Preparation method of solid lactic acid bacteria high-activity bacterial agent for raising
A lactic acid bacteria, high-activity technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of single nutrient and probiotics, low fermentation bacteria, and limited fermentation scale.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
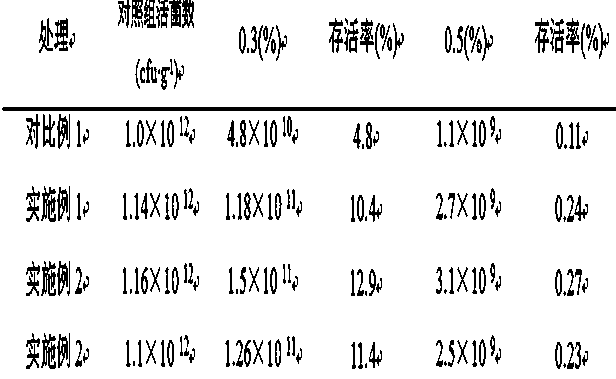
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] First, prepare 12% (W / V) skimmed milk powder, add 3% trehalose and 0.3 mM glutathione, and sterilize at 110°C for 10 minutes. After cooling to room temperature, insert Bifidobacterium bifidum in a ratio of 3%, and ferment to produce live lactic acid bacteria agent. Ferment at a constant temperature of 35°C for 6 hours until the skim milk powder coagulates, and the fermentation ends when the pH is 4.5. After stirring at 150 rpm and cooling to room temperature, the active lactic acid bacteria agent was obtained, and the effective number of viable bacteria was 2.0×10 9 cfu / mL.
[0029] Then, the above-mentioned live lactic acid bacteria agent is formulated into a basic formula solid preparation. Mix and stir the live lactic acid bacteria agent with each component, and add water while stirring. In terms of parts by weight, the components are: 5 parts of xylooligosaccharide, 4 parts of sulfomethylcellulose sodium, 25 parts of sodium alginate, 50 parts of cornstarch and 40...
Embodiment 2
[0034] First, prepare 15% (W / V) skimmed milk powder, add 2% pullulan, 2% resistant starch and 0.3% mM iso-VC acid, and sterilize at 110°C for 12 min. After being cooled to room temperature, inoculate according to the ratio of 3% Lactobacillus lactis and 2% Bacillus bulgaricus, and ferment to produce live lactic acid bacteria agent. Ferment at a constant temperature of 39°C for 5 hours until the skim milk powder coagulates, and the fermentation ends when the pH is 4.0. After stirring at 200 rpm and cooling to room temperature, the active lactic acid bacteria agent was obtained, and the effective number of viable bacteria was 3.6×10 9 cfu / mL.
[0035] Then, the above-mentioned live lactic acid bacteria agent is formulated into a basic formula solid preparation. Mix and stir the live lactic acid bacteria agent with each component, and add water while stirring. In parts by weight, each component is: 10 parts of fructooligosaccharide, 8 parts of microcrystalline cellulose, 10 pa...
Embodiment 3
[0040] First, prepare 15% (W / V) skimmed milk powder, add 3.5% (W / V) trehalose and 0.5% montmorillonite, and sterilize at 108°C for 12 min. After cooling to room temperature, insert Lactobacillus acidophilus at a ratio of 3%, and ferment to produce live lactic acid bacteria agent. Ferment at a constant temperature of 37°C for 6 hours until the skim milk powder coagulates, and the fermentation ends when the pH is 4.3. After stirring at 180 rpm and cooling to room temperature, the active lactic acid bacteria agent was obtained, and the effective number of viable bacteria was 2.5×10 9 cfu / mL.
[0041] Then, the above-mentioned live lactic acid bacteria agent is formulated into a basic formula solid preparation. Mix and stir the live lactic acid bacteria agent with each component, and add water while stirring. In parts by weight, each component is: 5 parts of xylooligosaccharide, 5 parts of sodium sulfamethycellulose, 35 parts of polyacrylic resin II, 50 parts of wheat starch an...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Effective viable count | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bacteria | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com