Breeding method for regulating mir156 and its target gene ipa1 to simultaneously improve rice disease resistance and yield
A technology of transgenic rice and target gene, applied in the field of rice genetics and breeding to achieve the effect of enhancing resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
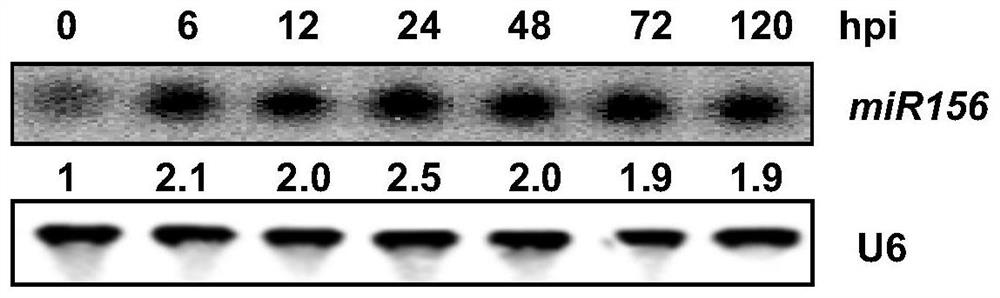
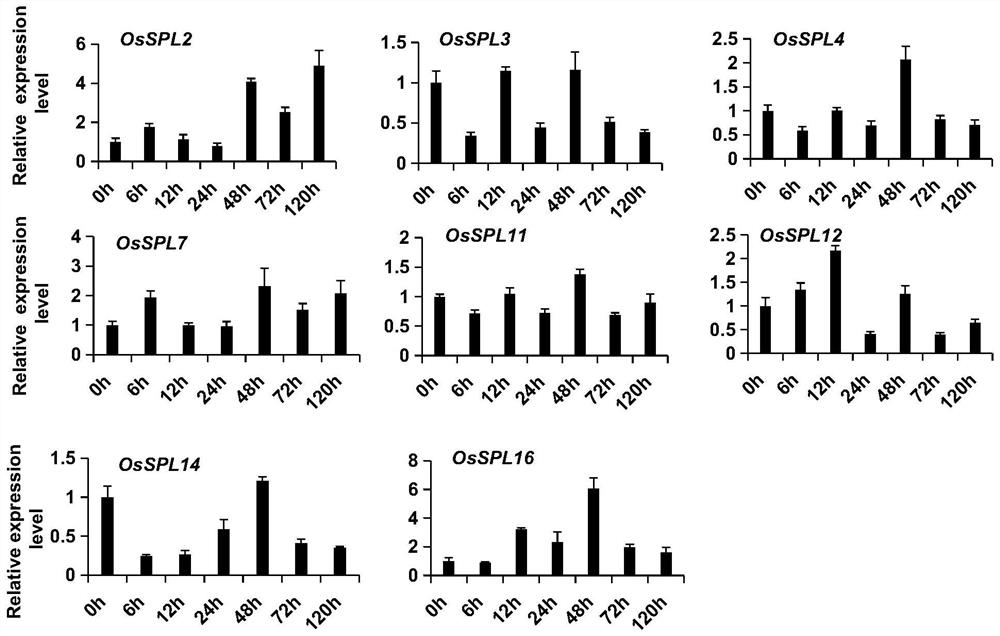
[0063] Example 1 miR156northern analysis and OsSPLs expression pattern identification
[0064] The leaves of rice Nipponbare in the tillering stage were injected with Xanthobacterium blight PXO99A (OD value 0.6), and the inoculated leaves were sampled at 7 time points (0, 6, 12, 24, 48, 72, 120 hpi). The samples were mixed with three leaves, and the total RNA of 7 inoculation periods was extracted to identify the expression of miR156 and the target gene OsSPLs gene. (hpi: hours postinoculation, hours after inoculation)
[0065] 1.1 Culture of bacterial blight PXO99A:
[0066] PSA medium
[0067]
[0068] 1.2 Trizol method to extract total RNA:
[0069] The rice leaf samples taken during the 7 inoculation periods were respectively operated as follows to obtain the total RNA of the 7 inoculation periods:
[0070] (1) Weigh 0.1 g of fresh leaves, grind them quickly in liquid nitrogen with a mortar, and transfer them to a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube (pre-cooled with liquid nitro...
Embodiment 2
[0104] Example 2 Construction of rice miR156-specifically down-regulated transgenic plants using miRNA target gene simulation technology
[0105] The rice used for transformation is: wild type rice Zhonghua 11 (ZH11).
[0106] 2.1 The construction method of the overexpression vector MIM156OE containing miR156MIMIC is as follows:
[0107] 1) Use IPSF and IPSR primers to clone the cDNA sequence of the Arabidopsis gene IPS, digest with BamHI and SacI, and connect the fragment to the PBSk vector.
[0108] 2) Using the pairing of MIM156-I primers and IPSR primers and MIM156R primers and IPSF primers, using the plasmid after IPS ligated with PBSK as a template, two sequences containing terminal homology were amplified.
[0109] 3) Using the two sequences obtained in the second step as templates, using overlapping PCR technology and using IPSF and IPSR as primers, amplify the IPS fragment (IPS-MIMI156) containing the sequence of MIMIC156.
[0110] 4) The target fragment was amplifi...
Embodiment 3
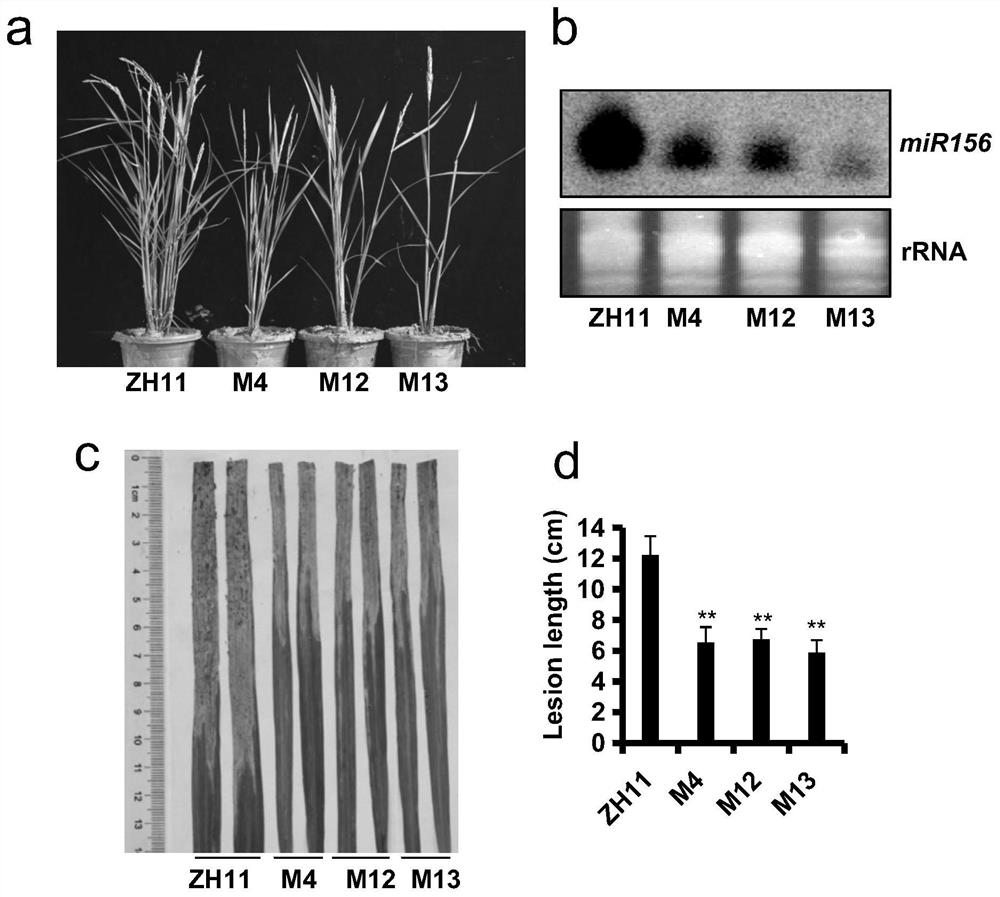
[0119] Example 3 Rice mutants up-regulated by miR156
[0120] The rice used for transformation is: wild type rice Zhonghua 11 (ZH11).
[0121] 3.1 The construction method of the overexpression vector miR156fOE containing miR156f is as follows:
[0122] Using rice Nipponbare DNA as a template, using miR156fOE-F and miR156fOE-R primers to clone rice miR156 precursor miR156f, and connecting the p1301-35SNos plasmid to obtain the overexpression vector mi156fOE containing miR156f (shown in SEQ ID NO.2).
[0123] miR156fOE-F: GGGATCCttttgggtggtggcagttga (SEQ ID NO. 31)
[0124] miR156fOE-R: GGGTACcaaagccgtctcctccctcc (SEQ ID NO. 32)
[0125] 3.2 Transformation and infection methods are the same as in Example 2.
[0126] The miR156fOE vector was transformed into commercially available Agrobacterium EHA105 by freeze-thaw method, and then genetically transformed into wild-type rice Zhonghua 11 (ZH11). By overexpressing miR156f, the precursor of miR156, two transgenic lines miR156fOE...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com