Method for preparing glass ceramic from waste residues related to severe hazards
A technology of glass ceramics and waste slag, which is applied in the field of waste resource utilization, can solve the problems of unbearable economic costs, high operating costs, and high energy consumption, and achieve the effects of energy saving, strong market competitiveness, and good performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
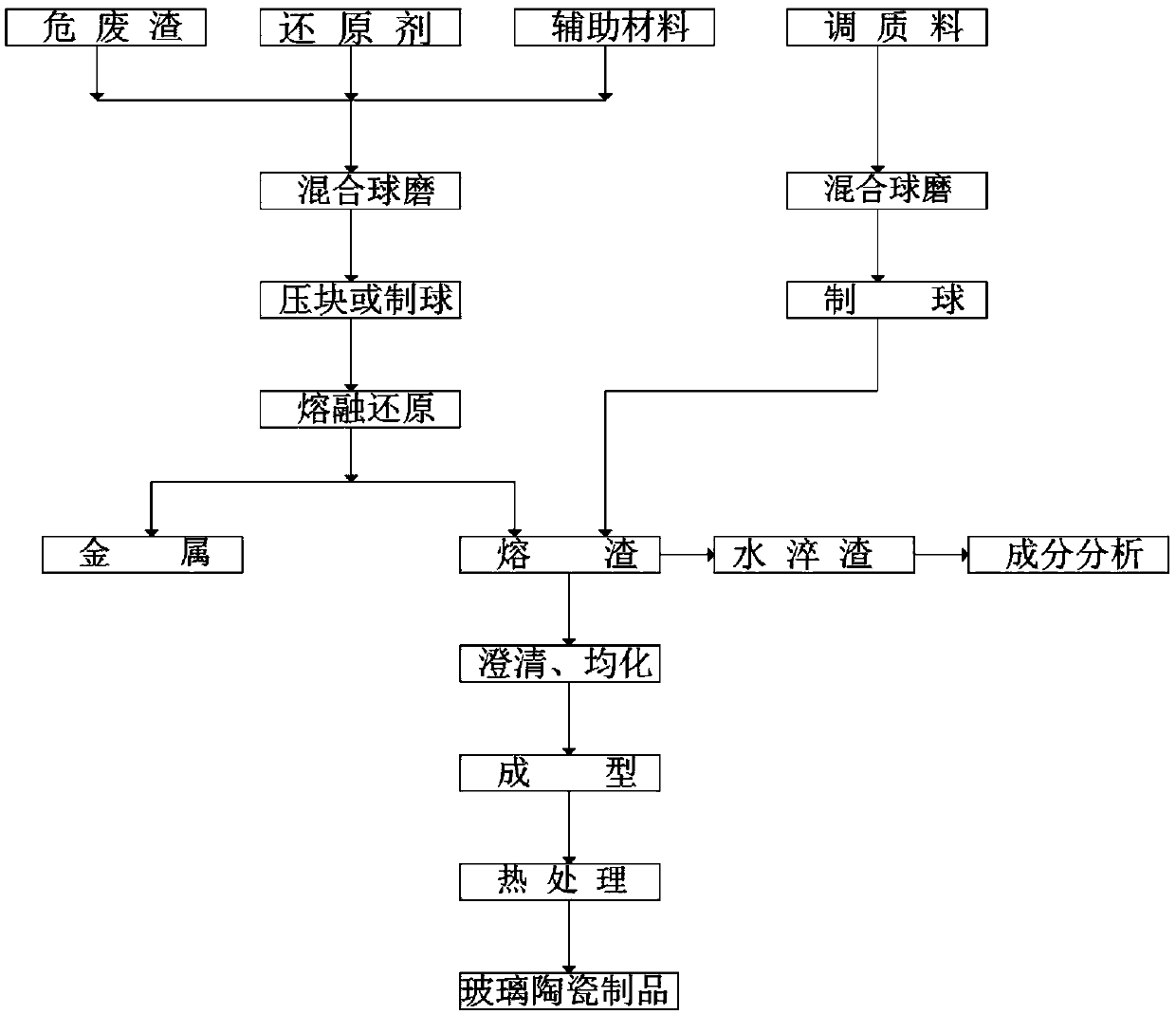
[0032] Embodiment 1 A method for preparing glass-ceramics by utilizing heavy and hazardous waste residues, comprising the following steps:
[0033] (1) Using heavy and hazardous waste residue as the main material, 17 parts of iron ore, 15 parts of quicklime, 15.9 parts of quartz sand, 3.5 parts of fluorite as auxiliary materials, 2.2 parts of coke and 4.6 parts of spent anode carbon blocks as reducing substances , mix auxiliary materials and reducing substances with 100 parts of heavy hazardous waste residue HW17 (electroplating sludge), and press them into block materials;
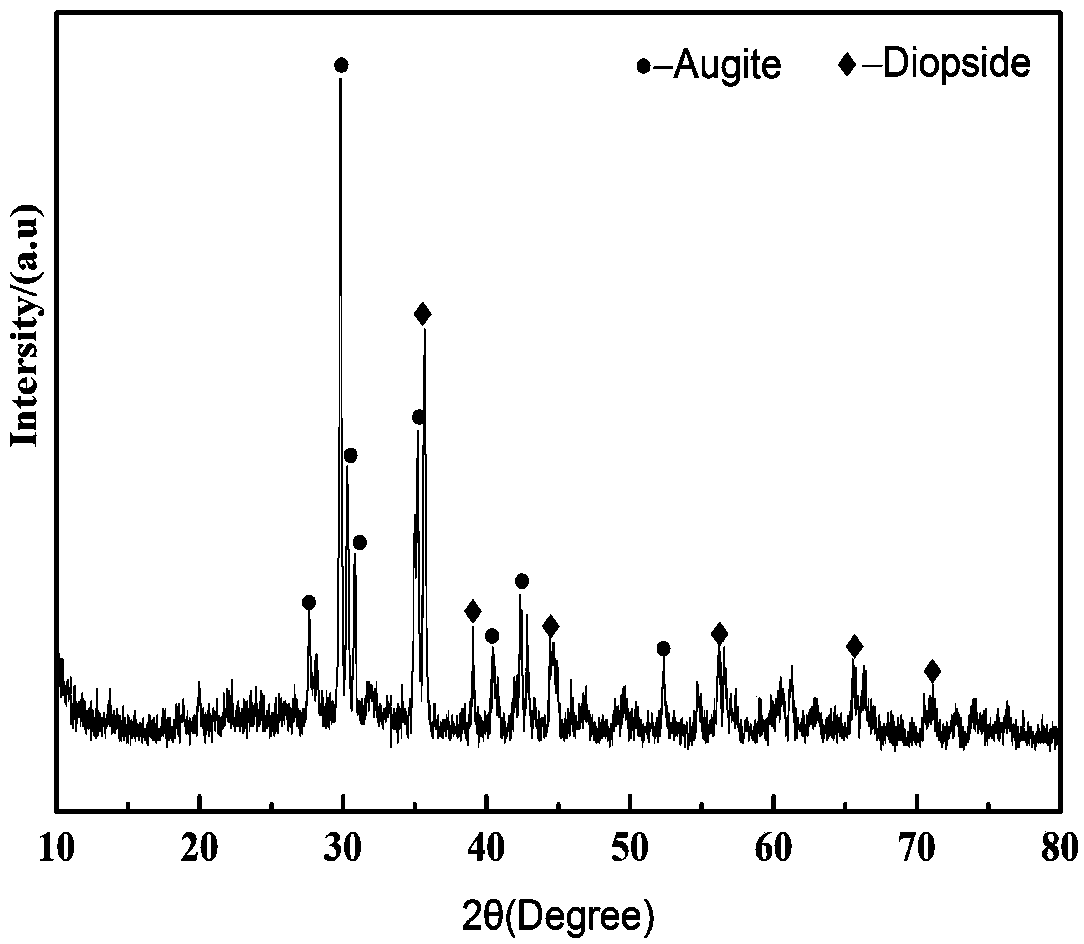
[0034] (2) Put the bulk material into the heating furnace, and heat and melt at 1250°C for reduction, the obtained metal alloy flows out from the tap hole, and the obtained hot slag flows out from the slag discharge port; take a little hot slag and quench it with water The water-quenched slag was obtained, and the chemical composition of the water-quenched slag was analyzed (see Table 1 for the compositio...
Embodiment 2
[0047] A method for preparing glass-ceramics by utilizing heavy and hazardous waste slag, comprising the following steps:
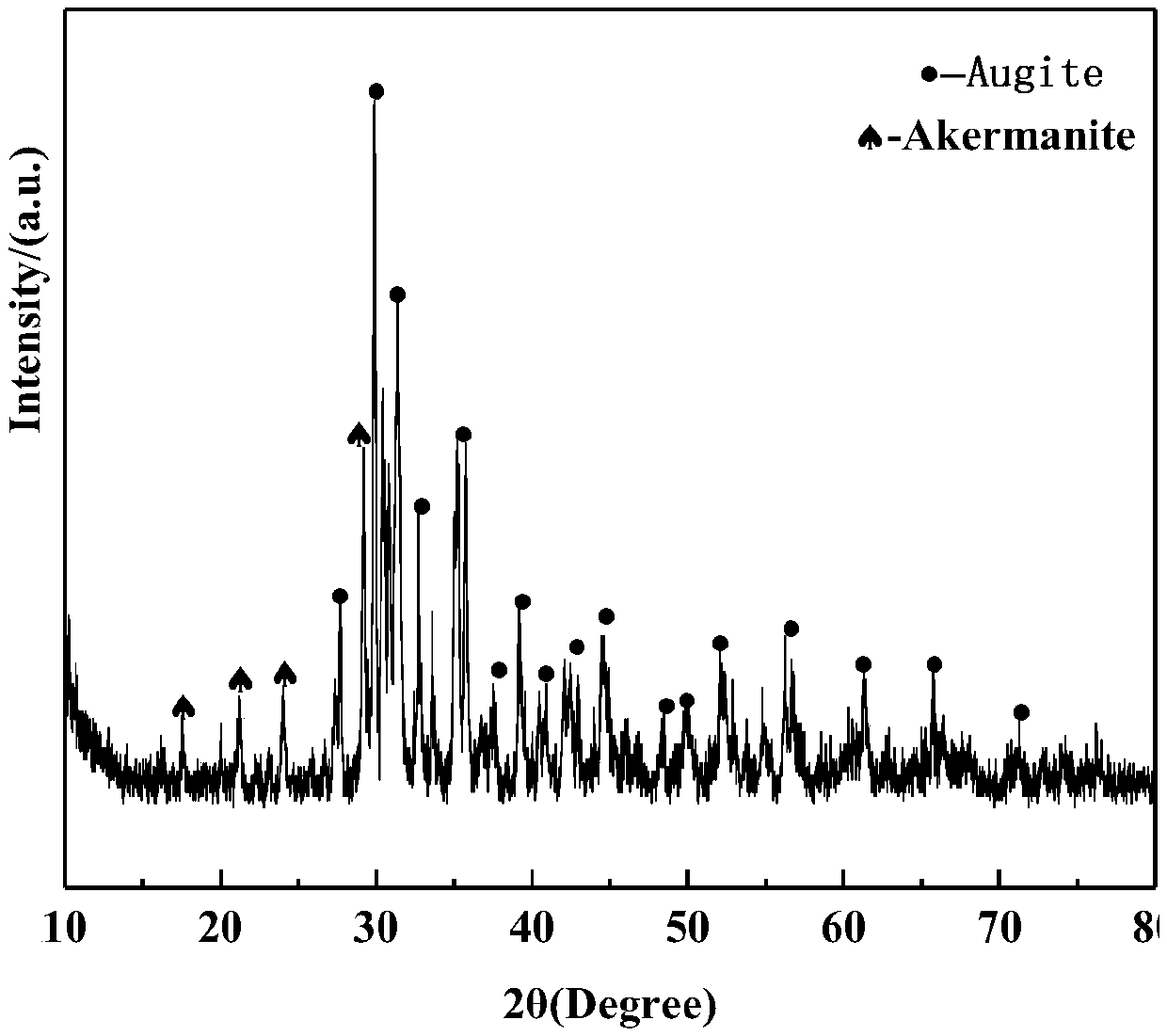
[0048] (1) With 15 parts of quicklime, 2 parts of fluorite, and 3 parts of soda ash as auxiliary materials, and 10 parts of coke powder as reducing substances, the auxiliary materials and reducing substances are mixed with 100 parts of heavy hazardous waste residue HW48 (copper slag), and pressed Form into lumps, heat and melt at 1300°C, take a small amount of hot molten slag from the slag outlet and water-quench to obtain water-quenched slag after hazardous waste treatment, and analyze the chemical composition of the water-quenched slag (results are shown in Table 2).
[0049] (2) 10 parts of stainless steel slag and 5 parts of soda ash are mixed evenly, and then made into 5 mm spherical conditioning material particles;
[0050] (3) Introduce the hot slag involved in the treatment of heavy hazardous waste slag into the melting furnace through the slag di...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Basically the same as Example 1, the difference is:
[0062] (1) 54 parts of quartz sand, 6.5 parts of magnesium oxide, and 3.6 parts of soda ash are ball milled and mixed to make spherical conditioning material particles;
[0063] (2) According to the weight ratio of thermal slag: conditioning material 100:55, the spherical conditioning material is added to the thermal slag obtained in step (4) of Example 1;
[0064] (3) Add heat to the hot slag mixed with tempering material by electrode heating, perform high temperature tempering, and keep it in the high temperature range of 1400 ° C for 2 hours to obtain a melt;
[0065] (4) Preheating the pipe-making mold to 550°C, pouring the melt into the preheated mold for molding;
[0066] (5) Send the formed glass tube into a microwave roller kiln, heat it at 580°C for 30 minutes for annealing treatment, then raise the temperature to 800°C, hold it for 50 minutes for crystallization;
[0067] (6) Cool to room temperature to o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com