A low-wear disc friction plate and its preparation method
A friction lining and low-wear technology, which is applied to friction linings, chemical instruments and methods, and brake parts, can solve problems such as unstable braking coefficients on local friction surfaces, braking deviation, and rollover, so as to avoid Effects of scratches and grooves, stable friction coefficient, and increased bonding strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0053] The embodiment of the present invention also provides a method for preparing a disc friction plate, comprising the following steps:
[0054] (1) Surface treatment of the steel back: Sandblast and polish the steel back, then spray high-temperature-resistant glue on the contact surface between the steel back and the buffer layer, and spray noise-absorbing and damping paint on the other sides of the steel back.
[0055] Among them, the high temperature resistant glue can be phenolic resin liquid glue, its viscosity is 1500-1700 (25°C CP), the free phenol content is ≤1.0%, and the gelation time is 5-6 minutes.
[0056] The weight composition of the raw materials of the sound-absorbing and damping paint is as follows: 45% of the above-mentioned phenolic resin liquid glue, 35% of thinner, 10% of mica, and 10% of wood powder. Its viscosity is 150-200 (25°C CP).
[0057] (2) Mixing of buffer layer: PLC program-controlled feeding is adopted, and the raw materials of the buffer ...
Embodiment 1
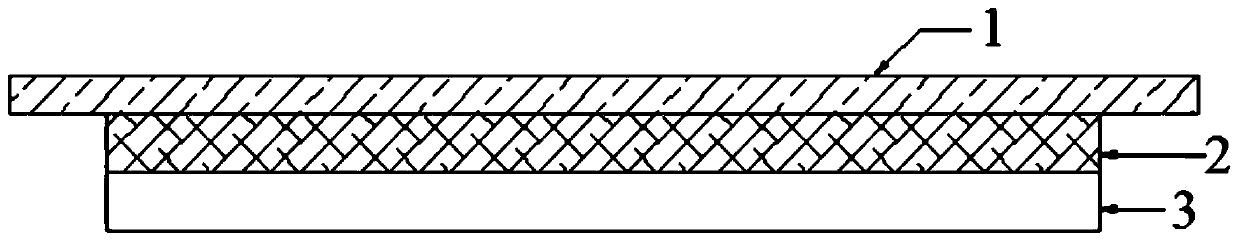
[0063] A disc type friction plate includes a steel back, a buffer layer and a ceramic layer laminated in sequence.
[0064] Wherein, the buffer layer is prepared from raw materials including the following parts by weight: 15 parts of glass fiber, 5 parts of vermiculite, 13 parts of phenolic resin, 20 parts of light calcium carbonate, 5 parts of hemp fiber, 5 parts of calcium hydroxide, neodymium iron 6 parts of boron powder alloy, 5 parts of petroleum coke powder, 10 parts of mineral fiber, 8 parts of EPDM rubber powder, and 6 parts of barium sulfate.
[0065] The ceramic layer is prepared from raw materials including the following parts by weight: 10 parts of carbon fiber, 1018 parts of ceramic fiber, 14 parts of light calcium carbonate, 16 parts of phenolic resin, 4 parts of calcium hydroxide, 10 parts of diatomaceous earth, 15 parts of barium sulfate 6 parts of graphite, 6 parts of petroleum coke powder, 4 parts of mica, 3 parts of alumina, 4 parts of aramid fiber.
[0066...
Embodiment 2~5
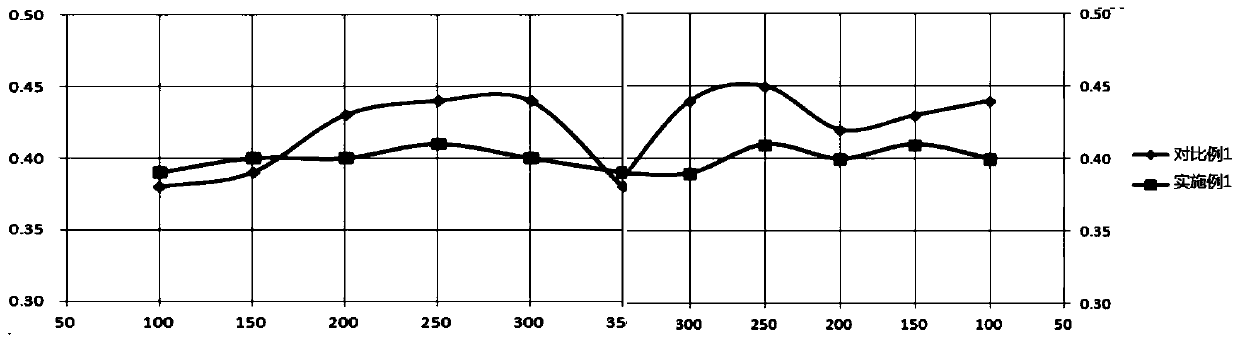
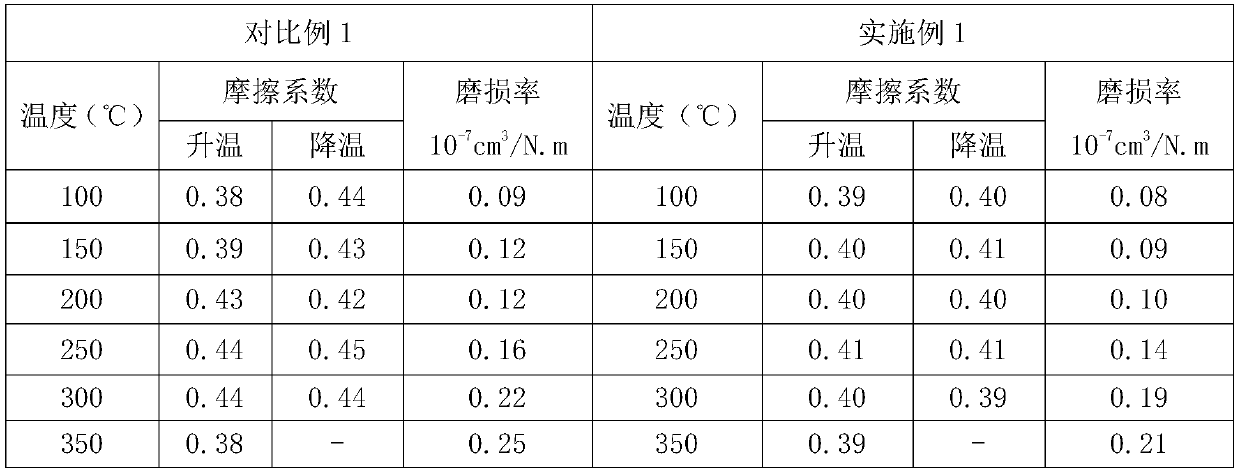
[0085] In Examples 2-5, the thickness ratio of the buffer layer to the ceramic layer and the amount of magnetic material added were changed, and other raw materials and preparation processes were the same as in Example 1. The corresponding changing parameters and the wear rate at 100 °C are shown in Table 3.
[0086] table 3
[0087]
[0088] It can be seen from Table 3 that when the thickness ratio of the buffer layer to the ceramic layer is not in the range of 1:3, or the amount of magnetic material added changes, the wear rate will increase.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com