Zirconia ceramic plastic processing method assisted by direct-current electric field
A zirconia ceramic and plastic processing technology, applied in the field of zirconia ceramic plastic processing assisted by DC electric field, can solve the problems of large deformation resistance, high temperature required for deformation, and reduced material strength, so as to reduce plastic processing temperature and improve production. Efficiency, the effect of shortening the processing cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
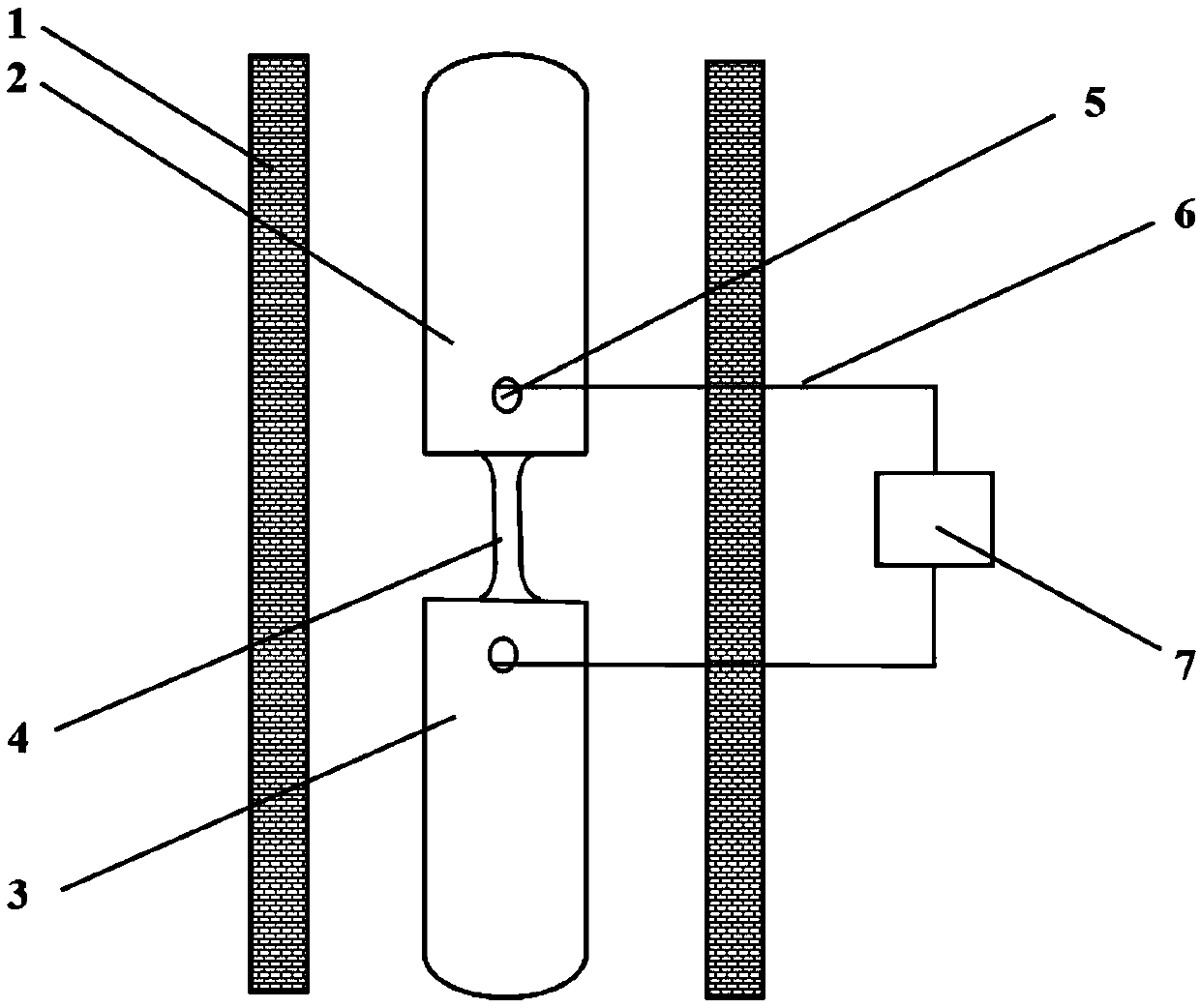
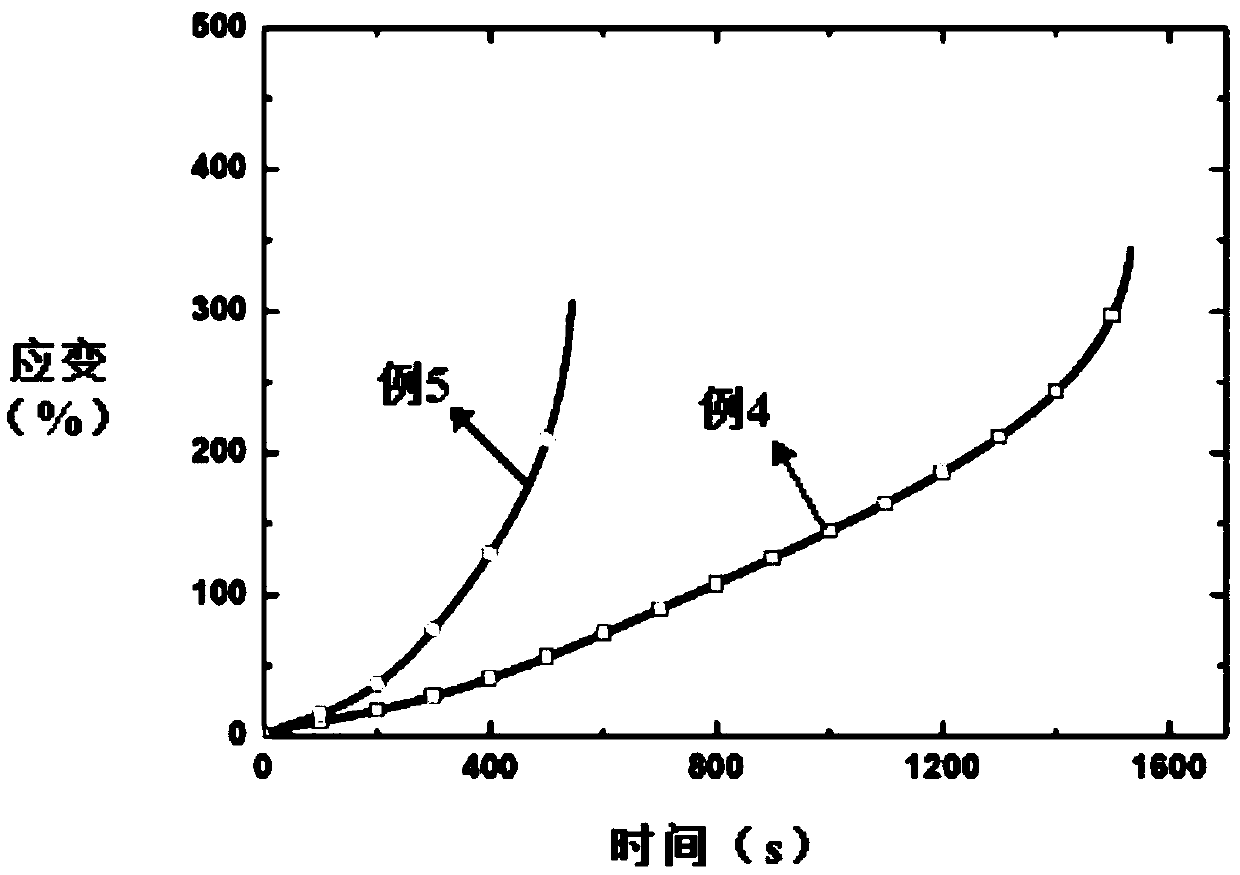
[0034]Put the dense 3YSZ zirconia ceramic sample into the temperature-controlled heating furnace 1, heat it up to 700°C at a heating rate of 10°C / min, and keep it at this temperature for 30 minutes to ensure that the furnace temperature and the sample temperature are balanced; 4 Apply 240mA / mm at both ends 2 When the current density reaches the set value, it is stable for 5 minutes to ensure the stability of the current and the uniformity of the temperature; through the universal testing machine with 10 -3 the s -1 Tensile plastic processing of the sample at a constant strain rate; ensure that the current density of the sample is constant at 240mA / mm throughout the plastic processing process 2 , until the end of plastic working, an elongation of 250% can be obtained.
Embodiment 2
[0036] Put the dense 3YSZ zirconia ceramic sample into the temperature-controlled heating furnace 1, heat it up to 900°C at a heating rate of 10°C / min, and keep it at this temperature for 30 minutes to ensure that the furnace temperature and the sample temperature are balanced; 4 Apply 200mA / mm at both ends 2 When the current density reaches the set value, it is stable for 5 minutes to ensure the stability of the current and the uniformity of the temperature; through the universal testing machine with 10 -2 the s -1 Tensile plastic processing of the sample at a constant strain rate; ensure that the current density of the sample is constant at 200mA / mm throughout the plastic processing process 2 , until the end of plastic working, an elongation of 360% can be obtained.
Embodiment 3
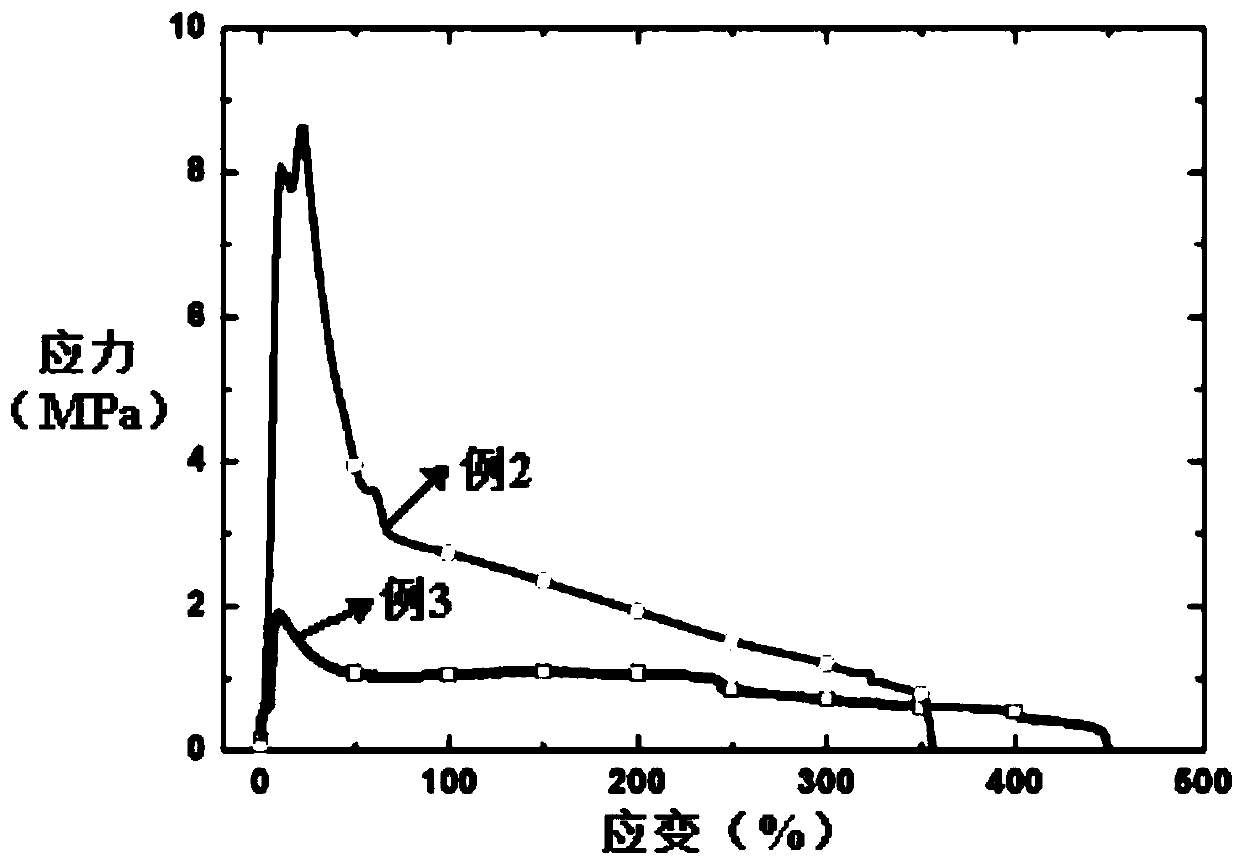
[0038] Put the dense 3YSZ zirconia ceramic sample into the temperature-controlled heating furnace 1, heat it up to 900°C at a heating rate of 10°C / min, and keep it at this temperature for 30 minutes to ensure that the furnace temperature and the sample temperature are balanced; 4 Apply 200mA / mm at both ends 2 When the current density reaches the set value, it is stable for 5 minutes to ensure the stability of the current and the uniformity of the temperature; through the universal testing machine with 10 -3 the s -1 Tensile plastic processing of the sample at a constant strain rate; ensure that the current density of the sample is constant at 200mA / mm throughout the plastic processing process 2 , until the end of plastic working, an elongation of 450% can be obtained.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com