, and concentrating the extract to obtain a concentrate; and carrying out alcohol precipitation and vacuum drying on the concentrate to obtain mulberry leaf crude polysaccharide, wherein a step of the fermentation pretreatment of mucor racemosus SY5-47 is carried out before ultrasonic water treatment of mulberry leaf polysaccharide. According to the technical scheme, the Mucor racemosus SY5-47 grows moderately in mulberry leaf powderto generate various polysaccharide hydrolases to hydrolyze cell walls of mulberry leaves, so that structural tissues of the mulberry leaves are loose, dissociation of combined soluble polysaccharidesis promoted, and the polysaccharide hydrolases are easier to dissolve out during hot water ultrasonic extraction. Compared with an ultrasonic water extraction method without fermentation pretreatment, the extraction yield of the mulberry leaf polysaccharide can be increased by 35% or above.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Bioenzyme formaldehyde remover and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109731461AGood removal effectComprehensive and balanced nutritionDispersed particle separationAir quality improvementCitrobacterAmygdala
The invention provides a bioenzyme formaldehyde remover and a preparation method and relates to the field of formaldehyde. The bioenzyme formaldehyde remover comprises, by weight, 5-10 parts of soybean protein, 0.5-2 parts of bioenzymes, 3-5 parts of bacillus subtilis, 1-3 parts of pseudomonas amygdala, 3-5 parts of citrobacter, 1-3 parts of alcaligenes faecalis, 3-5 parts of plant extracts, 1-3 parts of tea polyphenol, 0.5-2 parts of citric acid, 1-2 parts of protective agent and 0.2-1 part of active agent, the bioenzymes include formaldehyde dehydrogenase, polyphenol oxidase, protease and polysaccharide hydrolase, and the plant extracts include aloe extract, ivy extract, maguey extract and dayflower extract. Various microorganisms, the bioenzymes and the plant extracts are adopted to jointly act to remove formaldehyde, so that removal effect is improved; the bioenzyme formaldehyde remover is safe and nonhazardous.
Owner:浙江健煦环境科技有限公司
Method for extracting atractylodes macrocephala polysaccharide by utilizing microbial fermentation method
ActiveCN111471727AHigh extraction yieldIncrease fermentation pretreatmentMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologySpore
The invention discloses a method for extracting atractylodes macrocephala polysaccharide by using a microbial fermentation method. The method comprises the following steps: inoculating rhizopus oryzaeGDMCC No:60990 spores into atractylodes macrocephala koidz powder containing sterile water, performing fermenting at 28-30 DEG C for 2-3 days, carrying out ultrasonic water extraction on the fermented product, and then performing concentrating to obtain a concentrate; and carrying out alcohol precipitation and vacuum drying on the concentrate to obtain crude atractylodes macrocephala polysaccharide. Fermentation pretreatment of rhizopus oryzae CH5 is additionally added before ultrasonic water treatment of atractylodes macrocephala polysaccharide. The rhizopus oryzae CH5 grows moderately in the atractylodes macrocephala koidz powder, generate some polysaccharide hydrolase to hydrolyze insoluble polysaccharide structure tissues of the atractylodes macrocephala koidz, and promotes dissociation of combined soluble polysaccharide, so that the polysaccharide can be dissolved out more easily during hot water ultrasonic extraction. Compared with a conventional method without fermentation pretreatment, the extraction yield of the atractylodes macrocephala polysaccharide can be increased by 50% or above.
Owner:深圳立专信息科技有限公司
Isolated polypeptide for increasing activity of polysaccharide hydrolase and methods of use
InactiveUS20110177565A1Peptide/protein ingredientsLighting and heating apparatusPolysaccharide HydrolaseHydrolase
An isolated polypeptide is disclosed that improves the hydrolyzing capacity of a polysaccharide hydrolase such as cellulase, is capable of binding to a polysaccharide, is deficient in polysaccharide hydrolase activity, and includes a GH45 or a pollen-allergen domain. Methods of hydrolyzing polysaccharides using the isolated polypeptide are also disclosed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Isolated polypeptide for increasing activity of polysaccharide hydrolase and methods of use
InactiveUS8492126B2Peptide/protein ingredientsLighting and heating apparatusPolysaccharide HydrolaseHydrolase
An isolated polypeptide is disclosed that improves the hydrolyzing capacity of a polysaccharide hydrolase such as cellulase, is capable of binding to a polysaccharide, is deficient in polysaccharide hydrolase activity, and includes a GH45 or a pollen-allergen domain. Methods of hydrolyzing polysaccharides using the isolated polypeptide are also disclosed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Biological lysis treatment method for sludge
PendingCN111138054AFast dissolution rateCarbon savingWater contaminantsSustainable biological treatmentBiotechnologyThermus
The invention discloses a method for quickly lysing sludge by utilizing thermophilic bacteria. A thermophilic microbial population includes the following species that secrete hydrolases capable of dissolving sludge: bacteria of thermus and geobacillus sp. and thermophilic aerobic bacteria. The hydrolases secreted by the thermophilic bacteria comprise proteolytic enzyme, polysaccharide hydrolase and peptidoglycan hydrolase, so the floc structure of the sludge can be quickly hydrolyzed. The specific method comprises the operation step that with sludge as a matrix, and potential thermophilic bacteria in the sludge are revived through long-time domestication under a heating condition to form a microbial preparation containing a stable thermophilic bacterial group. The microbial preparation disclosed by the invention can be used for treating biological sludge discharged from sewage treatment plants, chemical plants, food factories and the like, and rapid dissolution of the sludge can be realized through the synergistic effect of various hydrolases generated by the thermophilic bacteria. When the method is used for dissolving the sludge, a device is simple in structure, small in occupiedarea, easy to operate and low in energy consumption.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Negative ion biomass aldehyde removing agent
InactiveCN107433124AGood for healthNo pollutionGas treatmentDispersed particle separationElectrophilic additionIon content
The invention discloses a negative ion biomass aldehyde removing agent. Through combination of natural herbal plants and combination of biomass raw materials and negative ions, the negative ion biomass aldehyde removing agent utilizes raw materials having a wide source and low prices and contains a variety of active groups. An amino group and formaldehyde undergo a nucleophilic addition reaction, hydroxyl and formaldehyde undergo an electrophilic addition reaction and an aldehyde substance and formaldehyde undergo an aldol condensation reaction. The formaldehyde reactions are irreversible chemical reactions so that the elimination of formaldehyde is realized, a formaldehyde removal rate is 95% and a sterilizing rate is 95%. The biomass produces glucose and fructose under action of glycohydrolase and the glucose and fructose undergo an aldol condensation reaction with formaldehyde so that formaldehyde is further eliminated. The negative ion biomass aldehyde removing agent is toxic to the human body, does not produce the environmental pollution, acts fast, has durability, has effects of elimination of formaldehyde, air purification, sterilization, disinfection and mosquito repellent, can relieve fatigue, restore consciousness, improve spirit and increase negative ion content of indoor air, is conducive to human health, is produced by simple processes and realizes a low production cost.
Owner:TAICANG HONGSHAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Mucor racemosus SY5-47 and application thereof in extraction of flavones from mulberry leaves
ActiveCN112574890ALoose structureHigh extraction yieldFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
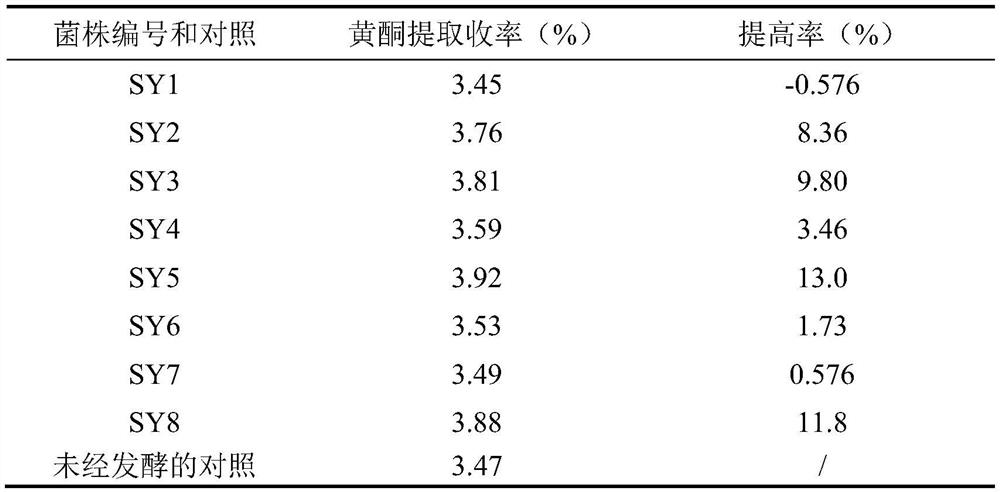
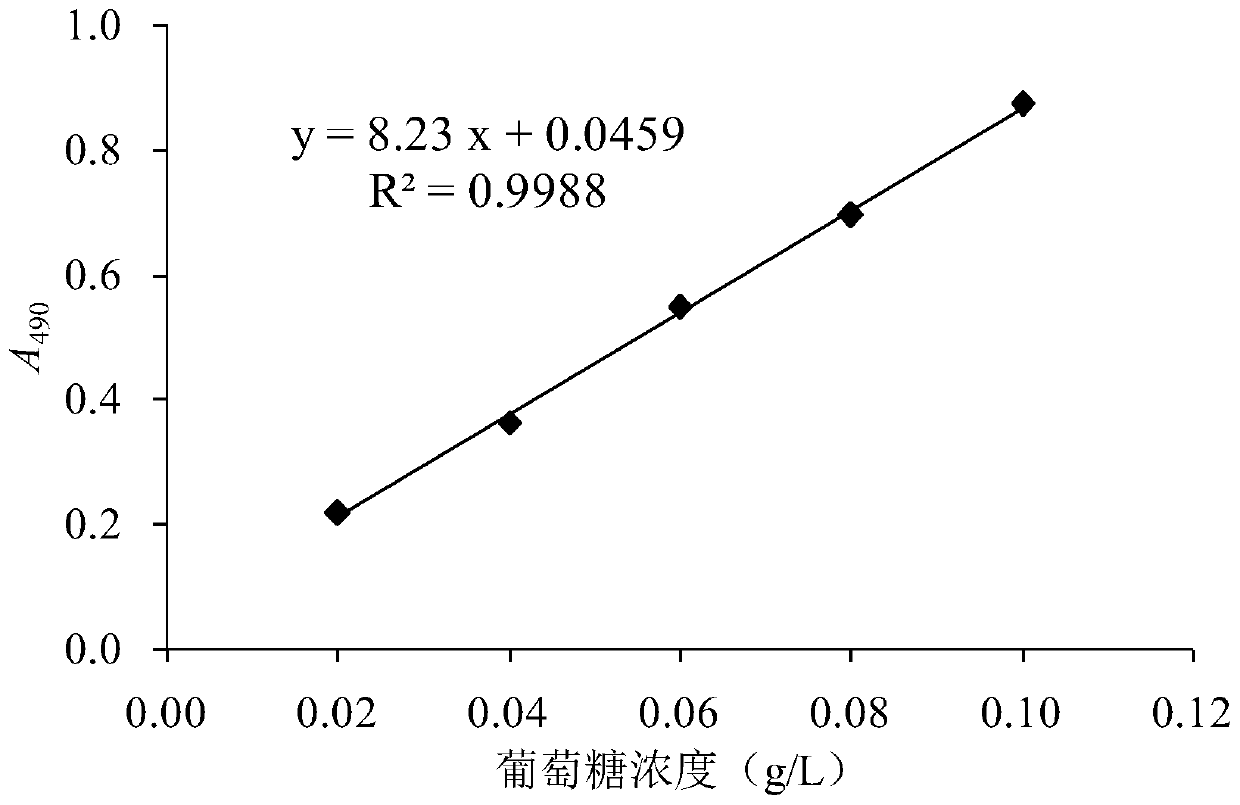
The invention relates to amucor racemosus SY5-47 and an application thereof in extraction of flavones from mulberry leaves. The application method comprises the following steps: adding sterile normalsaline into mulberry leaf powder, inoculating spores of the mucor racemosus SY5-47, fermenting at 28-30 DEG C for 3-4 days, carrying out ultrasonic ethanol extraction on the fermented product, concentrating to obtain a concentrate, and carrying out vacuum drying to obtain the mulberry leaf flavone extract. Before flavone is extracted from mulberry leaves by ultrasonic ethanol, fermentation pretreatment of mucor racemosus SY5-47 is added. The mucor racemosus SY5-47 is an excellent strain obtained by screening from a mulberry leaf microorganism enrichment culture and mutation breeding, polysaccharide hydrolase is generated by moderate growth in mulberry leaf powder, mulberry leaf cell walls are hydrolyzed, so that mulberry leaf structure tissues are loose, flavonoid compounds are easier to dissolve out during ultrasonic ethanol extraction, compared with an ultrasonic ethanol extraction method without fermentation pretreatment, the method has the advantage that the extraction yield of themulberry leaf flavone can be increased by nearly 50%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Strain of rhizopus stolonifer FL-3 and application thereof in extracting pachymaran
ActiveCN111394258AHigh extraction yieldIncrease fermentation pretreatmentFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a strain of rhizopus stolonifer FL-3 and application thereof in extracting pachymaran. The application method comprises the following steps: inoculating rhizopus stolonifer FL-3 spores into poria cocos powder containing sterile water, fermenting at 28-30 DEG C for 2-3 days, and concentrating the fermented product after ultrasonic water extraction to obtain a concentrate; and precipitating the concentrate and performing vacuum drying to obtain the pachymaran. In advance of ultrasonic water extraction of the pachymaran, fermentation pretreatment of the rhizopus stoloniferFL-3 is added. The rhizopus stolonifer FL-3 is separated from a microbial enrichment culture of poria cocos, and an excellent strain obtained by screening moderately grows in the poria cocos powder to generate polysaccharide hydrolase, so that hydrolysis of insoluble polysaccharide structural tissues of the poria cocos promotes dissociation of combined soluble polysaccharide; and compared with aconventional method without fermentation pretreatment, the extraction yield of the pachymaran can be improved by over 30%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Rhizopus oryzae ch5 and its application in the extraction of polysaccharide from Zizhizhi
ActiveCN111334440BHigh extraction yieldIncrease fermentation pretreatmentFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
Owner:深圳立专信息科技有限公司
Polysaccharide hydrolase gene from pyrococcus horikoshii and application
ActiveCN106554966AIncrease enzyme activityImprove stabilityFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementCelluloseBiotechnology
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering and enzyme engineering, and discloses a polysaccharide hydrolase gene from pyrococcus horikoshii and application. A nucleotide sequence of the polysaccharide hydrolase gene Tk1765 is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. A coding sequence of the polysaccharide hydrolase gene Tk1765 is shown as SEQ ID NO:2. Polysaccharide hydrolase has the efficient cellulose gum and chitose double digest character. According to cellulose gum of the polysaccharide hydrolase, the optimum pH value is 10.0, and the optimum enzyme reaction temperature is 65 DEG C. According to hydrolysis chitose, the optimum pH value is 11.0, and the optimum enzyme reaction temperature is 80 DEG C. The hydrolase is heated for 4 h at the temperature being 100 DEG C, and the activity of the hydrolase can be kept to be 40% or above. A recombinant vector of the hydrolase is constructed and excessively expressed in pichia pastoris, a product of the hydrolase has the function of hydrolyzing maize straw, and the polysaccharide hydrolase and the coding gene thereof can be widely applied to cellulose and chitin degradation.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Methods for distinguishing and identifying plant varieties
ActiveUS20170101663A1Rapid and reliable assayMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymesBiological bodyHeterologous
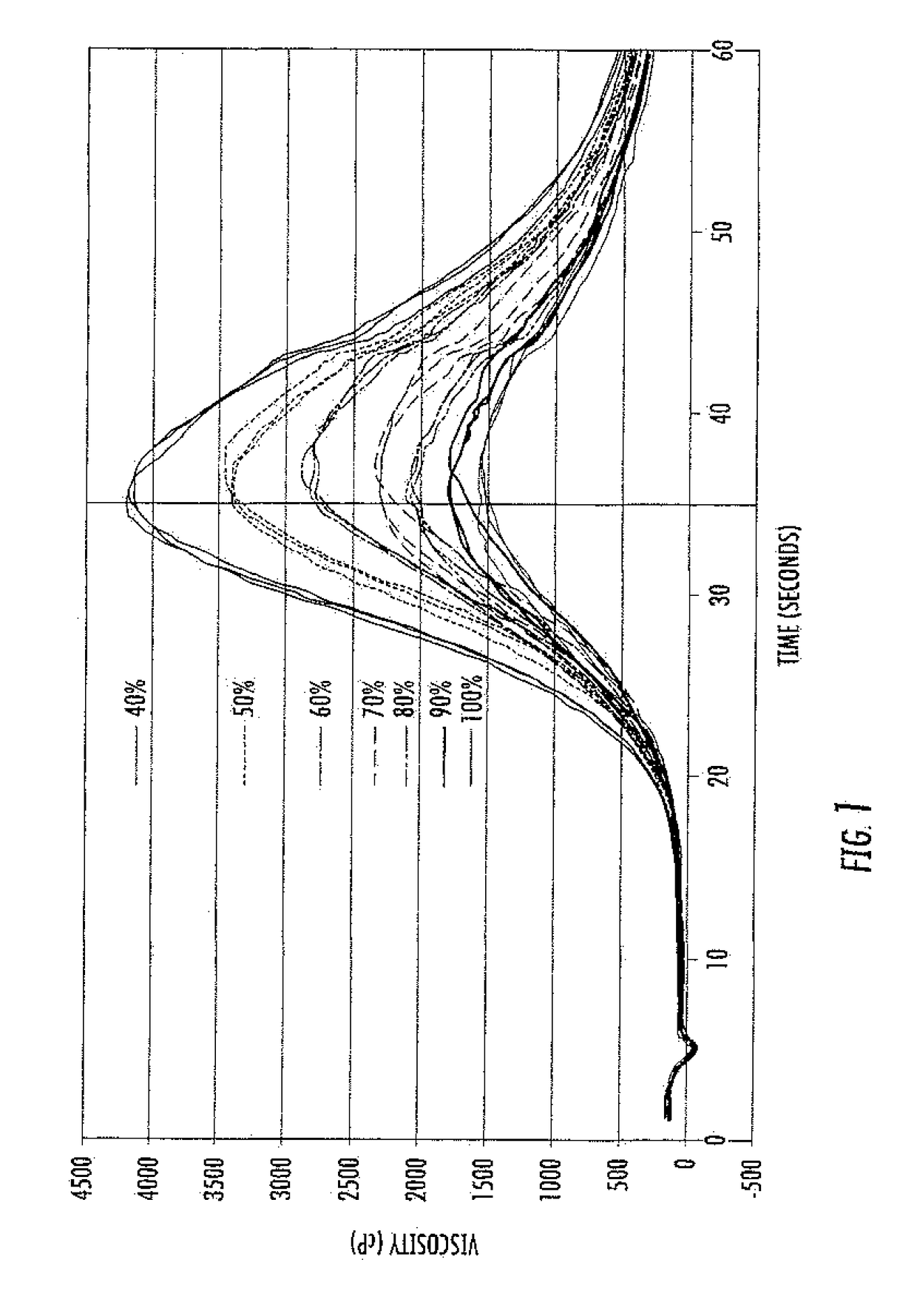
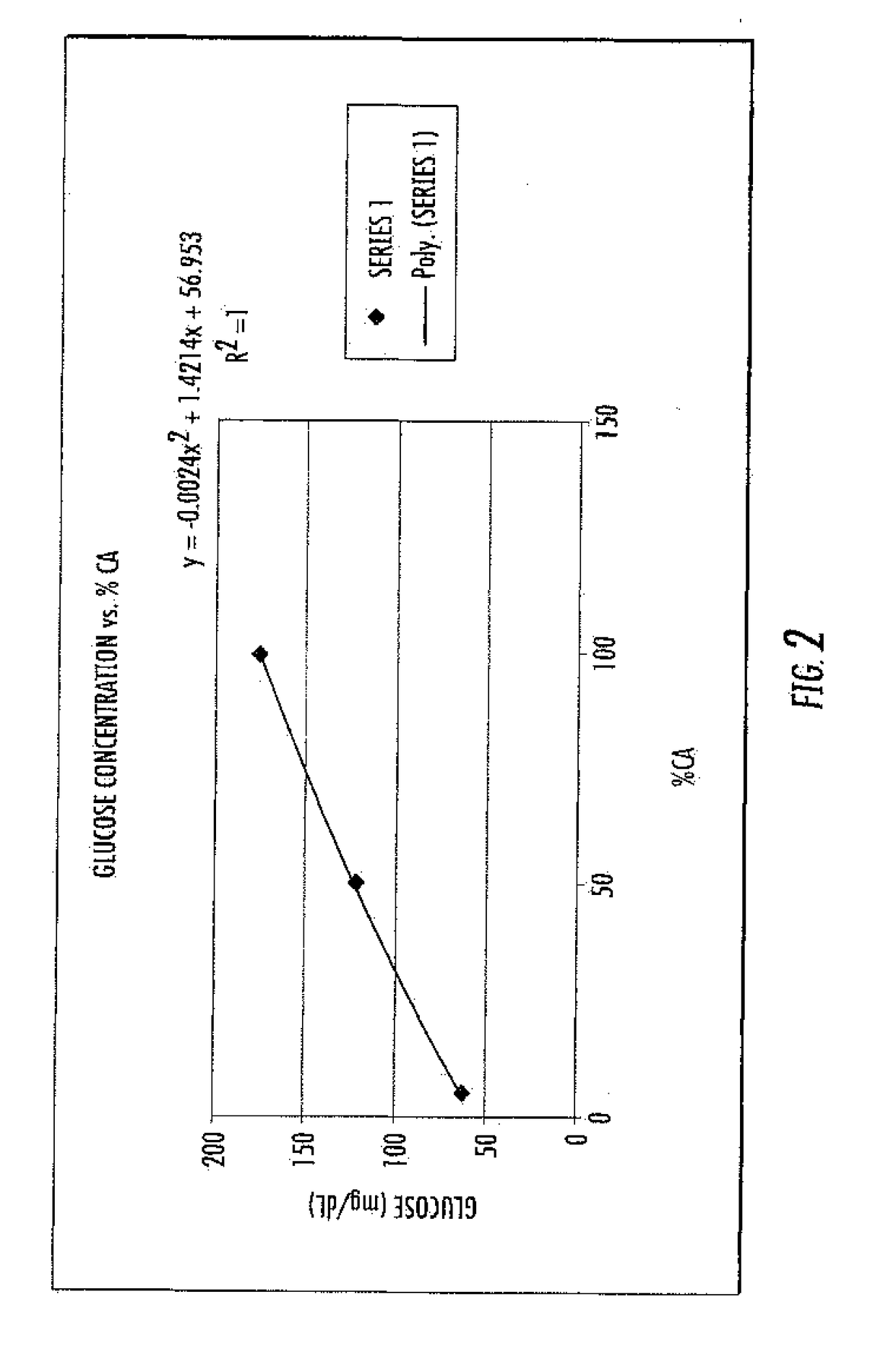
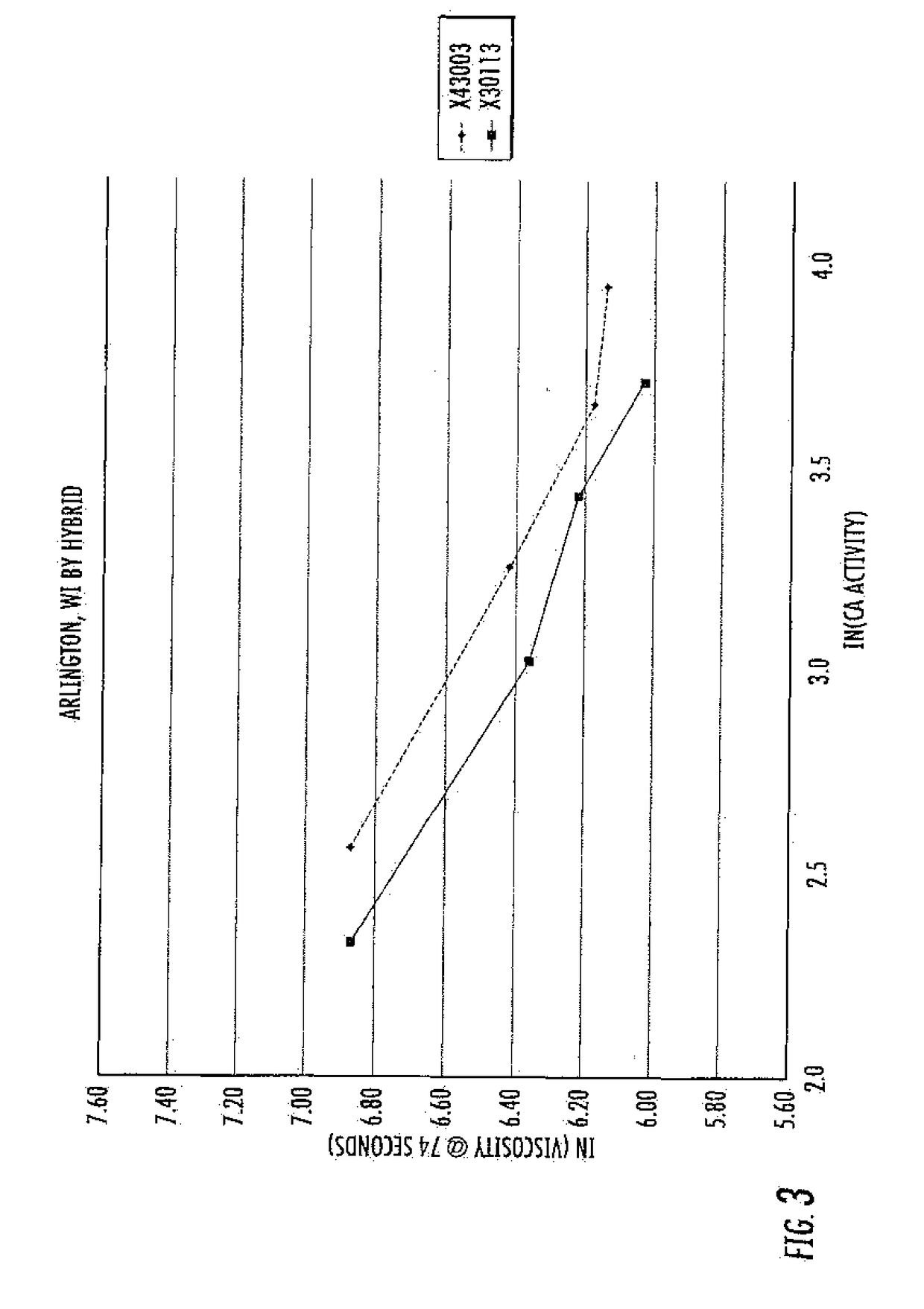
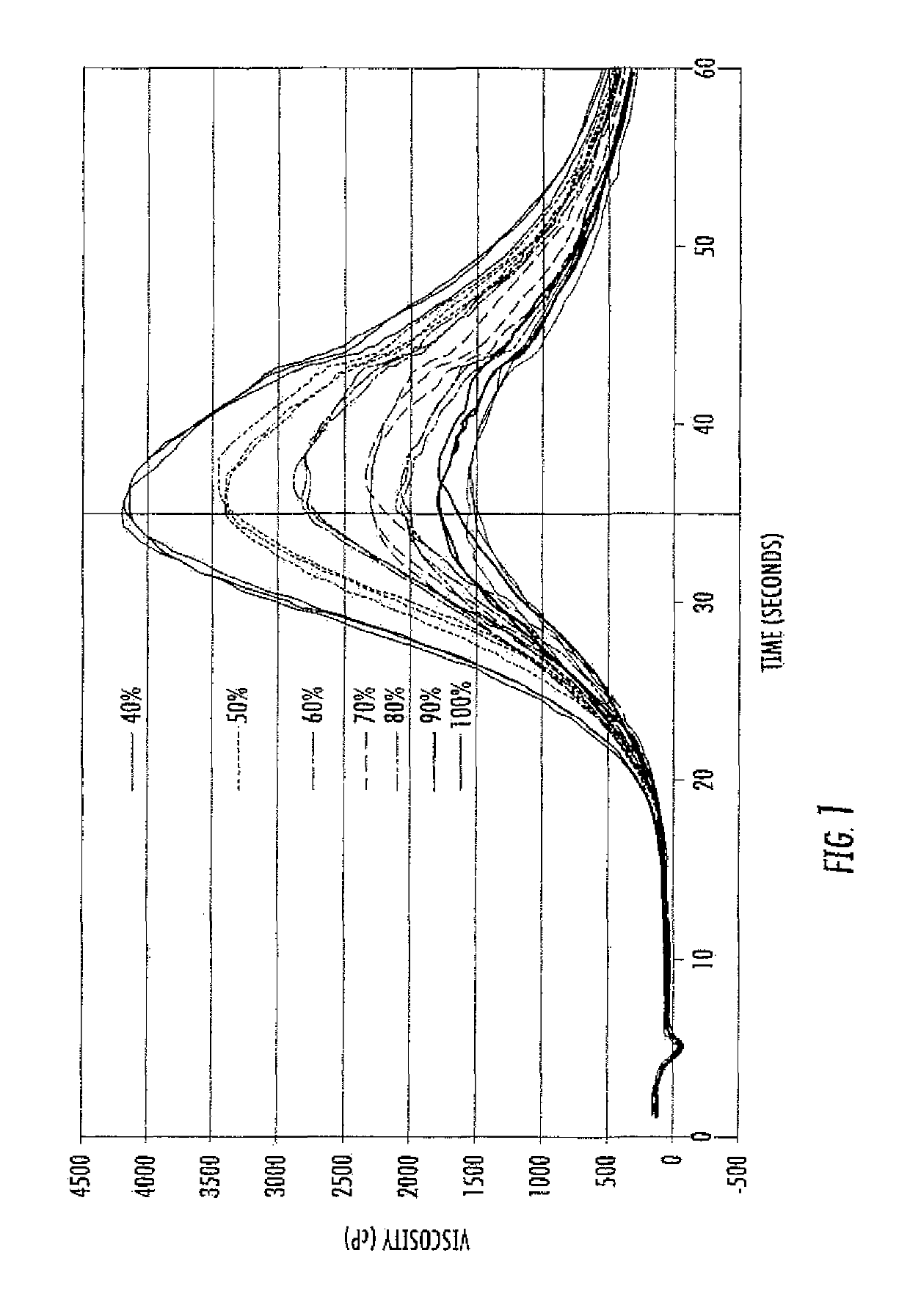
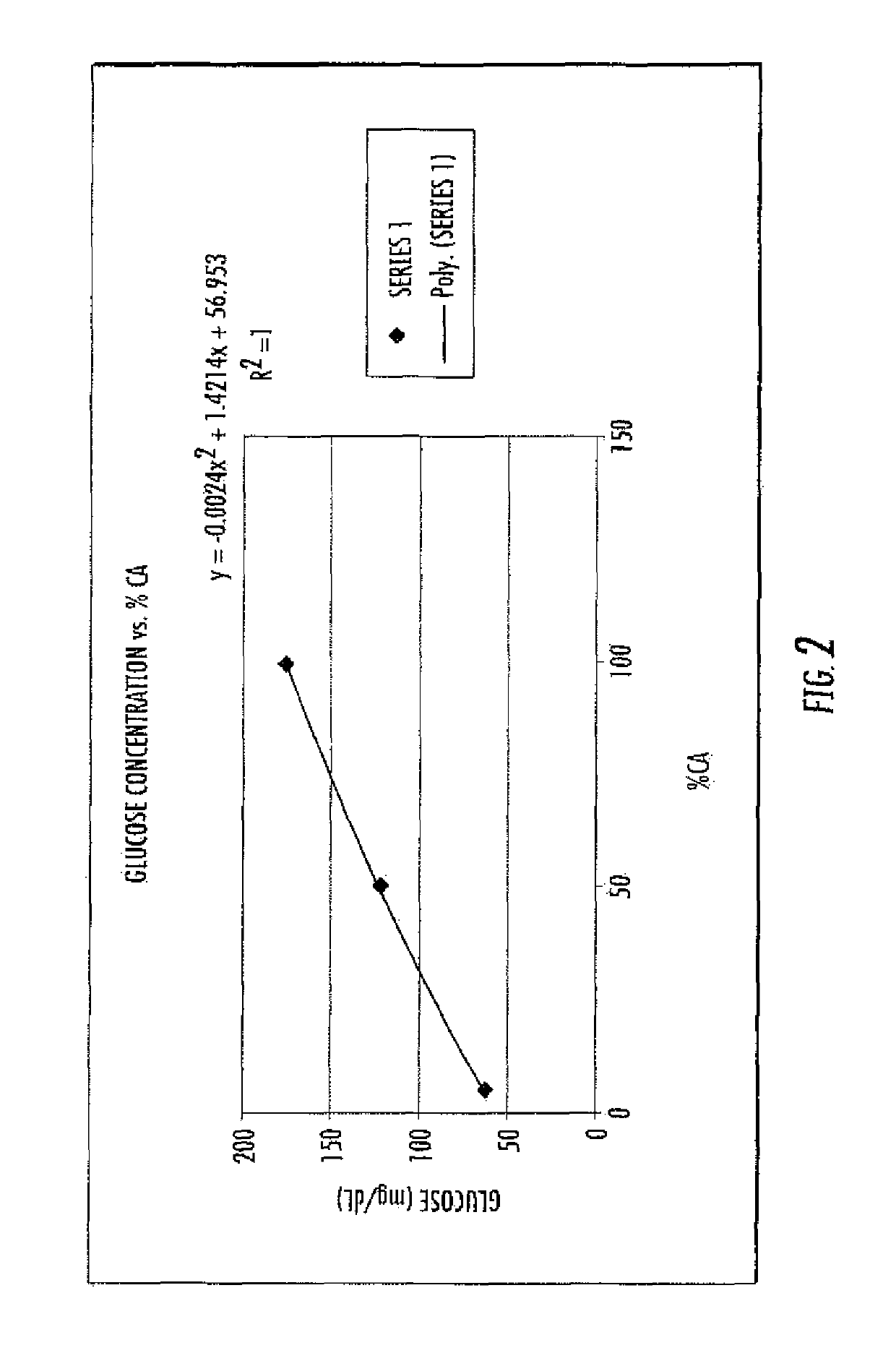
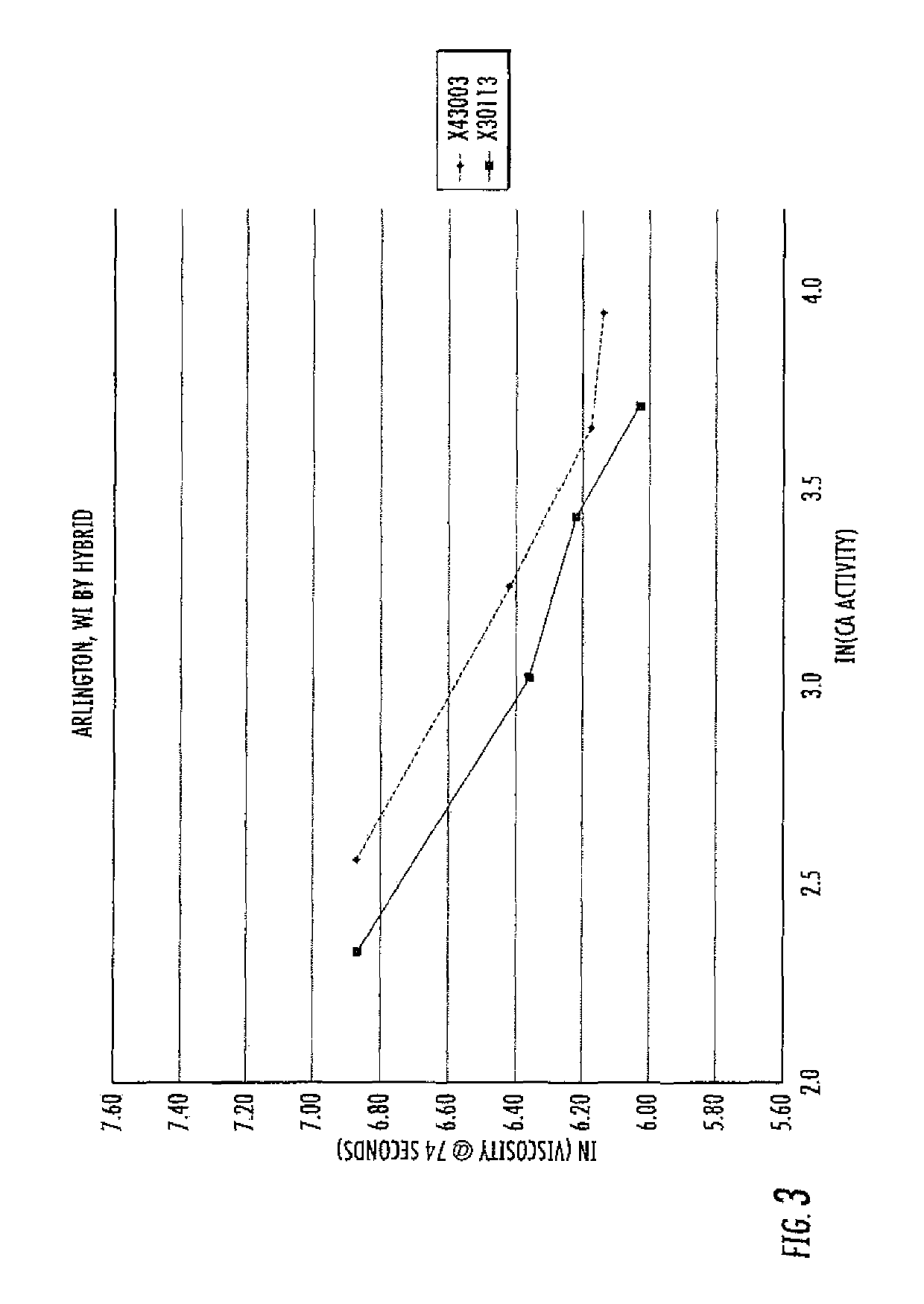
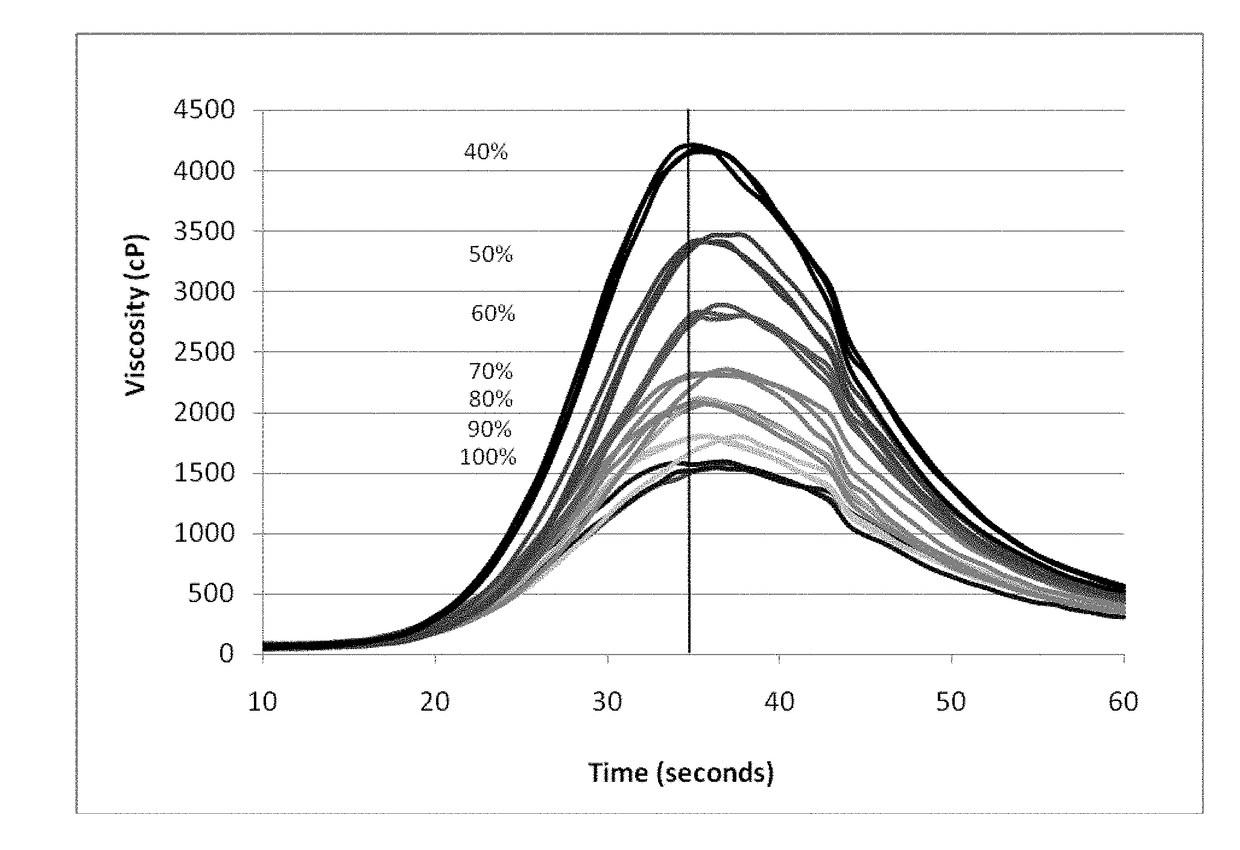
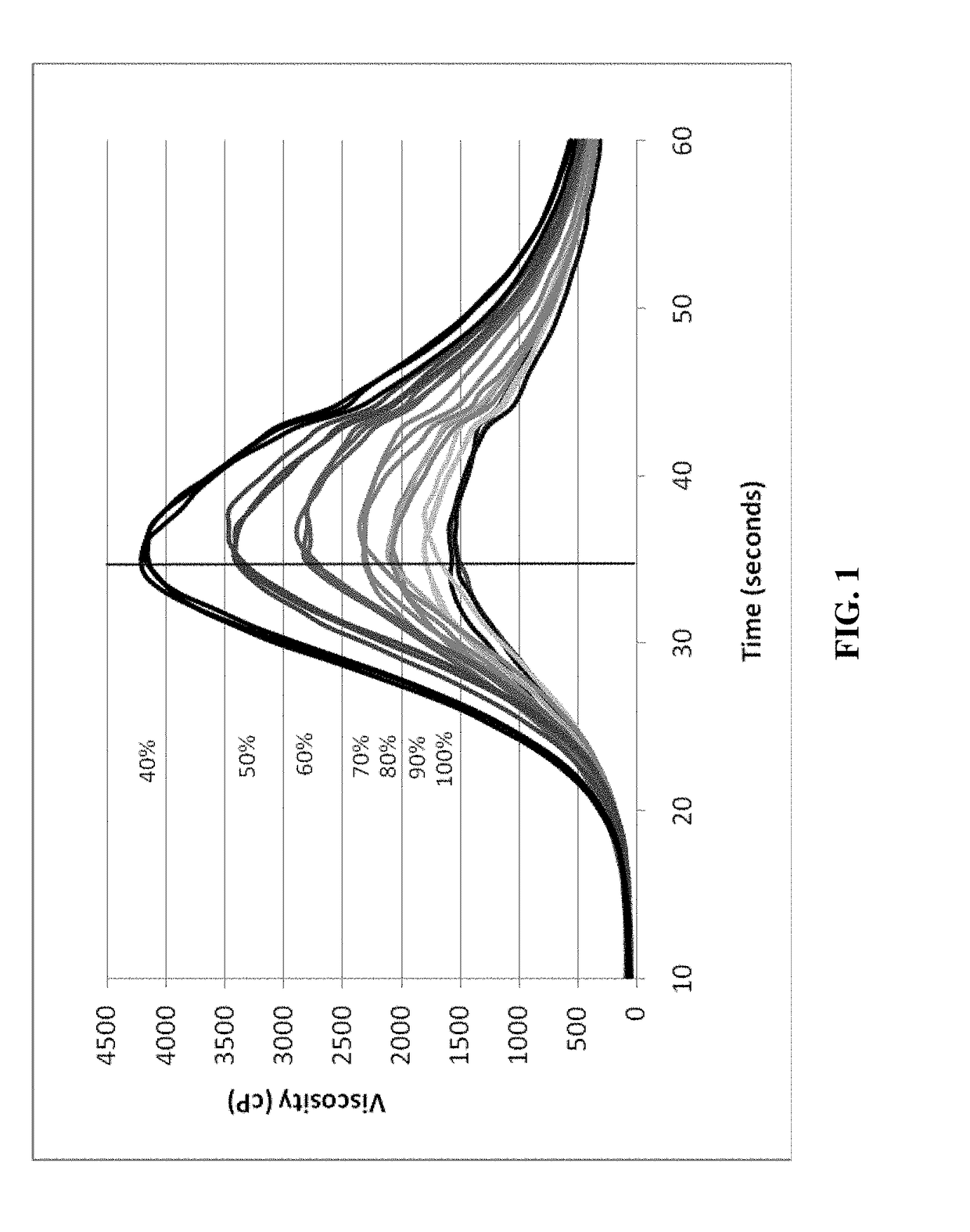
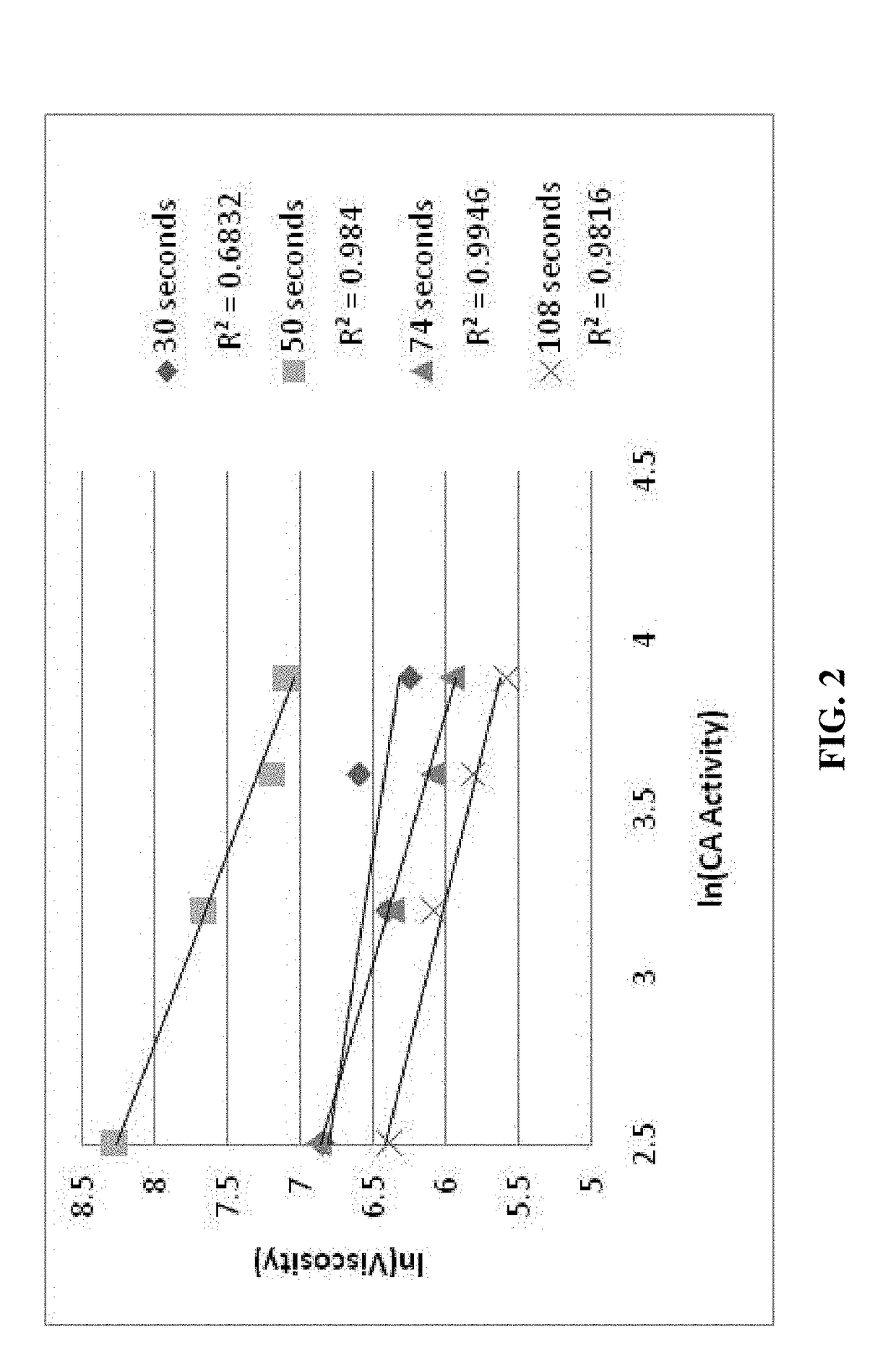
Methods are disclosed for distinguishing and identifying plants by measuring partial hydrolysis of polysaccharides on account of polysaccharide-hydrolyzing enzyme activity at pre-determined incubation times and temperatures. Methods also are disclosed for identifying the source organism of a heterologous polysaccharide-hydrolyzing enzyme in a plant by measuring partial hydrolysis of polysaccharides on account of polysaccharide-hydrolyzing enzyme activity at pre-determined incubation times and temperatures. The reaction mixture has unique chemical and physical properties that can be used to construct viscosity curves for measuring polysaccharide-hydrolyzing enzyme activity. The viscosity curves can be compared among plants to distinguish or identify the plants from one another. Likewise, viscosity curves can be compared among source organisms to identify the source organism of the heterologous polysaccharide-hydrolyzing enzyme in the plant.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Edible mushroom polysaccharide, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111718429AImprove in vitro antioxidantImprove anti-tumor activityOrganic active ingredientsAntinoxious agentsPolysaccharide HydrolaseEdible mushroom
The invention discloses edible mushroom polysaccharide, and a preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of food biology. The preparation method of the edible mushroom polysaccharide comprises the following steps: (1) pretreating edible mushrooms; (2) carrying out autolysis and enzymolysis on the edible mushrooms; (3) stopping autolysis of the edible mushrooms; and (4) extracting the edible mushroom polysaccharide to obtain crude edible mushroom polysaccharide. According to the preparation method of the edible mushroom polysaccharide, endogenous enzymes of edible mushrooms are fully used for enzymolysis of polysaccharide in the edible mushrooms, and polysaccharide hydrolase is used for degradation, so the in-vitro antioxidant activity and anti-tumor activity of the edible mushroom polysaccharide is improved.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
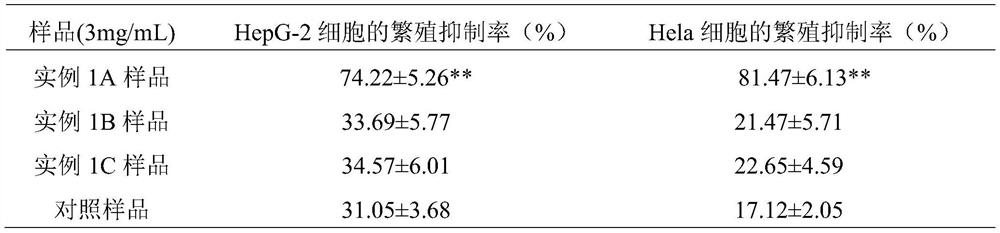
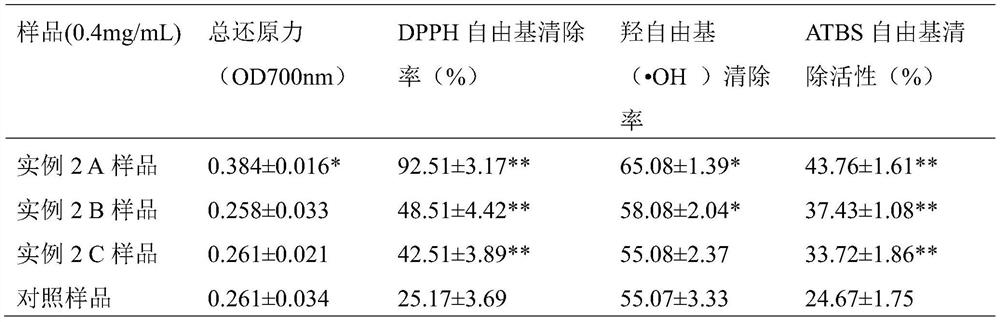
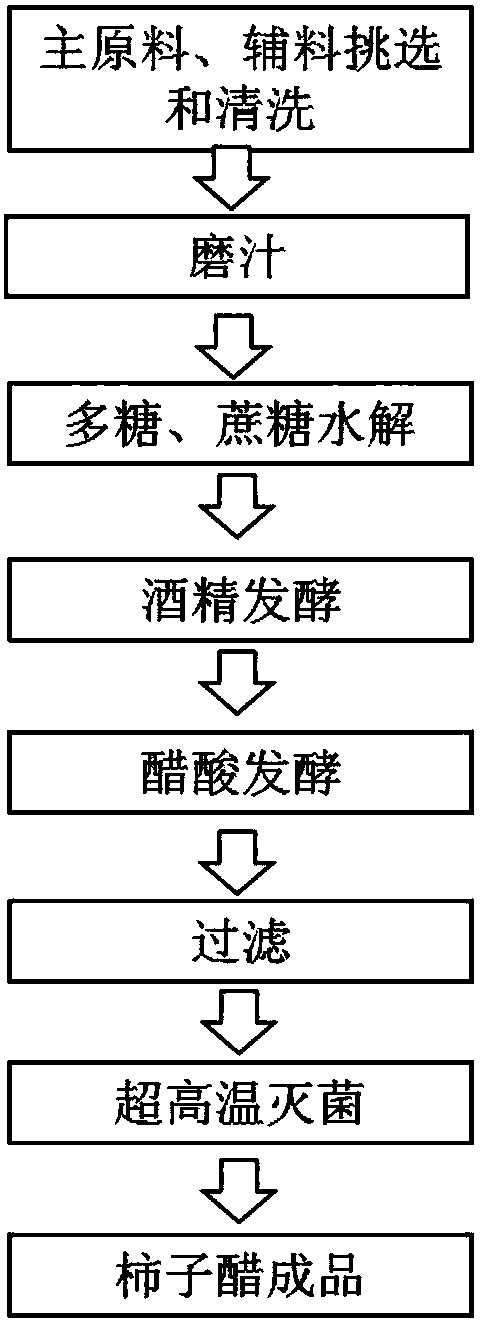
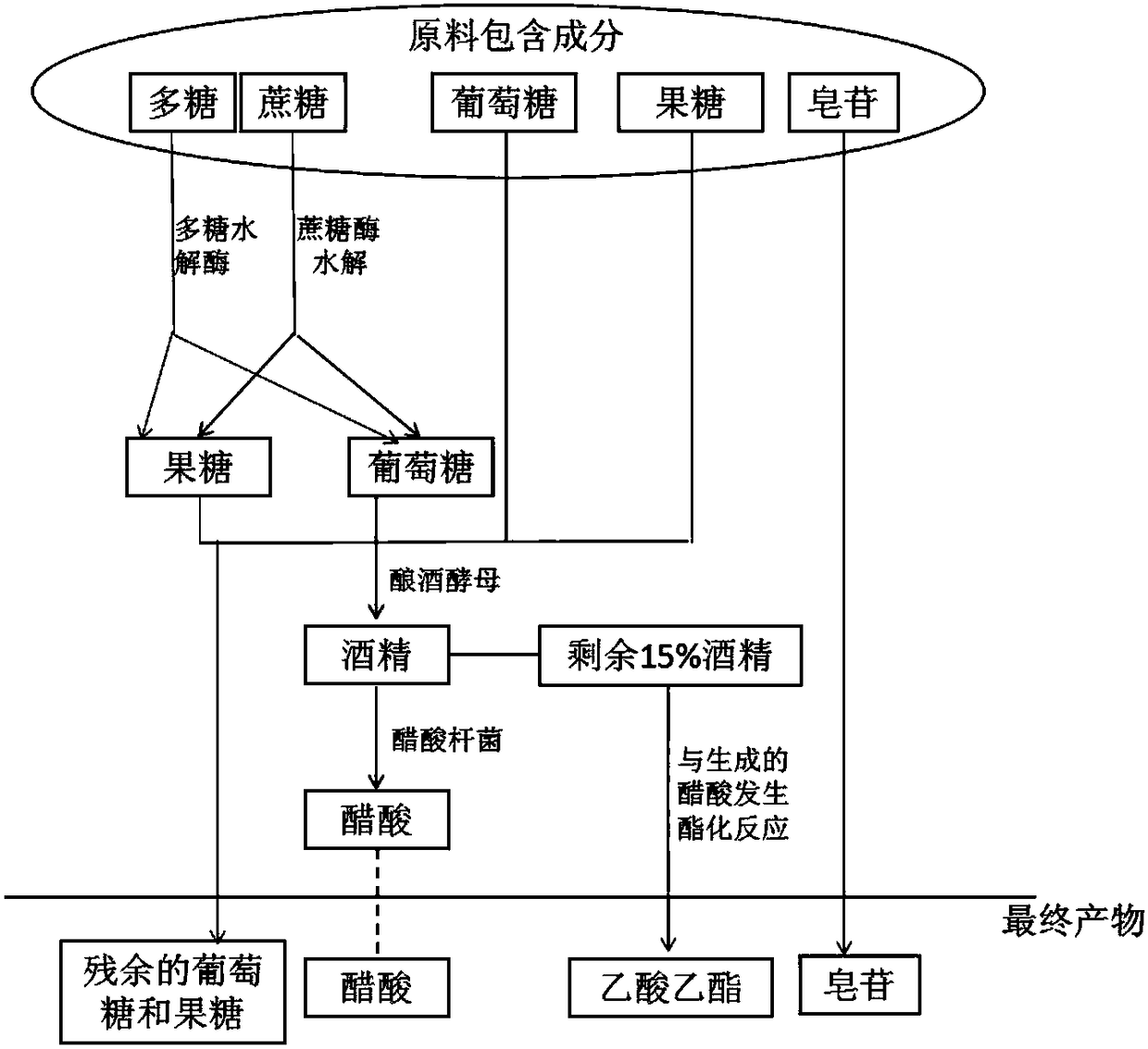
Novel persimmon vinegar capable of clearing lung-heat and preparation method thereof
PendingCN108277143AHas the function of clearing the lungsReduce lossesRespiratory disorderVinegar preparationPolysaccharide HydrolaseEthyl acetate
The invention provides a preparation method for novel persimmon vinegar capable of clearing lung-heat. The novel persimmon vinegar uses persimmons as a main raw material, and pears, oranges, Chinese yam rhizomes, carrots, radishes, pumpkins, lotus rhizomes, lily and loquat leaves as accessory materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps: washing all the raw materials, drying theraw materials in the air, putting the raw materials into an electric stone mill for grinding, adding polysaccharide hydrolase and sucrose accounting for 0.2 to 0.5% the amount of the obtained raw juice, adjusting a pH value to 4.5 to 5.0 with acetic acid, adjusting the temperature of a reaction solution 45 DEG C, maintaining the temperature and carrying out a stirring reaction for 72 h; adding Saccharomyces cerevisiae accounting for 0.01 to 0.03% the amount of a reaction solution, carrying out uniform mixing under stirring, and carrying out fermentation for 6 to 8 d with a temperature maintained at 25 to 30 DEG C so as to complete alcoholic fermentation; then adding 8 to 10% of Acetobacter, allowing the temperature of the reaction solution to be 28 to 35 DEG C and then carrying out aceticacid fermentation; in the late stage of acetic acid fermentation, adjusting the temperature of the reaction solution to 40 DEG C, maintaining the temperature for 6 h, and reacting acetic acid with unreacted alcohol to produce ethyl acetate; and then carrying out filtering, carrying out instant sterilization at 120 DEG C for 3 s, and then carrying out cooling to room temperature to obtain a finished persimmon vinegar product which mainly comprises 1 to 2% of sugar, 3.5 to 4% of acetic acid, 1 to 2% of ethyl acetate and 0.001 to 0.005% of saponin.
Owner:保定市柿柿红食品有限公司
Oxidation hydrolase gene BtLPMO10B and oxidation hydrolase and application
The present invention discloses an oxidation hydrolase gene and preparation and application of an oxidization hydrolase encoded by the oxidation hydrolase gene. The oxidation hydrolase BtLPMO10B gene is derived from bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki (ACCC 10066). The present invention also provides a method for preparation of the oxidization hydrolase BtLPMO10B, to be more specific, by use of a technical method of genetic engineering, the oxidation hydrolase BtLPMO10B gene is cloned to an Escherichia coli expression vector to obtain an escherichia coli recombinant strain capable of expressing the oxidation hydrolase, and the oxidation hydrolase BtLPMO10B prepared by the engineered strain expression has a strong ability to bind insoluble chitin, and is capable of oxidative hydrolysis of a polysaccharide substance to obtain saccharic acids having different degrees of polymerization. The oxidation hydrolase BtLPMO10B may assist polysaccharide hydrolase and can improve the efficiency of hydrolysis of polysaccharides.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bacteriostatic mouthwash
InactiveCN109125154AInhibition formationPromote healingCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSodium acetatePolysaccharide Hydrolase
The invention discloses a bacteriostatic mouthwash. The bacteriostatic mouthwash comprises, by weight, 3-5 parts of bacterial film polysaccharide hydrolase, 12-25 parts of chamomile extract, 10-18 parts of radix angelicae extract, 5-13 parts of paeonia tacti lora extract, 5-7 parts of honeysuckle extract, 3-6 parts of lemon extract, 0.1-0.3 part of sodium fluoride, 80-100 parts of deionized water,10-19 parts of sorbitol, 0.5-1 part of boric acid, 3-7 parts of xylosic alcohol, 2-10 parts of polyethyleneglycol, 1-5 parts of essence, 12-24 parts of ethanol, 5-14 parts of sodium acetate, 10-16 parts of glycerol, 0.2-0.6 part of lauryl sodium sulfate and 1-2 parts of methyl-p-hydroxybenzoate. By means of the bacteriostatic mouthwash, oral cavity odor can be effectively removed, sterilization and bacteria resisting can be achieved to inhibit the forming of bacterial plaque, and healing of oral cavity ulcer can be effectively promoted.
Owner:HAIMEN BIWEI INTPROP SERVICE CO LTD
Kidney invigorating product and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105920196ASignificant effect of nourishing the kidneyReduce dosageFood hydrolysisUnknown materialsCelluloseSide effect
The invention relates to the field of kidney invigorating products, in particular to a kidney invigorating product and a preparation method thereof. The kidney invigorating product is mainly prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 0.5-1.5 parts of Lepidinm meyenii Walp, 0.2-0.4 part of Herba Cistanches, 0.5-1.5 parts of Fructus Lycii and 0.1-0.3 part of Cornu Cervi Pantotrichum. The preparation method of the kidney invigorating product provided by the invention comprises the following steps: pulverizing the various raw materials; and then respectively carrying out enzymolysis by using cellulose, proteolytic enzyme and polysaccharide hydrolase successively. Through step-by-step enzymolysis, the content of active ingredients in the obtained product is high, and when eating the kidney invigorating product, a person absorbs the product well. The dosage of the prepared kidney invigorating product is smaller than the conventional dosage. The kidney invigorating product has the features of good curative effect, small side effects, avoidance of suffering from excessive internal heat and the like. In addition, the whole preparation method is simple and convenient, does not contain harmful reagents, and is safe to eat.
Owner:北京解脂生物科技有限公司
Eextracellular-polysaccharide-hydrolase-based engineering bacteria and implementation method thereof
The invention discloses extracellular-polysaccharide-hydrolase-based engineering bacteria and an implementation method thereof in the technical field of biological engineering. A polysaccharide hydrolase gene is cloned from streptomyces griseus JSD-1; the streptomyces griseus JSD-1 is connected to an expression vector to obtain a recombinant expression vector; the recombinant expression vector is further introduced into escherichia coli and induced to synthesize polysaccharide hydrolase. According to the extracellular-polysaccharide-hydrolase-based engineering bacteria, the defects of low expression quantity and the like caused by inducible expression of most of polysaccharide hydrolases in the prior art are overcome, the polysaccharide hydrolase is prepared by using the polysaccharide hydrolase gene expressed by genetic engineering bacteria, and a new method for producing the polysaccharide hydrolase can be provided by virtue of industrial fermentation.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Application and method of pslg protein or its coding sequence in detecting the number of microorganisms
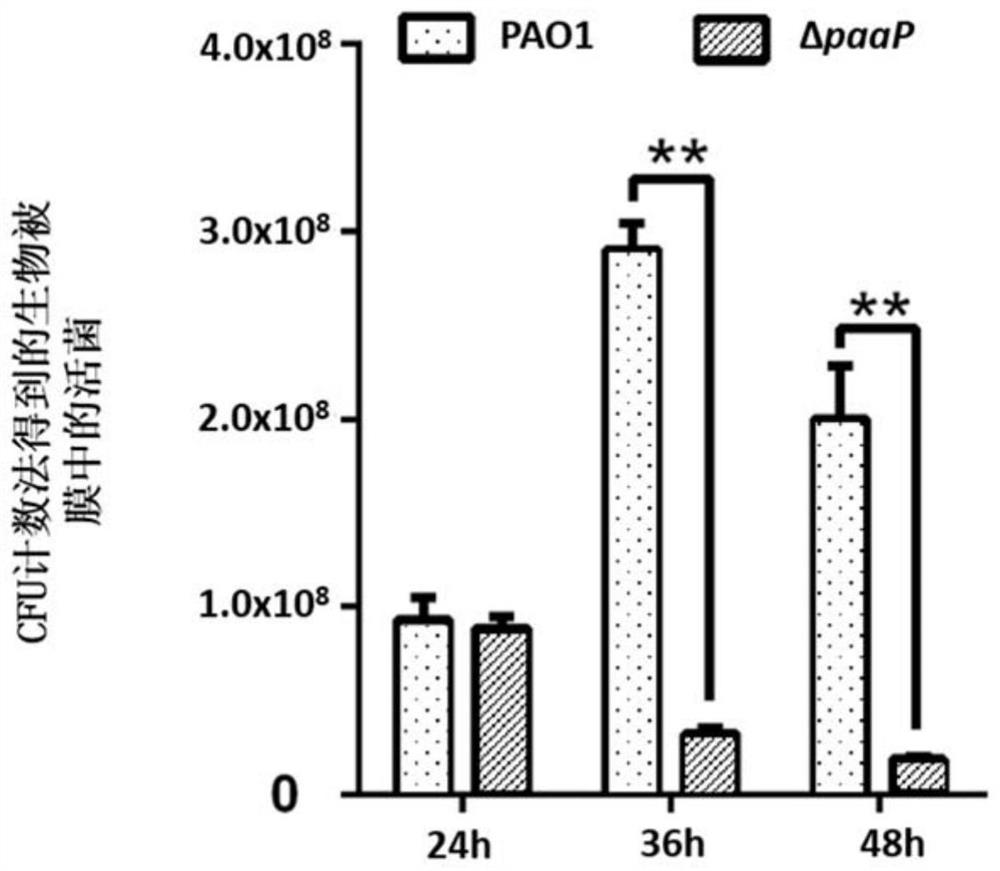
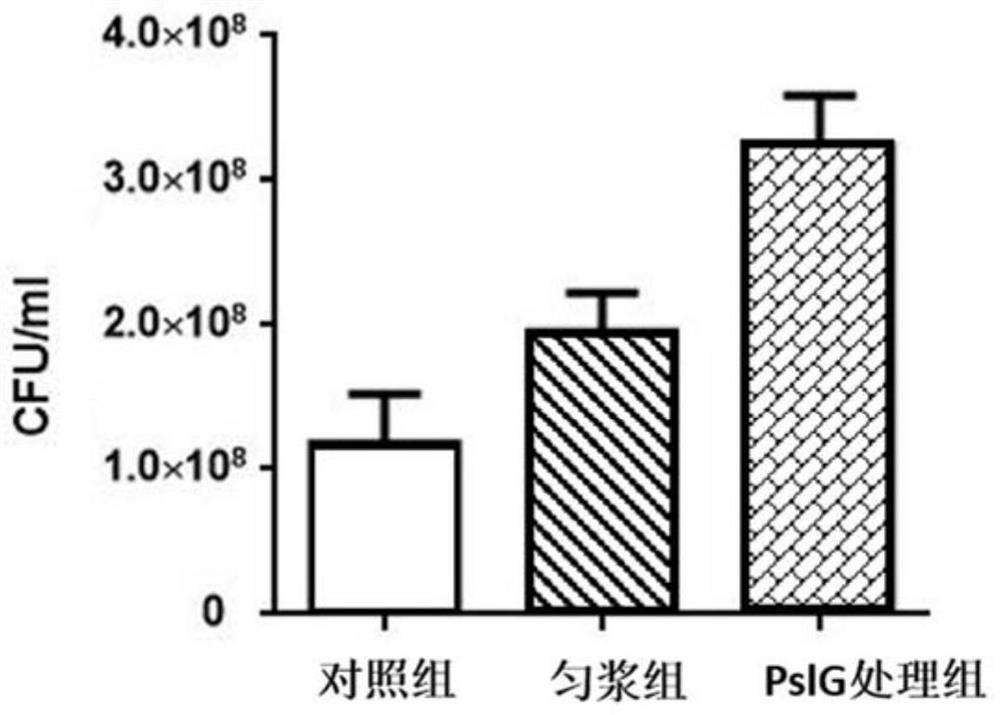
ActiveCN108660123BAccurate measurementHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyPolysaccharide Hydrolase
The invention discloses an application and method of PslG protein or coding sequence of PslG protein in detecting microbial quantity, specifically, the invention provides extracellular polymeric substances degrading enzyme, particularly the application and method of polysaccharide hydrolytic enzyme Ps1G in detecting the microbial quantity of biofilms or bacteria solution containing cenobium. The method includes the steps that a composition is used for inhibiting, dispersing, or disintegrating the biofilms or the cenobium formed by microorganisms, thereby detecting the number of the microorganisms. The composition comprises the PslG protein. The invention also provides amino acid sequence and the coding gene sequence of the PslG protein.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
A kind of mushroom edible fungus polysaccharide and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN111718429BImprove in vitro antioxidantImprove anti-tumor activityOrganic active ingredientsAntinoxious agentsPolysaccharide HydrolaseMicrobiology
The invention discloses a mushroom edible fungus polysaccharide and a preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the field of food biotechnology. The preparation method of the edible mushroom polysaccharide comprises the following steps: (1) pretreatment of the edible mushroom; (2) autolysis and enzymolysis of the edible mushroom; (3) stopping the autolysis of the edible mushroom; (4) Extraction of mushroom edible fungus polysaccharide to obtain mushroom edible fungus crude polysaccharide. The preparation method of the edible mushroom polysaccharide of the present invention makes full use of the endogenous enzyme of the edible mushroom to enzymolyze the polysaccharide in the edible mushroom, and is supplemented by polysaccharide hydrolase for degradation, so as to improve the in vitro performance of the edible mushroom polysaccharide. Antioxidant and antitumor activity.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Application of polysaccharide lyase coding gene 04147 in preparation of recombinant peach gum polysaccharide hydrolase
ActiveCN113088505AStrong cracking activityHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPolysaccharide Hydrolase
The invention discloses application of a polysaccharide lyase coding gene 04147 in preparation of recombinant peach gum polysaccharide hydrolase. According to the invention, the optimized polysaccharide lyase coding gene as shown in SEQ ID No. 3 is connected to an expression vector pET28a with a 6*His tag, and is transformed to escherichia coli to obtain a recombinant expression strain; then the recombinant expression strain is subjected to IPTG-induced expression of a recombinant protein; and then nickel affinity chromatography purification is performed to obtain the recombinant peach gum polysaccharide hydrolase and a single enzyme. The recombinant peach gum polysaccharide hydrolase has good peach gum cracking activity, can be used for preparing hydrolase of low-molecular-weight and small-molecular-weight peach gum, and has relatively great application prospects.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Application of arabinogalactosidase coding gene 00578 in preparation of recombinant peach gum polysaccharide hydrolase
PendingCN114134161AGood degradation activityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPolysaccharide HydrolaseHydrolase
The invention discloses an application of an arabinogalactosidase coding gene 00578 in preparation of recombinant peach gum polysaccharide hydrolase, which is characterized in that the arabinogalactosidase coding gene shown as SEQ ID NO: 1 is connected to an expression vector pET22b (+) with a 6 * His tag, and is converted to escherichia coli to obtain recombinant expression bacteria; the method comprises the following steps: preparing a recombinant peach gum polysaccharide hydrolase, performing IPTG (isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactoside) induced expression on the recombinant expression bacteria to obtain a recombinant protein, and performing nickel affinity chromatography purification to obtain the recombinant peach gum polysaccharide hydrolase which has good peach gum splitting decomposition activity and arabinogalactan and galactan hydrolysis activity. The peach gum polysaccharide hydrolase can be used for preparing peach gum polysaccharide hydrolase and polysaccharide hydrolase containing arabinogalactan and galactan, and has a great application prospect.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Methods for distinguishing and identifying plant varieties
ActiveUS10344316B2Rapid and reliable assayMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymesHeterologousPartial hydrolysis
Methods are disclosed for distinguishing and identifying plants by measuring partial hydrolysis of polysaccharides on account of polysaccharide-hydrolyzing enzyme activity at pre-determined incubation times and temperatures. Methods also are disclosed for identifying the source organism of a heterologous polysaccharide-hydrolyzing enzyme in a plant by measuring partial hydrolysis of polysaccharides on account of polysaccharide-hydrolyzing enzyme activity at pre-determined incubation times and temperatures. The reaction mixture has unique chemical and physical properties that can be used to construct viscosity curves for measuring polysaccharide-hydrolyzing enzyme activity. The viscosity curves can be compared among plants to distinguish or identify the plants from one another. Likewise, viscosity curves can be compared among source organisms to identify the source organism of the heterologous polysaccharide-hydrolyzing enzyme in the plant.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Methods for detecting and measuring polysaccharide-hydrolyzing enzymes
ActiveUS20170275668A1Rapid and reliable assayMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPartial hydrolysisPolysaccharide Hydrolase
Methods are disclosed for detecting and measuring polysaccharide-hydrolyzing enzyme activity or concentration by partial hydrolysis using a pre-determined, yet short, incubation time and a pre-determined temperature. The resulting reaction mixture has unique chemical (i.e., reaction products) and physical (i.e., viscosity) properties that can be used to detect or measure the polysaccharide-hydrolyzing enzyme activity or concentration.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
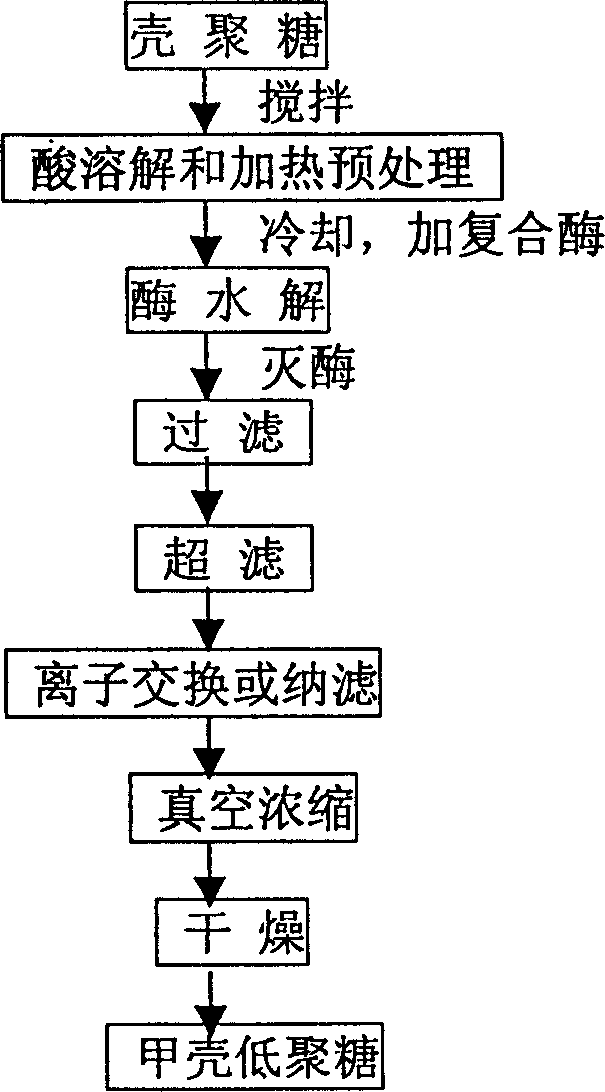
Preparation of crust oligosaccharide and use
The present invention relates to preparation and application of crust oligosaccharide and belongs to the field of deep chitin processing technology. Non-specific enzyme is used to raise the hydrolysis degree of chitosan and the separation and purification of hydrolytic product. The key point of the present invention is that the chitosan material is produced into crust oligosaccharide powder through acid dissolving, heating, enzymolysis and hydrolysis with compoiste, enzyme comprising polysaccharide hydrolase, proteinase and lipase, deactivating enzyme, filtering, ultrafiltering, ion exchange or nanometer filtering, vacuum concentration and drying. The product is used in producing various functional health foods with the functions of immunological regulation and blood fat regulation.
Owner:上海华宝孔雀香精有限公司
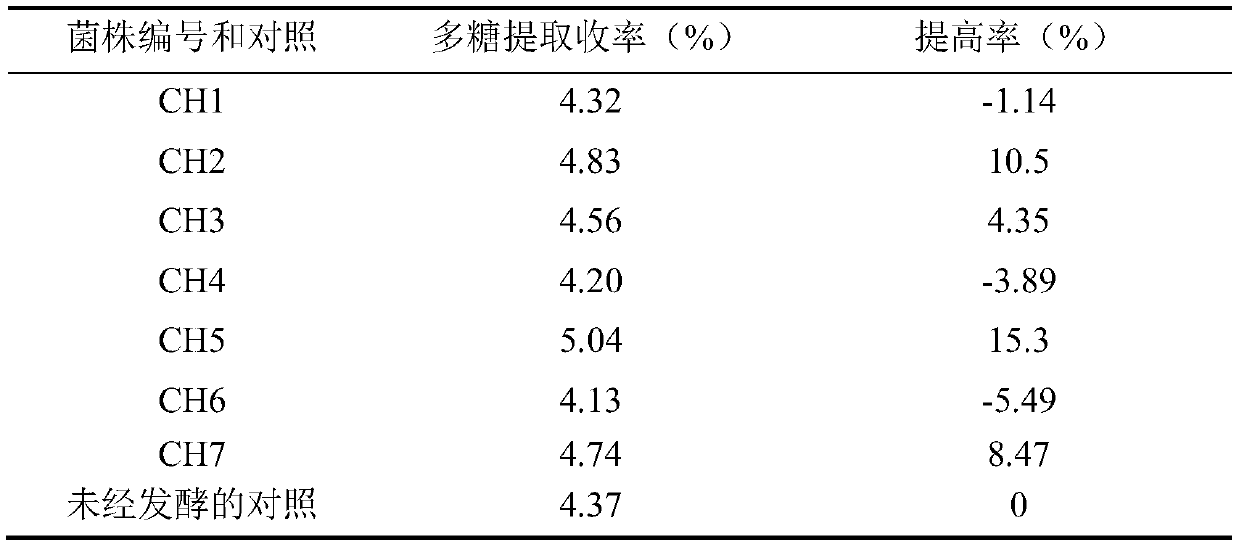
Rhizopus oryzae CH5 and application thereof in extracting ganoderma sinensis polysaccharide
ActiveCN111334440AHigh extraction yieldIncrease fermentation pretreatmentFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismSpore
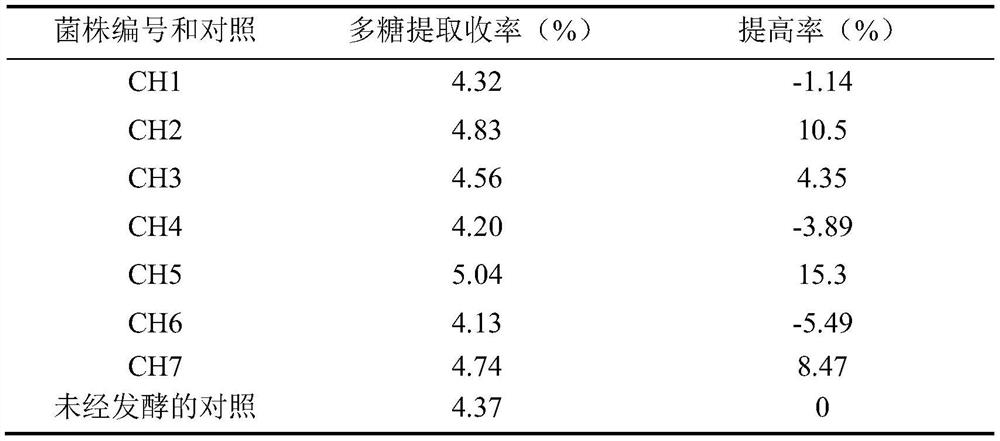
The invention discloses rhizopus oryzae CH5 and application thereof in extracting ganoderma sinensis polysaccharide. The application method comprises the following steps of: inoculating rhizopus oryzae CH5 spores into ganoderma sinensis powder containing sterile water, fermenting at 28-30 DEG C for 2-3 days, and drying the fermented product to obtain fermented ganoderma sinensis powder; decolorizing the fermented ganoderma sinensis powder to obtain decolorized ganoderma sinensis powder; performing water extraction and concentration on the decolorized ganoderma sinensis powder to obtain a concentrated solution; and performing alcohol precipitation and vacuum drying on the concentrated solution to obtain ganoderma sinensis crude polysaccharide. The rhizopus oryzae CH5 is separated from a microbial enrichment culture of ganoderma sinensis, and a screened excellent strain moderately grows in the ganoderma sinensis powder to generate polysaccharide hydrolase, so that hydrolysis of insolublepolysaccharide structural tissues of ganoderma sinensis is realized, dissociation of combined soluble polysaccharide is promoted, and the extraction yield of ganoderma sinensis polysaccharide is remarkably increased. Under the optimal process conditions, the extraction yield of ganoderma sinensis polysaccharide is 5.92 percent, which is increased by over 35 percent compared with that of an unfermented extraction method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHUREN COLLEGE ZHEJIANG SHUREN UNIV
A method for extracting polysaccharides from mulberry leaves by microbial fermentation
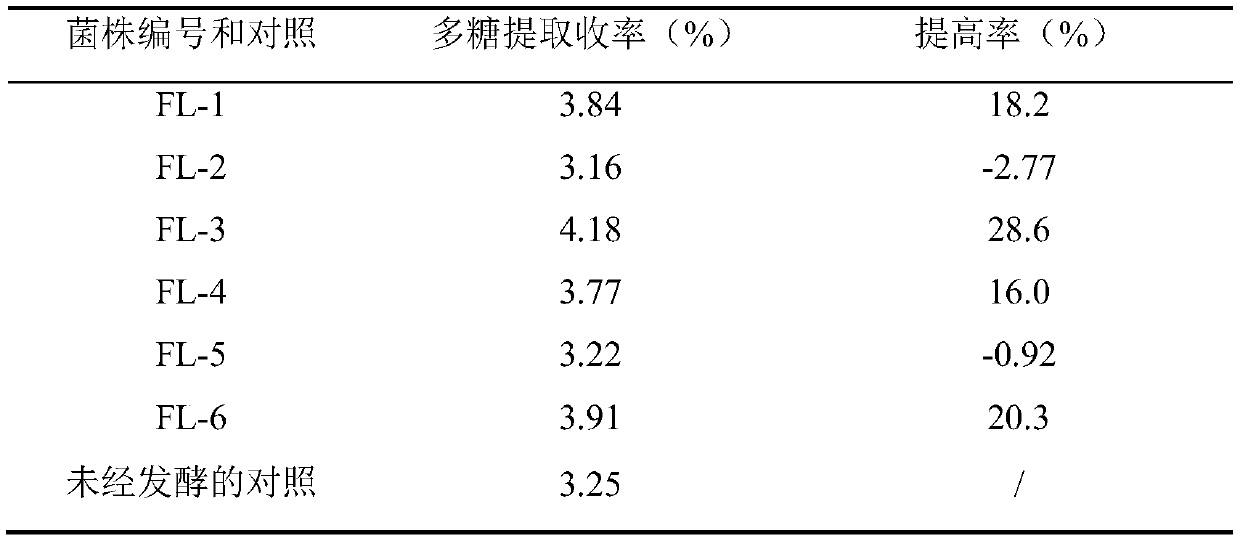
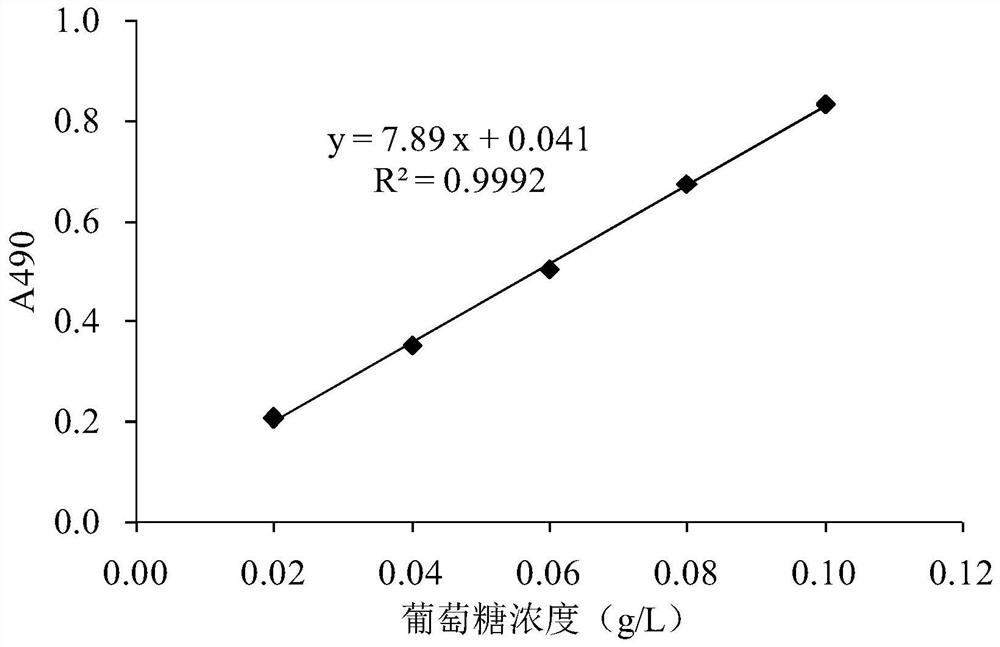
ActiveCN112481134BHigh extraction yieldPromote hydrolysisFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismSpore
The invention discloses a method for extracting polysaccharides from mulberry leaves by microbial fermentation. The method is as follows: add sterile saline to mulberry leaf powder, inoculate the spores of Mucor racemosus SY5-47, and inoculate 28- Fermentation at 30°C for 3–4 days, the fermented product was concentrated by ultrasonic water extraction to obtain a concentrate; the concentrate was subjected to alcohol precipitation and vacuum drying to obtain mulberry leaf crude polysaccharide; in advance of mulberry leaf polysaccharide ultrasonic water, Mucor racemosa was added Fermentation pretreatment of SY5‑47. Mucor racemosa SY5‑47 grows moderately in mulberry leaf powder, produces a variety of polysaccharide hydrolytic enzymes, hydrolyzes the cell wall of mulberry leaves, loosens the structure of mulberry leaves, and promotes the dissociation of bound soluble polysaccharides. Easier to dissolve when lifted. Compared with the ultrasonic water extraction method without fermentation pretreatment, the extraction yield of the mulberry leaf polysaccharide can be increased by more than 35%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
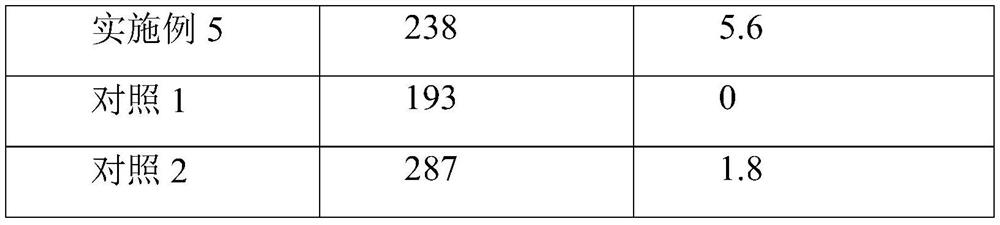
Apricot kernel oil scald ointment as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN114504636AImprove permeabilityPromote absorptionOrganic active ingredientsHydrolysed protein ingredientsPolysaccharide HydrolaseSubcutaneous tissue
The invention belongs to the technical field of scald ointment, and discloses almond oil scald ointment as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: 1) reacting almonds with protease, and centrifuging to obtain supernatant which is sweet almond oil; filtering and drying the subnatant to obtain the almond polypeptide; (2) reacting the apricot pulp with polysaccharide hydrolase to obtain apricot oligosaccharide; (3) reacting the almond oil with lipase, adding a water-insoluble organic solvent and apricot oligosaccharide, and continuously reacting to obtain an almond oil and apricot oligosaccharide conjugate; (4) respectively preparing the almond polypeptide and the almond oil and oligosaccharide conjugate into dispersion liquid; under the stirring condition, the almond polypeptide dispersion liquid and the almond oil and oligosaccharide conjugate dispersion liquid are mixed and filtered through a filter membrane, and the almond oil scald ointment is obtained. The scald ointment disclosed by the invention can prevent infection and regulate metabolism balance of fat, sugar and protein of subcutaneous tissues, so that formation of scars is reduced while wound healing is promoted. The scald ointment is used for preparing medicines for preventing and treating scalds and repairing scars.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com