Bio-based environment-friendly degradable material, film prepared from bio-based environment-friendly degradable material and preparation method of film
A biodegradable material and bio-based technology, applied in the field of bio-based environmentally friendly degradable materials, can solve the problems of inability to obtain modified materials for film materials, large differences in intermolecular forces, and difficulty in obtaining performance products, etc., to eliminate white pollution and improve Compatibility, low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
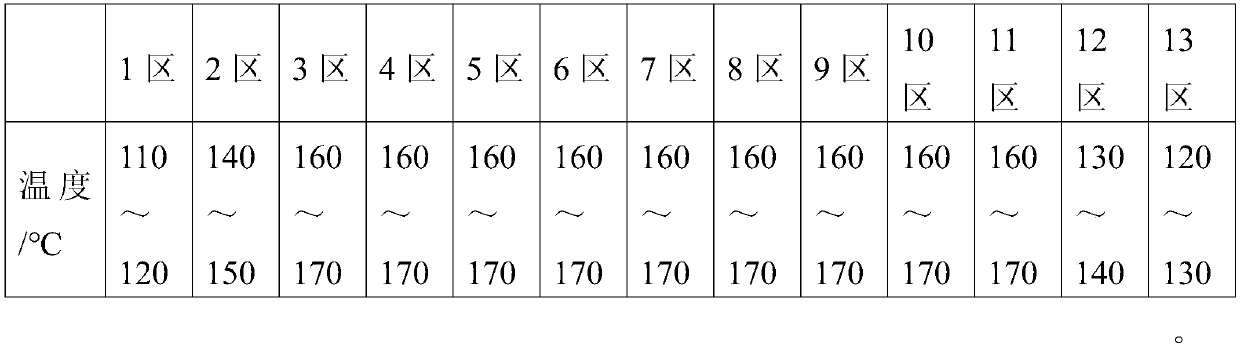
[0025] The preparation method of described bio-based environment-friendly degradable material, it comprises the following processing steps:
[0026] (1) Preparation of micronized starch: after uniformly mixing starch and magnesium stearate and drying, grinding into a micronized starch whose particle size is 2-5 μm;
[0027] (2) Preparation of auxiliary material mixture A: stirring and mixing epoxidized soybean oil, glycerin, diphenylmethane diisocyanate and 2-phenyl-2-oxazoline to obtain auxiliary material mixture A;
[0028] (3) Preparation of auxiliary material mixture B: 1,3-dimethyl-6-aminouracil, N,N'-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)carbodiimide, dioctadecyl Alkyl pentaerythritol bisphosphite, cerium stearate, phenylbis(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl)phosphine oxide and potassium chloride are stirred and mixed, and auxiliary material mixture B;
[0029] (4) Preparation of primary mixture: Stir the micronized starch obtained in step (1), the auxiliary material mixture A obtained in ste...
Embodiment 1
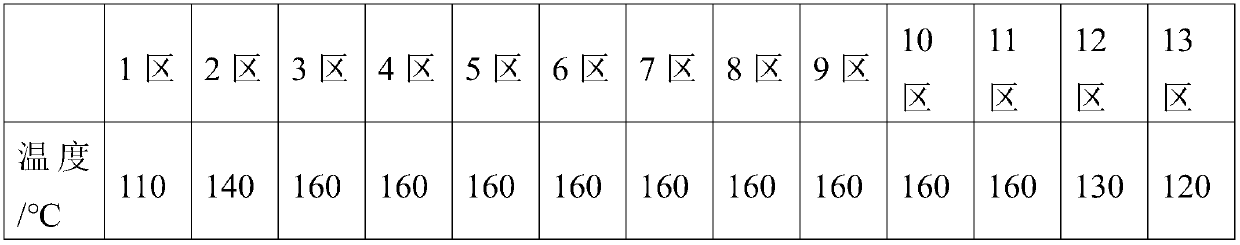
[0051] A bio-based environmentally friendly degradable material, which includes the following raw materials calculated in parts by weight: 55 parts of starch, 25 parts of polylactic acid, 25 parts of glycidyl methacrylate, 5 parts of magnesium stearate, 3 parts of epoxy soybean oil 2 parts of glycerin, 2 parts of diphenylmethane diisocyanate, 2 parts of 2-phenyl-2-oxazoline, 1 part of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate, 1,3-dimethyl-6-amino 2 parts of uracil, 3 parts of N, N'-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl) carbodiimide, 1 part of dioctadecyl pentaerythritol bisphosphite, 2 parts of cerium stearate, 0.2 parts of phenylbis(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl)phosphine oxide and 5 parts of potassium chloride.
[0052] The polylactic acid is NatureWorks-4032D polylactic acid;
[0053] The starch is tapioca starch.
[0054] The preparation method of described bio-based environment-friendly degradable material, it comprises the following processing steps:
[0055] (1) Preparation of micronized starch...
Embodiment 2
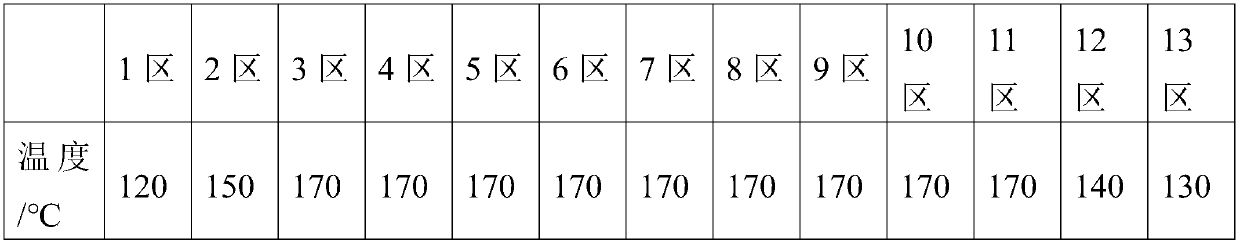
[0071] A bio-based environmentally friendly degradable material, which includes the following raw materials calculated in parts by weight: 60 parts of starch, 30 parts of polylactic acid, 30 parts of glycidyl methacrylate, 7 parts of magnesium stearate, 5 parts of epoxy soybean oil Parts, 5 parts of glycerin, 4 parts of diphenylmethane diisocyanate, 4 parts of 2-phenyl-2-oxazoline, 3 parts of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate, 1,3-dimethyl-6-amino 3 parts of uracil, 5 parts of N, N'-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl) carbodiimide, 3 parts of dioctadecyl pentaerythritol bisphosphite, 5 parts of cerium stearate, 0.3 parts of phenylbis(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl)phosphine oxide and 7 parts of potassium chloride.
[0072] The polylactic acid is REVODE101 polylactic acid;
[0073] The starch is corn starch.
[0074] The preparation method of described bio-based environment-friendly degradable material, it comprises the following processing steps:
[0075] (1) Preparation of micronized starch: ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com