Method for extracting mulberry leaf polysaccharide by utilizing microbial fermentation method
A microbial fermentation method and the technology of mulberry leaf polysaccharide, which are applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of increased production cost, long time consumption, low polysaccharide extraction rate, etc., to promote dissociation, The effect of easy dissolution and improved extraction yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Screening and identification of embodiment 1 fermentation strain
[0024] 1. Strain screening
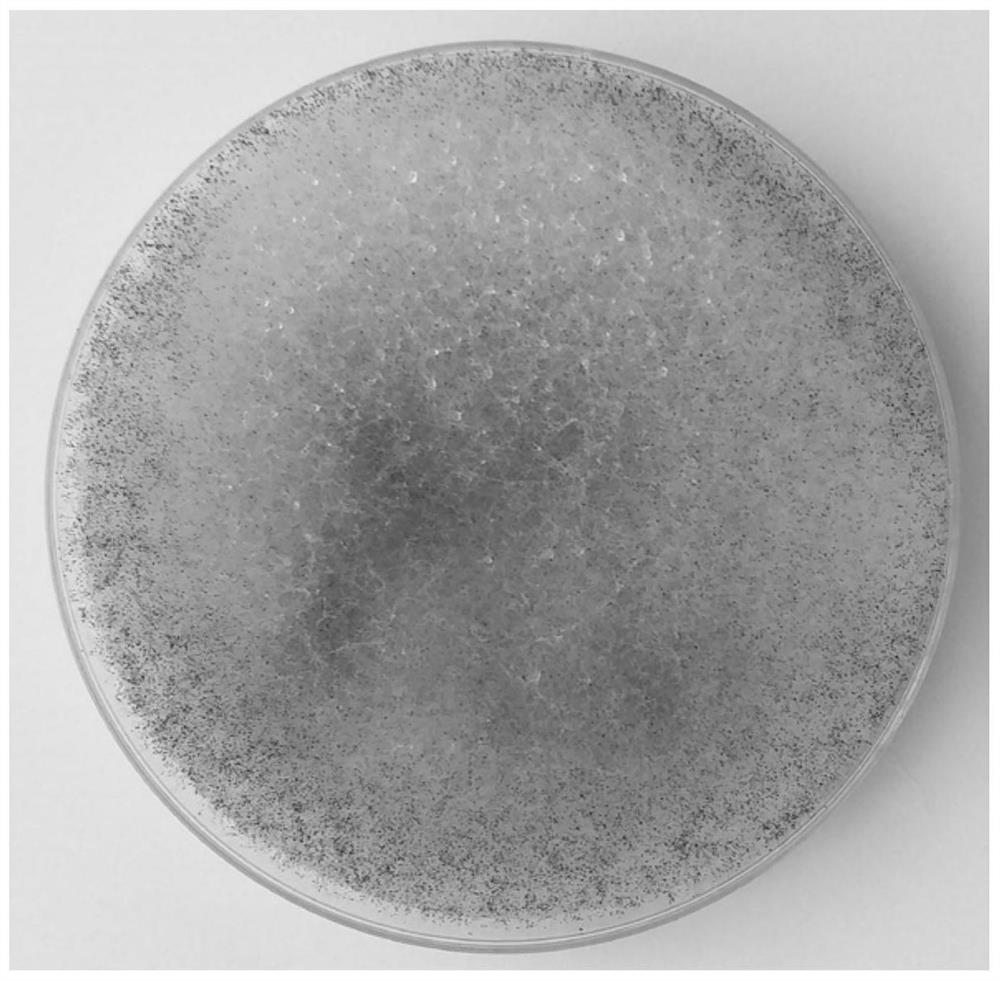
[0025] (1) Add about 10 g of mulberry leaf powder to a 250-mL Erlenmeyer flask, then add 25 mL of sterile saline to moisten it, and incubate at a constant temperature of 28°C for 3 days. Dilute the mold-covered enrichment culture 1×10 with sterile saline 8 After doubling, spread it on the PDA plate medium, culture at 28°C for 2 days, pick out mold colonies with different colors and shapes, transfer them to fresh PDA medium, and place them in 28°C for 2 days to obtain 8 purely cultured strains. They were numbered SY1–SY8. Add 5 mL of sterile saline to the fresh plate cultures of the 8 strains, stir with an inoculation loop to suspend the spores, transfer the spore liquid to a sterile test tube, and adjust the concentration of spores with sterile saline to 3×10 8 individual / mL.
[0026] (2) Dry heat sterilize 250-mL flask at 160°C for 2 hours, add 10 g of mulberry leaf powd...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Embodiment 2 mutation breeding
[0042] Carry out mutation breeding to Mucor racemos SY5, and screen the strain with excellent fermentation performance, the specific method is as follows:
[0043] (1) Preparation of spore liquid: After mucormyces racemosa SY5 is activated and cultivated by PDA, add 5 mL of sterile normal saline, stir with an inoculation loop to suspend the spores, then transfer to a triangular flask containing 45 mL of sterile normal saline, at room temperature Shake for 30min. The spore suspension was filtered to remove mycelia (a cotton ball was placed on the neck of the triangular funnel to filter), and the spores in the suspension were counted with a hemocytometer under a microscope, and diluted with sterile saline to adjust the number of spores to 1 ×10 8 A / mL or so.
[0044] (2) Mutagenesis: mutagenesis was performed under red light. Take 2.0 mL of the above spore suspension and a sterile paper clip into a petri dish with a diameter of 6 cm, p...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3 Mucor racemosa SY5-47 is applied to the extraction of mulberry leaf polysaccharides
[0048] (1) Inoculate Mucor raceme SY5-47 (freeze-dried tube or plate colony) preserved at low temperature on fresh PDA plate medium, culture at a constant temperature of 28°C for 2 days, add 5 mL of sterile saline to the Petri dish, and inoculate with Ring agitation to suspend the spores, transfer the spore liquid to a sterile test tube, and adjust the spore concentration to 3×10 with sterile saline. 8 individual / mL. Described PDA plate medium composition and preparation method are the same as embodiment 1.
[0049] (2) 250-mL Erlenmeyer flask was sterilized by dry heat at 160°C for 2 hours, 10 g of mulberry leaf powder was added, 25 mL of sterile saline was added, and 1 mL of the spore liquid of Mucor racemosus SY5-47 prepared in step (1) was inoculated. , stir well. The mouth of the triangular flask was tied with eight layers of gauze, and cultured at 28°C for 3 days to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com