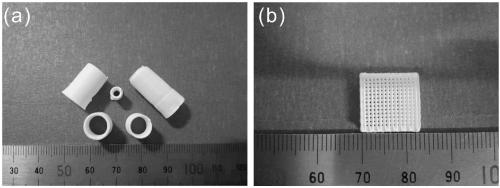
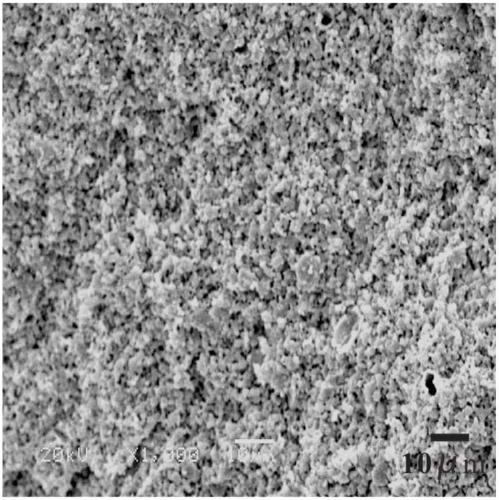
Biological ceramic and preparation method and application thereof
A bio-ceramic and ceramic powder technology, applied in dental preparations, pharmaceutical formulations, dental prostheses, etc., can solve the problems of low density and uniformity, shrinkage of ceramic body structure, easy to appear glue removal, etc., and reduce linear shrinkage. the effect of increasing density, reducing porosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0023] The invention provides a method for preparing bioceramics, comprising the following steps:
[0024] (1) mixing aluminum hydroxide and phosphoric acid at 95-105°C to obtain a phosphorus-containing binder;
[0025] (2) mixing the ceramic powder with the phosphorus-containing binder obtained in the step (1) and then ball milling to obtain a ceramic slurry;
[0026] (3) using 3D printing technology to print the ceramic slurry obtained in the step (2) into a ceramic green body;
[0027] (4) Dehydrating and sintering the ceramic body obtained in the step (3) sequentially to obtain bioceramics.
[0028] The invention mixes aluminum hydroxide and phosphoric acid at 95-105 DEG C to obtain the phosphorus-containing binder. In the present invention, the molar ratio of aluminum hydroxide to phosphoric acid is preferably 1:2.5-3.5, more preferably 1:2.8-3.2, more preferably 1:3. In the present invention, the phosphoric acid is preferably an aqueous phosphoric acid solution, and t...
Embodiment 1
[0038] Feed phosphoric acid and aluminum hydroxide in a molar ratio of 3:1, stir at 100°C for 3 hours to obtain a transparent and uniform phosphorus-containing binder, keep mechanically stirring during the reaction, and the final mass of aluminum phosphate in the phosphorus-containing binder The fraction is 15% by weight. Cool the phosphorus-containing binder to room temperature, and then add the yttrium-stabilized zirconia nanopowder into the phosphorus-containing binder in batches, wherein the average grain size of the yttrium-stabilized zirconia nanopowder is 25nm, and the yttrium-stabilized zirconia nanopowder The mass ratio of nano-powder to phosphorus-containing binder is 1:1, and mechanically stirred for 3 hours to obtain a uniform ceramic slurry.
[0039] The ceramic slurry is injected into the barrel of the 3D printer, the printing parameters are adjusted, and the designed ceramic body is printed out using a computer control program. Dry the ceramic body naturally at...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The test was carried out according to the method of Example 1, except that yttrium-stabilized zirconia was replaced by alumina, wherein the mass ratio of alumina nanopowder to phosphorus-containing binder was 0.9:1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Apparent density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Apparent density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com