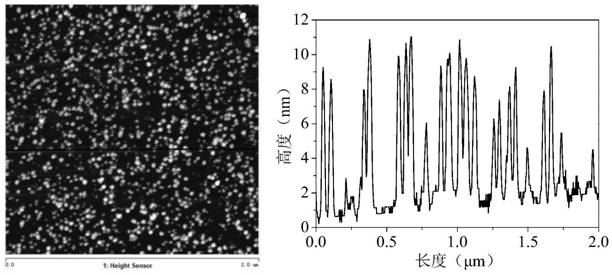
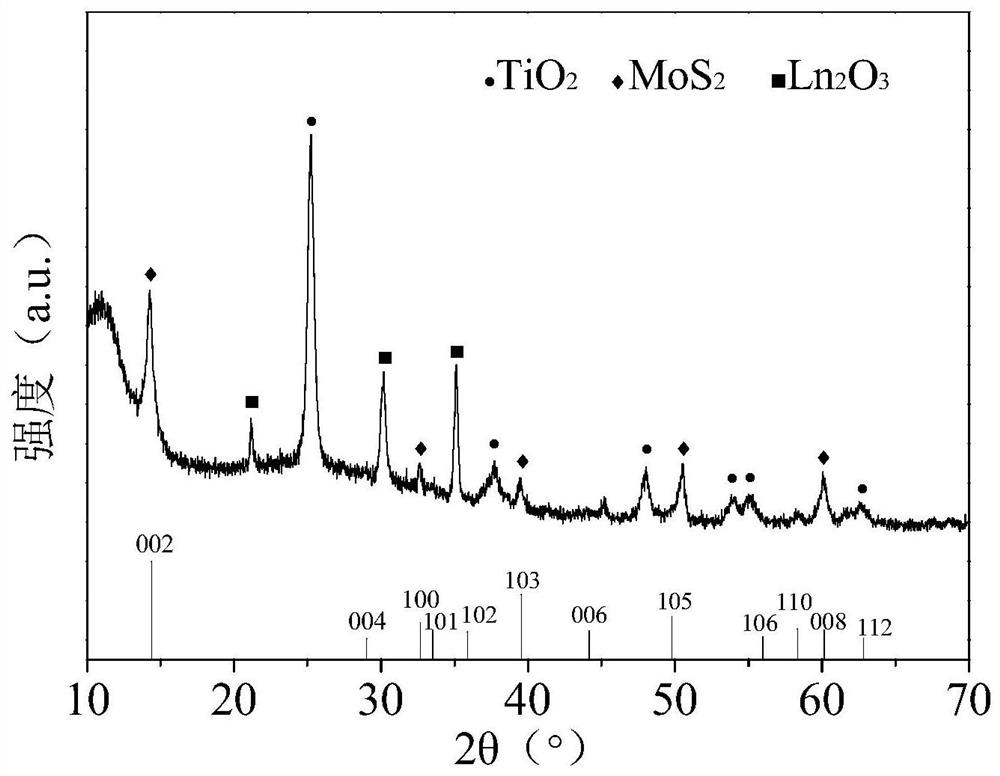
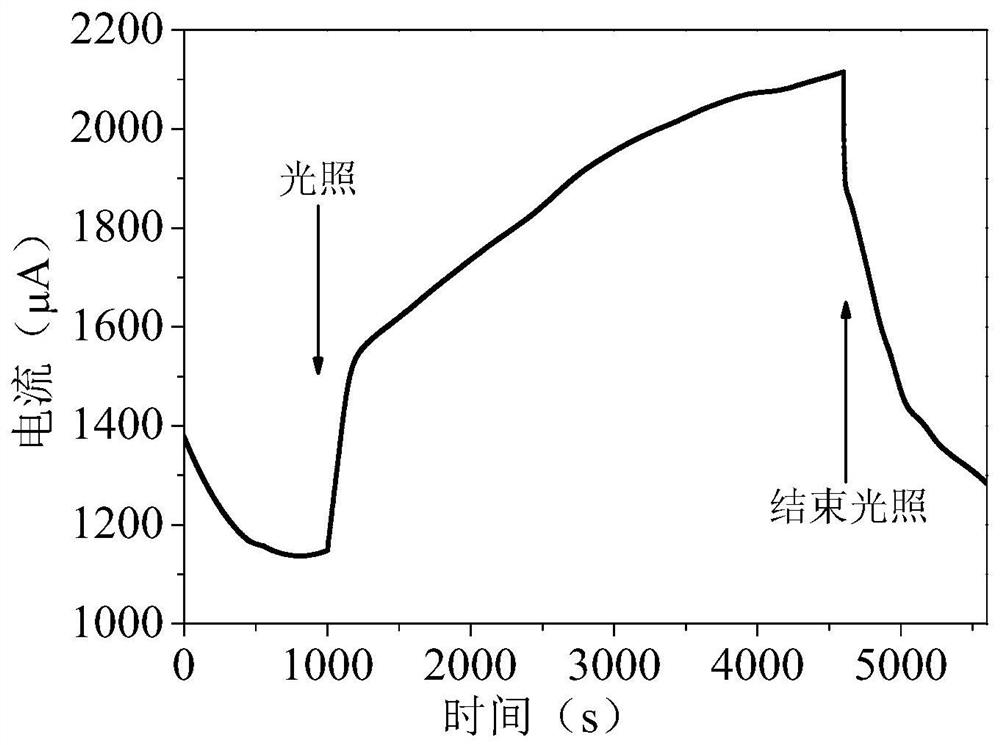
A method for treating ammonia nitrogen pollutants in water by activating sulfite with sulfide photoanode
A technology for activating sulfite and photoanode, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, light water/sewage treatment, oxidized water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problem of inability to remove ammonia species, etc., to facilitate degradation and avoid interaction Conversion and cost reduction effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] The concentration of ammonia nitrogen in 100ml of water is 10mg / L, the concentration of sodium sulfite is 0.1M (pH=9~10), the bias voltage is 0.6V, and the air is slowly introduced to increase the dissolved oxygen in the water. cm 2 ) irradiation, using 1cm 2 The molybdenum disulfide electrode is used as the photoanode, and the graphite electrode is used as the cathode. After 6 hours of reaction in the photochemical reaction cell, the removal rate of ammonia nitrogen can reach 77%.
[0036] If no light source is used and the electrochemical reaction is only performed under the bias voltage of 0.6V, under the same conditions, the removal rate of ammonia nitrogen is only 27% after 6 hours of reaction. The corresponding changes in ammonia nitrogen concentration are shown in Figure 4 shown. Analysis diagram of ammonia nitrogen degradation products Figure 5 As shown, the results show that a small part of ammonia nitrogen is converted into nitrate nitrogen, and most of ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] The degradation effects of ammonia nitrogen under different pH conditions were compared. The concentration of ammonia nitrogen in 100ml of water is 20mg / L, the concentration of sodium sulfite is 0.1M, and the bias voltage is 0.6V, and the air is slowly introduced to increase the dissolved oxygen in the water. 2 ) irradiation, using 1cm 2 The molybdenum disulfide electrode is used as the photoanode, and the graphite electrode is used as the cathode. The pH of the solution is adjusted to 4, 7 and 10 by using 0.1M hydrochloric acid. After 6 hours of reaction in the photochemical reaction cell, the degradation rates of ammonia nitrogen are respectively 8%, 16% and 77%.
Embodiment 3
[0040] The degradation effects of ammonia nitrogen under different sodium sulfite concentrations were compared. The concentration of ammonia nitrogen in 100ml of water is 10mg / L (pH=9~10), and the bias voltage is 0.6V, and the air is slowly introduced to increase the dissolved oxygen in the water. 2 ) irradiation, using 1cm 2 The molybdenum disulfide electrode is used as the photoanode, and the graphite electrode is used as the cathode. When the concentration of sodium sulfite is 0.01M, 0.05M and 0.1M, the degradation rates of ammonia nitrogen after 6h in the photochemical reaction cell are 10%, 33% and 77% respectively. %.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com