A kind of preparation method of fermented duck leg
A duck leg and yeast technology, applied in the directions of bacteria, lactobacillus, climate change adaptation, etc. used in food preparation, can solve problems such as flavor comparable
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
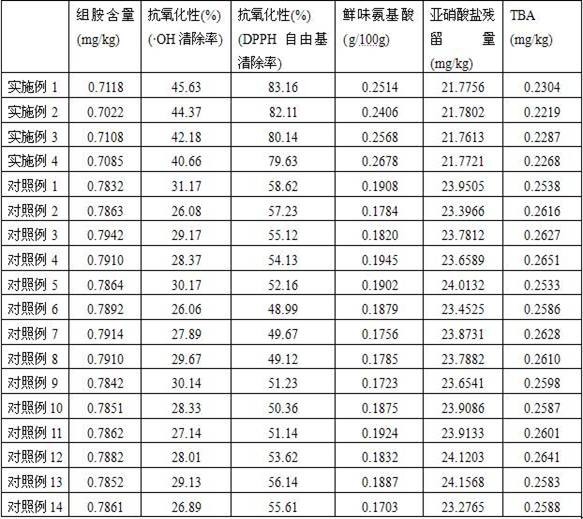
[0062] A preparation method for fermented duck legs, comprising the steps of:
[0063] (1) Duck leg treatment
[0064] Choose fresh duck legs. The fresh meat has a shiny surface and an inherent fragrance. It is elastic when pressed. The lean meat is bright red, the fat meat is white, uniform in color, slightly dry or moist in appearance, and not sticky. Wash the duck leg with blood, tap it with the back of a knife and cut a few small holes on the leg to facilitate the flavoring of the seasoning;
[0065] (2) Pickled
[0066] Based on the duck leg, add 1.5%~2% of salt, 0.013%~0.015% of sodium nitrite, 0.05%~0.08% of ascorbic acid, 1.3%~1.8% of sucrose, and 0.8% of glucose to the processed duck leg according to the mass percentage ~1.2%, monosodium glutamate 0.1%~0.3%, white pepper powder 0.05%~0.1%, cooking wine 3.7%~4.0%, pepper 0.13%~0.15%, onion powder 0.17%~0.2%, tea polyphenols 0.05~0.10%, Light soy sauce 6.5%~7%, stir well, refrigerate and marinate at 4°C, take out after...
Embodiment 2
[0080] With the above-mentioned Example 1, the difference is that the preservation number is Lactobacillus plantarum with preservation number ATCC14917, Saccharomyces cerevisiae with preservation number CGMCCNO. After mixing in the ratio of 2:3:1:1 to obtain a mixed starter, add the mixed starter to the marinated duck legs with an inoculation amount of 1.5% by volume, and put the duck legs in a constant temperature and humidity box at 30°C Continue to ferment for 28h.
Embodiment 3
[0082] With the above-mentioned Example 1, the difference is that the preservation number is Lactobacillus plantarum with preservation number ATCC14917, Saccharomyces cerevisiae with preservation number CGMCCNO. After mixing in the ratio of 1:2:1:2 to obtain a mixed starter, add the mixed starter to the marinated duck legs with an inoculation amount of 1.8% by volume, and put the duck legs in a constant temperature and humidity box at 27°C Continue to ferment for 30h.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com