Method and application of knocking out bnmax1 gene in Brassica napus using CRISPR-Cas9 system
A Brassica napus and gene technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as improving the difficulty of CRISPR-Cas9 targeting, and achieve the effects of increasing yield traits, efficient breeding methods, and simplifying construction steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
[0037] Experimental example 1: sgRNA design of BnMAX1 gene CRISPR-Cas9 in Brassica napus and construction of vectors BnMAX1-Cas9-1 and BnMAX1-Cas9-2
[0038] 1. sgRNA sequence determination
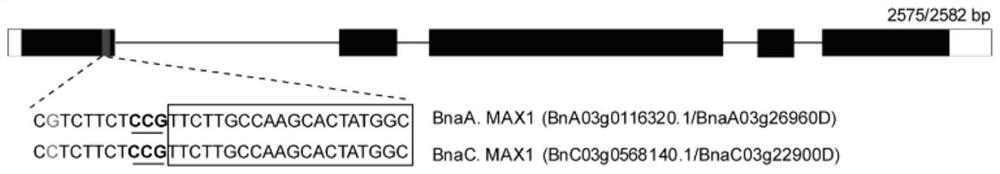
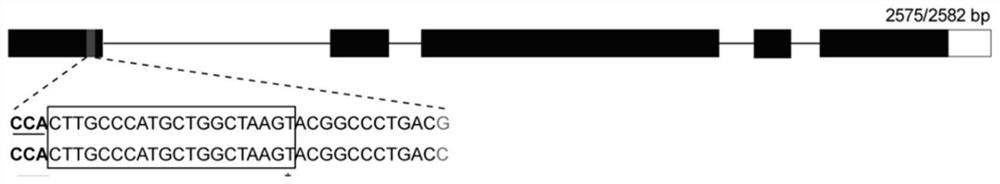
[0039]Brassica napus is a tetraploid crop with two genomes, A and C, and the BnMAX1 gene has one copy in each of the two genomes. Sequence comparison of the two copies was performed to find the PAM (proto adjacent motif) motif (NGG) in the conserved region, and a sequence of 20 bp at the 5' end of the PAM position was the sgRNA sequence. The present invention designs two sgRNAs, the sequences of which are shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2, and both are located in the first exon, and the target sites are as follows figure 1 , 2 shown.
[0040] 2. Synthesis of Oligo DNA single strand
[0041] The CRISPR-Cas9 vector construction kit used in the present invention was purchased from Hangzhou Baige Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Cat#BGK01). Therefore, when designing the Oligo DNA single strand...
experiment example 2
[0059] Experimental Example 2: Transformation of Agrobacterium GV3101 with BnMAX1-Cas9-1 and BnMAX1-Cas9-2 Vectors
[0060] Add 5 μl of BnMAX1-Cas9-1 and BnMAX1-Cas9-2 DNA to 100 μl of GV3101 Agrobacterium competent cells, mix well, ice-bath for 5 minutes, freeze in liquid nitrogen for 1 minute, bathe in 37°C water for 5 minutes, add 700 μl of liquid LB culture medium, 28°C, 200rpm shaker recovery culture for 4 hours. After the cultivation, take an appropriate amount of bacterial liquid and spread it on the LB solid plate containing 50mg / L kanamycin, 50mg / L gentamycin and 50mg / L rifampicin; , inoculated in LB liquid medium containing kanamycin, gentamycin and rifampicin, cultured overnight at 28°C at 200 rpm, and then used cas9-F primers and corresponding Low oligo for PCR identification.
[0061] The correctly identified BnMAX1-Cas9-1 and BnMAX1-Cas9-2 Agrobacterium liquids were mixed with 50% glycerol and stored at -80°C.
experiment example 3
[0062] Experimental example 3: BnMAX1-Cas9-1 and BnMAX1-Cas9-2 Agrobacterium transformed brassica napus hypocotyls respectively
[0063] 1. Explant Preparation
[0064] Seed surface disinfection of Brassica napus 862 (spring rape line collected in the laboratory) and winter rape cultivar Zhongshuang 6 as materials
[0065] (1) Add the seeds into a clean 50 ml centrifuge tube, soak the seeds with 75% alcohol for 5 minutes;
[0066] (2) Pour off the alcohol, add 10ml of 1.5% mercury liter, soak the seeds for 15 minutes, and shake them every few minutes to make the liquid fully contact with the seeds;
[0067] (3) pour off the mercuric acid, and clean the seeds about 4 times with sterilized single distilled water;
[0068] (4) Blot the remaining water with a pipette gun, put the seeds into the M0 medium with tweezers that have been burnt and sterilized in advance, 50 seeds per bottle, and 6 bottles of seeds for each transformation;
[0069] (5) 24 degrees, dark culture for 5-6...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com