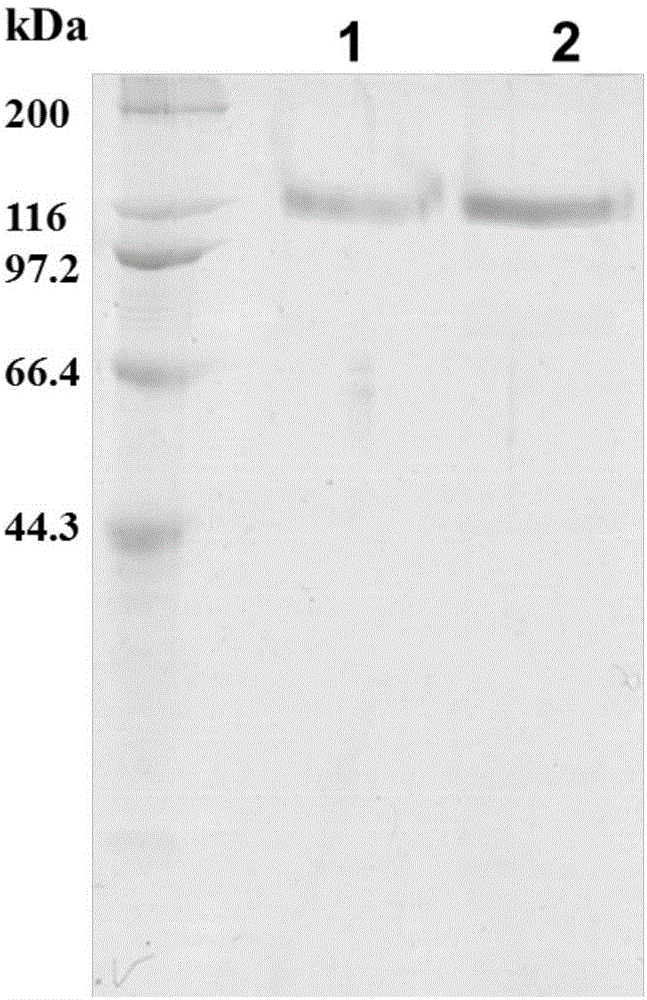
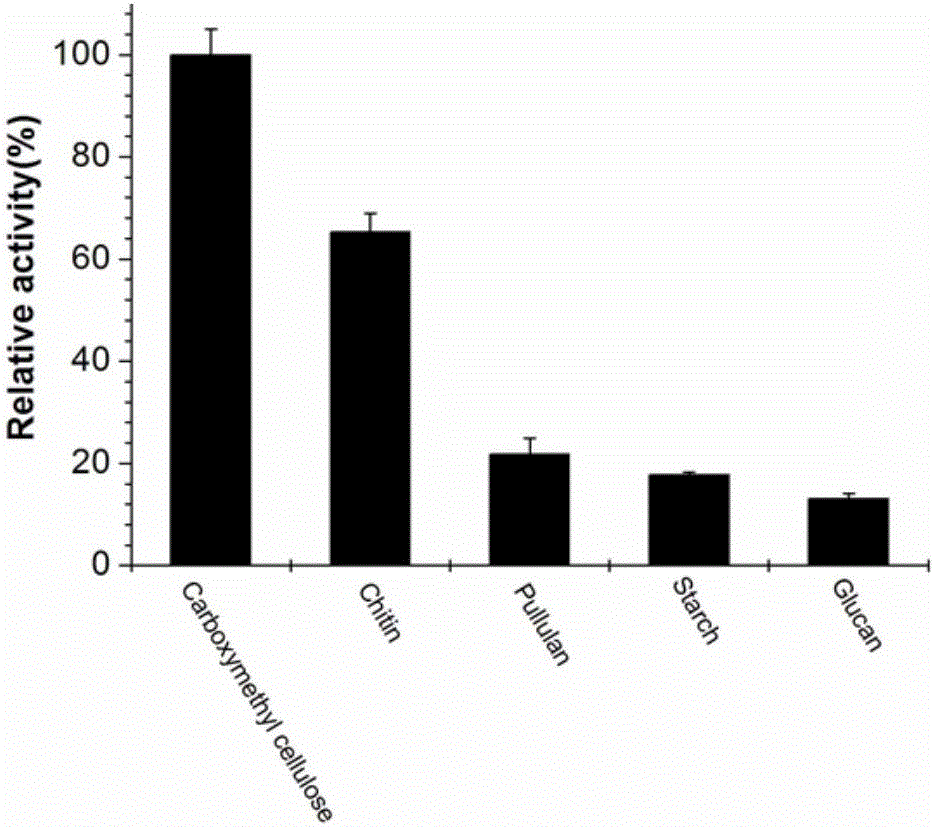
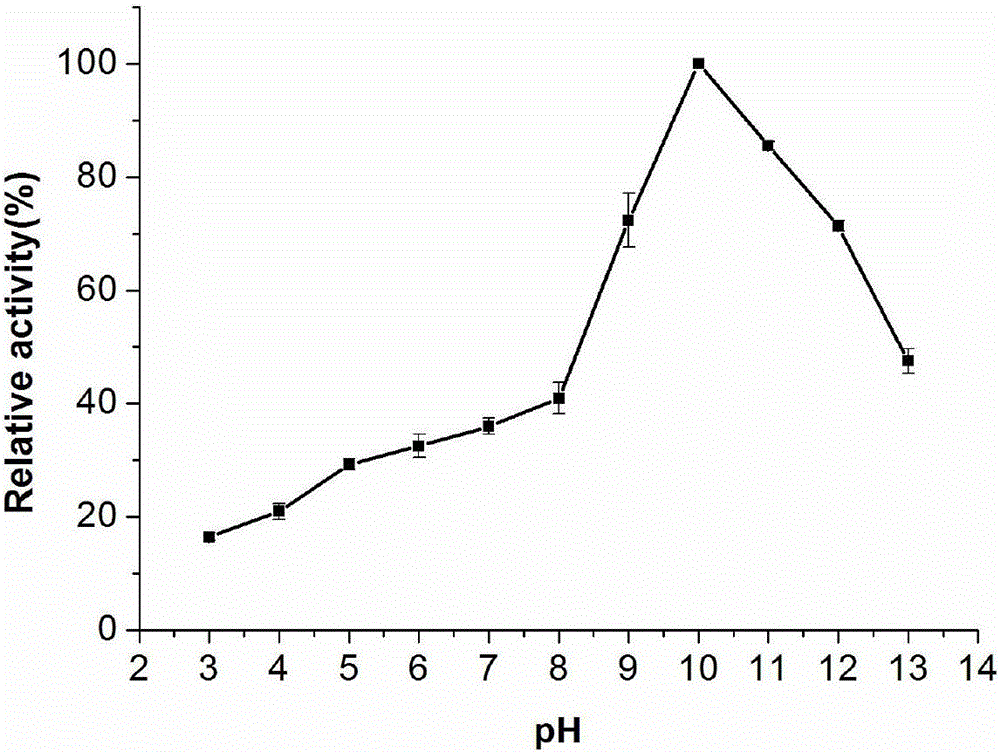
Polysaccharide hydrolase gene from pyrococcus horikoshii and application
A hydrolytic enzyme and gene technology, applied in the field of bioengineering and enzyme engineering, can solve the problems of refractory degradation and low efficiency, and achieve the effect of wide application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Example 1: Genomic DNA extraction of the extreme thermophilic anaerobic archaea T.kodakarensis KOD1
[0021] Cultivate an appropriate amount of thermophilic archaea T.kodakarensisKOD1, collect the bacteria by centrifugation at 4000rpm for 10 minutes, wash the bacteria twice with Washing TE (50mmol / LTris-HCl pH8.0, 10mmol / LEDTA pH8.0), and then fully suspend the bacteria Add 0.5ml 5mg / L protease and 0.5ml 10% SDS to 5ml 1×TE buffer, mix gently, place at 50°C for 3h-5h, then extract twice with an equal volume of Tris-saturated phenol, Extract once with phenol / chloroform / isoamyl alcohol. After extracting once with chloroform, precipitate DNA with ethanol. Use the tip of an automatic pipette to absorb the flocculent DNA pellet into an Ep tube, wash twice with 70% ethanol, and dissolve after drying. in 25 μL ddH 2 O middle.
Embodiment 2
[0022] Embodiment 2: the cloning of polysaccharide hydrolase gene Tk1765 and the construction of expression vector
[0023] (1) Primer design: According to the conserved region of the homologous sequence of the polysaccharide hydrolase gene, primers were designed in combination with the vector used, and EcoRI and NotI restriction sites (underlined parts) were introduced at the 5' ends of the primers:
[0024] Upstream primer: 5'-CCG GAATTC GTGAAGAAGATTTGG (SEQ ID NO: 3)
[0025] Downstream primer: 5'-TT GCGGCCGC AA TCAAACTGGAACTGCAACTG (SEQ ID NO: 4)
[0026] (2) PCR amplification: PCR amplification was performed using the genomic DNA of the extreme thermophilic anaerobic archaea T.kodakarensis KOD1 as a template, and the PCR reaction system (25 μL) was as follows:
[0027] 10×Ex Tag Buffer 2.5 μL, 2.5 mmol / L dNTPs mixture 1 μL, 10 μmol / L upstream and downstream primers 1 μL each, ExTag DNA amplification enzyme 0.5 μL, template 10-100ng, sterile deionized water 18 μL. P...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Example 3: Construction, screening and induced expression of yeast engineering strain expressing polysaccharide hydrolase gene Tk1765
[0030] (1) Linearization of the recombinant expression plasmid: the recombinant expression plasmid pPIC9K-Tk1765 was linearized with the restriction endonuclease SalI.
[0031] (2) Transformation: Yeast competent cells of the yeast strain PichiapastoriSGS115 were transformed by electric shock. For the transformation method, refer to the Pichia pastoris operation manual of nvitrogen company.
[0032](3) Screening: Use a sterilized toothpick to pick the corresponding spots of transformants on MM and MD plates, incubate at 30°C for 2-4 days, and pick transformants that grow well on both MD / MM plates as positive transformants. Pick positive transformants and plant them on 1mg / mL, 2mg / mL, 3mg / mL, 4mg / mL G418 YPD plates to screen for multi-copy transformants, and obtain yeast engineering strains expressing polysaccharide hydrolase gene Tk1765...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com